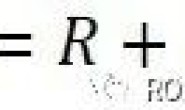目录

VIO 相关知识回顾
IMU 传感器模型:
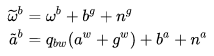
IMU 预积分:
将一段时间内的 IMU 数据直接积分起来就能得到两时刻 i,j 之间关于 IMU 的测量约束,即 预积分量:

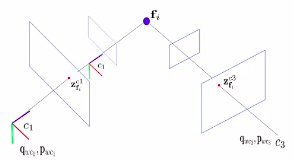
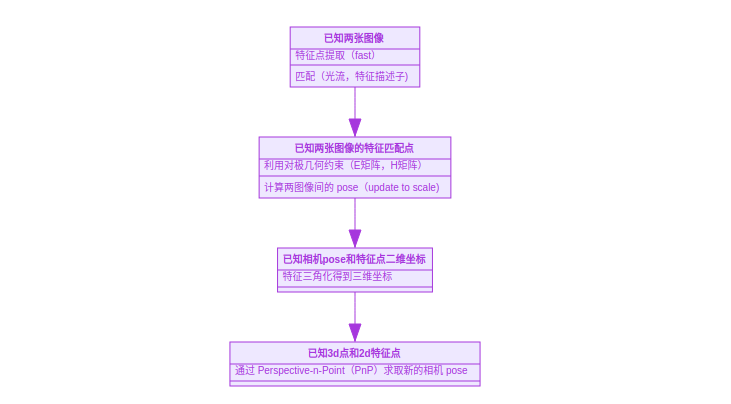
VINS 鲁棒初始化
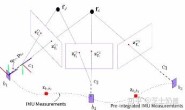
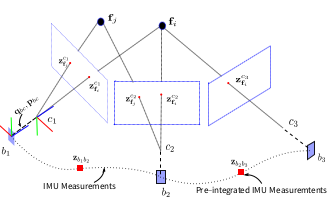
视觉和 IMU 之间的联系
相机坐标系
为世界坐标系,利用外参数
构建等式:
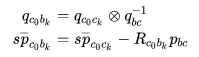
其中,
为尺度因子,
表示非米制单位的轨迹。等式(3)等价:
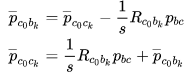
式子中的
这样理解:camera 和 imu body 之间有一个
轨迹的变换,这个变换是在 world 坐标系下,那
就是从 world 坐标系(
坐标系)变换到现在要计算轨迹的
坐标系下。(4)第一个中第一个式子也可以写成这样:
。
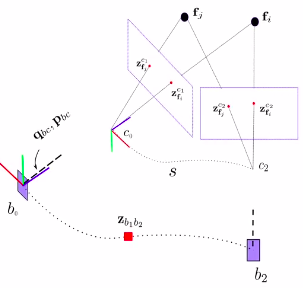
估计流程
① 旋转外参数
未知,则先估计旋转外参数. ② 利用旋转约束估计陀螺仪 bias.
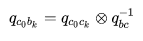
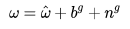
③ 利用平移约束估计重力方向,速度,以及尺度初始值.
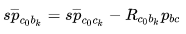
④ 对重力向量
进一步优化. ⑤ 求解世界坐标系
和初始相机坐标系
之间的旋转矩阵
,并将轨迹对齐到世界坐标系(可以用
也就是相机坐标系
的重力加速度,与
对比,求算出之间的旋转关系). 论文:
- Zhenfei, Yang, Shaojie,等. Monocular Visual–Inertial State Estimation With Online Initialization and Camera–IMU Extrinsic Calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science & Engineering, 2017.
2. Qin T , Shen S . Robust initialization of monocular visual-inertial estimation on aerial robots[C]// IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots & Systems. IEEE, 2017:4225-4232.
利用旋转约束估计外参数旋转
![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=q_%7Bbc%7D)
相邻两时刻
之间有:IMU 旋转积分
,视觉测量
。则有:

上式可写成:
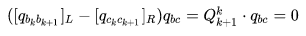
其中,
表示 left and right quaternion multiplication。

将多个时刻线性方程累计起来,并加上鲁棒核权重得到:
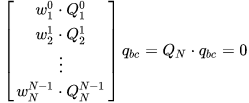
其中:
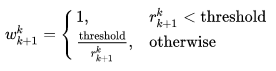
由旋转矩阵和轴角之间的关系
,能得到角度误差
的计算为:
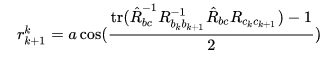
公式 (7) 最小二乘解仍使用 SVD 分解,取最小奇异值对应的奇异向量。 这里简单解释一下为什么取
的最小奇异值对应的奇异向量,能使得最小二乘问题
最接近零: 可以假设
是任意的奇异向量,
是系数,这样一对基向量可以表示在
的空间下所有向量。
就可以展开为:
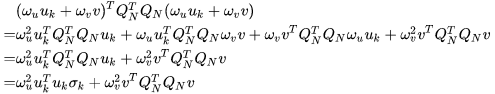
当
能使问题最小。最小奇异值对应的奇异向量是
分解后,
的最右边一列。
bool InitialEXRotation::CalibrationExRotation(vector<pair<Vector3d, Vector3d>> corres, Quaterniond delta_q_imu, Matrix3d &calib_ric_result)
{
frame_count++;
Rc.push_back(solveRelativeR(corres));
Rimu.push_back(delta_q_imu.toRotationMatrix());
Rc_g.push_back(ric.inverse() * delta_q_imu * ric);
Eigen::MatrixXd A(frame_count * 4, 4);
A.setZero();
int sum_ok = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= frame_count; i++)
{
Quaterniond r1(Rc[i]);
Quaterniond r2(Rc_g[i]);
double angular_distance = 180 / M_PI * r1.angularDistance(r2);
//ROS_DEBUG("%d %f", i, angular_distance);
double huber = angular_distance > 5.0 ? 5.0 / angular_distance : 1.0;
++sum_ok;
Matrix4d L, R;
double w = Quaterniond(Rc[i]).w();
Vector3d q = Quaterniond(Rc[i]).vec();
L.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = w * Matrix3d::Identity() + Utility::skewSymmetric(q);
L.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = q;
L.block<1, 3>(3, 0) = -q.transpose();
L(3, 3) = w;
Quaterniond R_ij(Rimu[i]);
w = R_ij.w();
q = R_ij.vec();
R.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = w * Matrix3d::Identity() - Utility::skewSymmetric(q);
R.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = q;
R.block<1, 3>(3, 0) = -q.transpose();
R(3, 3) = w;
A.block<4, 4>((i - 1) * 4, 0) = huber * (L - R);
}
JacobiSVD<MatrixXd> svd(A, ComputeFullU | ComputeFullV);
Matrix<double, 4, 1> x = svd.matrixV().col(3);
Quaterniond estimated_R(x);
ric = estimated_R.toRotationMatrix().inverse();
//cout << svd.singularValues().transpose() << endl;
//cout << ric << endl;
Vector3d ric_cov;
ric_cov = svd.singularValues().tail<3>();
if (frame_count >= WINDOW_SIZE && ric_cov(1) > 0.25)
{
calib_ric_result = ric;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
基于旋转约束的 Gyroscope Bias
如果外参数
已经标定好,利用旋转约束,可估计陀螺仪 bias:
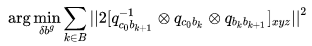
是相机测得的 k 到 k+1 的变换,
是 imu 测得的,这里用视觉修正 imu。 其中,
表示取虚部,对于这个问题来说,2倍的就是角度
,因为
。
表示所有的图像关键帧集合,另有预积分的一阶泰勒近似:
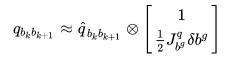
公式(10)是普通的最小二乘问题,求其雅可比矩阵,构建正定方程
即可求解。前面那个方程是超正定的,即方程个数超过更新变量的个数。
void solveGyroscopeBias(map<double, ImageFrame> &all_image_frame, Vector3d* Bgs)
{
Matrix3d A;
Vector3d b;
Vector3d delta_bg;
A.setZero();
b.setZero();
map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_i;
map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_j;
for (frame_i = all_image_frame.begin(); next(frame_i) != all_image_frame.end(); frame_i++)
{
frame_j = next(frame_i);
MatrixXd tmp_A(3, 3);
tmp_A.setZero();
VectorXd tmp_b(3);
tmp_b.setZero();
Eigen::Quaterniond q_ij(frame_i->second.R.transpose() * frame_j->second.R);
tmp_A = frame_j->second.pre_integration->jacobian.template block<3, 3>(O_R, O_BG);
tmp_b = 2 * (frame_j->second.pre_integration->delta_q.inverse() * q_ij).vec();
A += tmp_A.transpose() * tmp_A;
b += tmp_A.transpose() * tmp_b;
}
delta_bg = A.ldlt().solve(b);
// ROS_WARN_STREAM("gyroscope bias initial calibration " << delta_bg.transpose());
for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
Bgs[i] += delta_bg;
for (frame_i = all_image_frame.begin(); next(frame_i) != all_image_frame.end( ); frame_i++)
{
frame_j = next(frame_i);
frame_j->second.pre_integration->repropagate(Vector3d::Zero(), Bgs[0]);
}
}
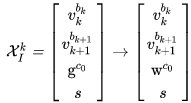
初始化速度、重力和尺度因子
需要估计的变量:
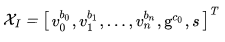
其中,
表示 k 时刻 body 坐标系的速度在 body 坐标系下的表示。
为重力向量在第 0 帧相机坐标系下的表示。
表示 scale 就是尺度因子,将视觉轨迹拉伸到米制单位,统一 imu 和视觉单位。 预积分量约束: 世界坐标系
下有:
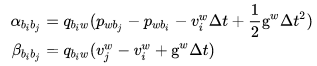
简单来说:公式就是就是把影响
和
的除预积分外的所有因素都减去了,其实就是等于预积分量。 把世界坐标系
换成相机初始时刻坐标系
有:
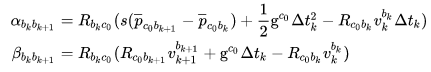
与↓
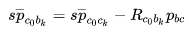
结合,有:
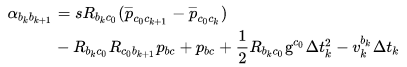
而不是
的原因是
的这个负号。 将待估计的变量放在方程右边,有:
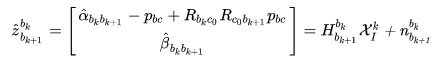
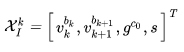
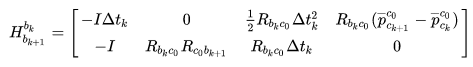
由于预积分的计算中 imu 测得的角速度和加速度并不是完全满足公式的,存在 bias 和高斯白噪声,可以用协方差矩阵的传递,最终得到公式估计值和真实值的偏差
,构建最小二乘问题求解,即
何值时,能使得偏差最小,估计值最接近真实值:
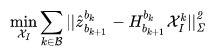
bool LinearAlignment(map<double, ImageFrame> &all_image_frame, Vector3d &g, VectorXd &x)
{
int all_frame_count = all_image_frame.size();
int n_state = all_frame_count * 3 + 3 + 1;
MatrixXd A{n_state, n_state};
A.setZero();
VectorXd b{n_state};
b.setZero();
map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_i;
map<double, ImageFrame>::iterator frame_j;
int i = 0;
for (frame_i = all_image_frame.begin(); next(frame_i) != all_image_frame.end(); frame_i++, i++)
{
frame_j = next(frame_i);
MatrixXd tmp_A(6, 10);
tmp_A.setZero();
VectorXd tmp_b(6);
tmp_b.setZero();
double dt = frame_j->second.pre_integration->sum_dt;
tmp_A.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = -dt * Matrix3d::Identity();
tmp_A.block<3, 3>(0, 6) = frame_i->second.R.transpose() * dt * dt / 2 * Matrix3d::Identity();
tmp_A.block<3, 1>(0, 9) = frame_i->second.R.transpose() * (frame_j->second.T - frame_i->second.T) / 100.0;
tmp_b.block<3, 1>(0, 0) = frame_j->second.pre_integration->delta_p + frame_i->second.R.transpose() * frame_j->second.R * TIC[0] - TIC[0];
//cout << "delta_p " << frame_j->second.pre_integration->delta_p.transpose() << endl;
tmp_A.block<3, 3>(3, 0) = -Matrix3d::Identity();
tmp_A.block<3, 3>(3, 3) = frame_i->second.R.transpose() * frame_j->second.R;
tmp_A.block<3, 3>(3, 6) = frame_i->second.R.transpose() * dt * Matrix3d::Identity();
tmp_b.block<3, 1>(3, 0) = frame_j->second.pre_integration->delta_v;
//cout << "delta_v " << frame_j->second.pre_integration->delta_v.transpose() << endl;
Matrix<double, 6, 6> cov_inv = Matrix<double, 6, 6>::Zero();
//cov.block<6, 6>(0, 0) = IMU_cov[i + 1];
//MatrixXd cov_inv = cov.inverse();
cov_inv.setIdentity();
MatrixXd r_A = tmp_A.transpose() * cov_inv * tmp_A;
VectorXd r_b = tmp_A.transpose() * cov_inv * tmp_b;
A.block<6, 6>(i * 3, i * 3) += r_A.topLeftCorner<6, 6>();
b.segment<6>(i * 3) += r_b.head<6>();
A.bottomRightCorner<4, 4>() += r_A.bottomRightCorner<4, 4>();
b.tail<4>() += r_b.tail<4>();
A.block<6, 4>(i * 3, n_state - 4) += r_A.topRightCorner<6, 4>();
A.block<4, 6>(n_state - 4, i * 3) += r_A.bottomLeftCorner<4, 6>();
}
A = A * 1000.0;
b = b * 1000.0;
x = A.ldlt().solve(b);
double s = x(n_state - 1) / 100.0;
// ROS_DEBUG("estimated scale: %f", s);
g = x.segment<3>(n_state - 4);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM(" result g " << g.norm() << " " << g.transpose());
if(fabs(g.norm() - G.norm()) > 1.0 || s < 0)
{
return false;
}
RefineGravity(all_image_frame, g, x);
s = (x.tail<1>())(0) / 100.0;
(x.tail<1>())(0) = s;
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM(" refine " << g.norm() << " " << g.transpose());
if(s < 0.0 )
return false;
else
return true;
}
优化重力向量
![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=%5CBbb+g%5E%7Bc_0%7D)
重力向量在三维空间下是三自由度的,但是加入
的限定,实际上只剩下两个自由度。多一个限制就少一个自由度这个很好理解吧,和机械设计中低副限制两个自由度、高副限制一个自由度是一样的。 重力向量参数化: 一种简单的参数化方法:一个三维向量,模长一定即
,和球面方程相同,可以通过求下图中
与球面相交于一点,球心到这一点即重力向量方向。这里的
就是两个自由度的参数化。
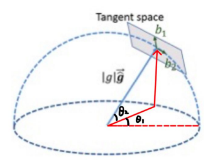
VINS-Mono中参数化方法:三维向量自由度为 2,采用球面坐标参数化:

可以构建一个新的坐标系,表示空间内任意一个三维向量。
是上一个步骤中估计出的重力向量,其中,
是待优化变量。

公式 (19) 带入公式 (16),待优化变量变成:
观测方程 (16) 也变成了:
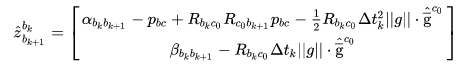
采用最小二乘对
重新优化。 相机坐标系对齐世界坐标系:
- 找到
到
世界坐标系的旋转矩阵
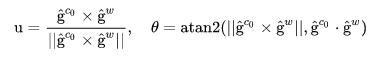
- 把相机坐标系下的变量旋转到世界坐标系下。
- 把相机平移和特征点尺度恢复到米制单位。
其他初始化方案:
- Mustaniemi J , Kannala J , Särkkä, Simo, et al. Inertial-Based Scale Estimation for Structure from Motion on Mobile Devices[J]. 2016.
- Dominguez-Conti J , Yin J , Alami Y , et al. Visual-Inertial SLAM Initialization: A General Linear Formulation and a Gravity-Observing Non-Linear Optimization[C]// 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR). IEEE, 2018.
VINS 系统
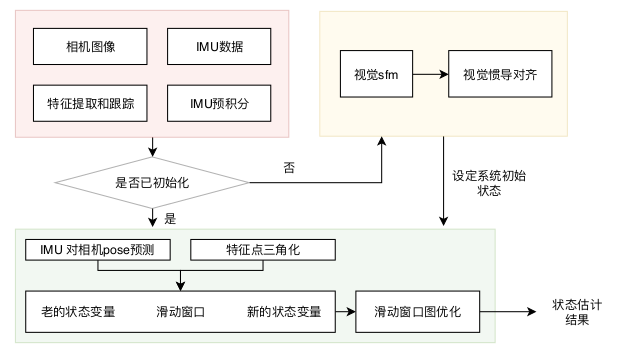
VINS 系统优化的状态变量为:
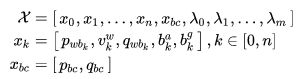
最小化滑动窗口中的残差项估计系统的状态变量:

鲁棒核函数
只用来处理 outlier。