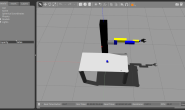
要建立自己的自主机器人,首先,必须要建立自己的机器人模型,
URDF(Unified Robot Description Format)模型。
Part 3 建立机器人URDF模型
机器人URDF模型主要由两个文件组成:.xacro 是主文件,包含URDF项,包括关节,连杆;.gazebo包含gazebo的具体信息以便在gazebo中仿真。 例子请见:How to Build a Differential Drive Simulation 以下工程的源码下载地址请见: http://download.csdn.net/download/ziqian0512/9816156 使用方法主要包括以下三个部分: rviz查看机器人
<code class="hljs avrasm has-numbering">roslaunch neurobot_description neurobot_rviz<span class="hljs-preprocessor">.launch </span></code>
gazebo 仿真
<code class="hljs avrasm has-numbering">groslaunch neurobot_gazebo neurobot_world<span class="hljs-preprocessor">.launch</span> </code>
控制机器人运动
<code class="hljs rust has-numbering">rostopic <span class="hljs-keyword">pub</span> /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist <span class="hljs-string">"linear: x: 0.1 y: 0.0 z: 0.0 angular: x: 0.0 y: 0.0 z: 0.0" </span></code>
如何一步步设计自己的工程请见以下部分的详细说明:
1. 创建工程
<code class="hljs has-numbering">catkin_create_pkg neurobot_description </code>
2. 差分驱动模型
<code class="hljs avrasm has-numbering">neurobot_description/urdf/ ├── macros<span class="hljs-preprocessor">.xacro</span> 帮助简化的宏 ├── materials<span class="hljs-preprocessor">.xacro</span> 材料说明 ├── neurobot<span class="hljs-preprocessor">.gazebo</span> gazebo具体信息 └── neurobot<span class="hljs-preprocessor">.xacro</span> URDF 主文件 </code>
 在
在neurobot.xacro中添加chassis, wheels,
添加chassis
<link name='chassis'>
<pose>0 0 0.1 0 0 0</pose>
<inertial>
<mass value="15.0"/>
<origin xyz="0.0 0 0.1" rpy=" 0 0 0"/>
<inertia
ixx="0.1" ixy="0" ixz="0"
iyy="0.1" iyz="0"
izz="0.1"
/>
</inertial>
<collision name='collision'>
<geometry>
<box size=".4 .2 .1"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<visual name='chassis_visual'>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy=" 0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size=".4 .2 .1"/>
</geometry>
</visual>
<collision name='caster_collision'>
<origin xyz="-0.15 0 -0.05" rpy=" 0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="0.05"/>
</geometry>
<surface>
<friction>
<ode>
<mu>0</mu>
<mu2>0</mu2>
<slip1>1.0</slip1>
<slip2>1.0</slip2>
</ode>
</friction>
</surface>
</collision>
<visual name='caster_visual'>
<origin xyz="-0.15 0 -0.05" rpy=" 0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="0.05"/>
</geometry>
</visual>
<collision name='caster_front_collision'>
<origin xyz="0.15 0 -0.05" rpy=" 0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="0.05"/>
</geometry>
<surface>
<friction>
<ode>
<mu>0</mu>
<mu2>0</mu2>
<slip1>1.0</slip1>
<slip2>1.0</slip2>
</ode>
</friction>
</surface>
</collision>
<visual name='caster_front_visual'>
<origin xyz="0.15 0 -0.05" rpy=" 0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="0.05"/>
</geometry>
</visual>
</link>
添加差分驱动轮子
<link name="left_wheel">
<!--origin xyz="0.1 0.13 0.1" rpy="0 1.5707 1.5707"/-->
<collision name="collision">
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 1.5707 1.5707"/>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.1" length="0.05"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<visual name="left_wheel_visual">
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 1.5707 1.5707"/>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.1" length="0.05"/>
</geometry>
</visual>
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 1.5707 1.5707"/>
<mass value="5"/>
<inertia
ixx=".1" ixy="0.0" ixz="0.0"
iyy=".1" iyz="0.0"
izz=".1"/>
</inertial>
</link>
添加hinges链接wheels和chassis
<joint type="continuous" name="left_wheel_hinge">
<origin xyz="0 0.15 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<!--origin xyz="0.1 0.13 0" rpy="0 1.5707 1.5707"/-->
<child link="left_wheel"/>
<parent link="chassis"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<limit effort="10000" velocity="1000"/>
<joint_properties damping="1.0" friction="1.0"/>
</joint>
<joint type="continuous" name="right_wheel_hinge">
<origin xyz="0 -0.15 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<!--origin xyz="0.1 -0.13 0" rpy="0 1.5707 1.5707"/-->
<child link="right_wheel"/>
<parent link="chassis"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<limit effort="10000" velocity="1000"/>
<joint_properties damping="1.0" friction="1.0"/>
</joint>要实现自主导航还需要添加camera和laser,有了激光器和摄像头我们才能让机器人去感知外部世界。
添加camera
<link name="camera">
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size="${cameraSize} ${cameraSize} ${cameraSize}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size="${cameraSize} ${cameraSize} ${cameraSize}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="green"/>
</visual>
<inertial>
<mass value="${cameraMass}" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<box_inertia m="${cameraMass}" x="${cameraSize}" y="${cameraSize}" z="${cameraSize}" />
<inertia ixx="1e-6" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyy="1e-6" iyz="0" izz="1e-6" />
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="camera_joint" type="fixed">
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
<origin xyz=".2 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<parent link="chassis"/>
<child link="camera"/>
</joint>
添加laser
<joint name="hokuyo_joint" type="fixed">
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
<origin xyz=".15 0 .1" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<parent link="chassis"/>
<child link="hokuyo"/>
</joint>
<!-- Hokuyo Laser -->
<link name="hokuyo">
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size="0.1 0.1 0.1"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://neurobot_description/meshes/hokuyo.dae"/>
</geometry>
</visual>
<inertial>
<mass value="1e-5" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<inertia ixx="1e-6" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyy="1e-6" iyz="0" izz="1e-6" />
</inertial>
</link>
3. 添加模型插件
只有添加了模型插件,我们才能编写代码控制机器人的运动,采用信息。插件是模型和代码的桥梁。
在neurobot.gazebo中添加gazebo具体描述信息和插件。
差分驱动
<gazebo>
<plugin name="differential_drive_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_diff_drive.so">
<legacyMode>false</legacyMode>
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>10</updateRate>
<leftJoint>left_wheel_hinge</leftJoint>
<rightJoint>right_wheel_hinge</rightJoint>
<wheelSeparation>0.4</wheelSeparation>
<wheelDiameter>0.2</wheelDiameter>
<torque>10</torque>
<commandTopic>cmd_vel</commandTopic>
<odometryTopic>odom</odometryTopic>
<odometryFrame>odom</odometryFrame>
<robotBaseFrame>chassis</robotBaseFrame>
</plugin>
</gazebo>
camera
<gazebo reference="camera">
<material>Gazebo/Green</material>
<sensor type="camera" name="camera1">
<update_rate>30.0</update_rate>
<camera name="head">
<horizontal_fov>1.3962634</horizontal_fov>
<image>
<width>800</width>
<height>800</height>
<format>R8G8B8</format>
</image>
<clip>
<near>0.02</near>
<far>300</far>
</clip>
</camera>
<plugin name="camera_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_camera.so">
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>0.0</updateRate>
<cameraName>neurobot/camera1</cameraName>
<imageTopicName>image_raw</imageTopicName>
<cameraInfoTopicName>camera_info</cameraInfoTopicName>
<frameName>camera</frameName>
<hackBaseline>0.07</hackBaseline>
<distortionK1>0.0</distortionK1>
<distortionK2>0.0</distortionK2>
<distortionK3>0.0</distortionK3>
<distortionT1>0.0</distortionT1>
<distortionT2>0.0</distortionT2>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo>
laser
laser的几何信息采用mesh文件hokuyo.dae放在meshes文件夹中,
<!-- hokuyo -->
<gazebo reference="hokuyo">
<sensor type="gpu_ray" name="head_hokuyo_sensor">
<pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
<visualize>false</visualize>
<update_rate>40</update_rate>
<ray>
<scan>
<horizontal>
<samples>720</samples>
<resolution>1</resolution>
<min_angle>-1.570796</min_angle>
<max_angle>1.570796</max_angle>
</horizontal>
</scan>
<range>
<min>0.10</min>
<max>30.0</max>
<resolution>0.01</resolution>
</range>
<noise>
<type>gaussian</type>
<!-- Noise parameters based on published spec for Hokuyo laser
achieving "+-30mm" accuracy at range < 10m. A mean of 0.0m and
stddev of 0.01m will put 99.7% of samples within 0.03m of the true
reading. -->
<mean>0.0</mean>
<stddev>0.01</stddev>
</noise>
</ray>
<plugin name="gazebo_ros_head_hokuyo_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_gpu_laser.so">
<topicName>/neurobot/laser/scan</topicName>
<frameName>hokuyo</frameName>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo
gazebo仿真材料信息
<gazebo reference="chassis">
<material>Gazebo/Orange</material>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="left_wheel">
<material>Gazebo/Blue</material>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="right_wheel">
<material>Gazebo/Blue</material>
</gazebo>
4.机器人控制
终于到了我们可以控制自己建立的机器人了。
在rviz中查看自己的机器人
roslaunch neurobot_description neurobot_rviz.launch
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<launch>
<param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro.py '$(find mybot_description)/urdf/mybot.xacro'"/>
<!-- send fake joint values -->
<node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher">
<param name="use_gui" value="False"/>
</node>
<!-- Combine joint values -->
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="state_publisher"/>
<!-- Show in Rviz -->
<node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz"/>
<!--node name="rviz" pkg="rviz" type="rviz" args="-d $(find mybot_description)/launch/myrobot.rviz"/-->
</launch>
在gazebo中加载机器人并控制机器人运动
依然采用在turtlebot中使用的world场景,加载机器人。
roslaunch neurobot_gazebo neurobot_world.launch
rostopic list
我们可以找到非常重要的四个topic
/cmd_vel 速度控制命令
/neurobot/camera1/image_raw 图像信息
/neurobot/laser/scan 激光数据
/odom 里程计
使用如下命令便可以控制机器人运动了,fancy。
rostopic pub /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist "linear:
x: 0.1
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
angular:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0"
也可以使用我们之前turtlebot中使用的keyboard_teleop.launch 和keyop.launch, 将topic主题映射到/cmd_vel。
References:
How to Build a Differential Drive Simulation urdf Tutorials