1. 简介
在移动机器人建图和导航过程中,提供相对准确的里程计信息非常关键,是后续很多工作的基础,因此需要对其进行测试保证没有严重的错误或偏差。实际中最可能发生错
误的地方在于机器人运动学公式有误,或者正负号不对,或者定义的坐标系之间方向不一致等。
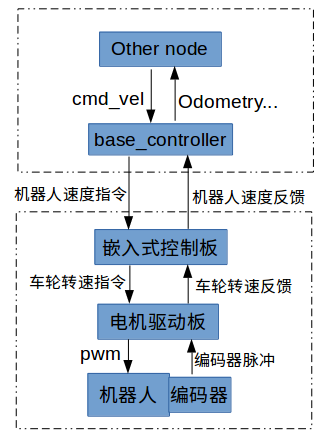
整个移动机器人的控制结构如下图所示,其中base_controller节点将订阅的cmd_vel信息通过串口或其它通信接口发送给下位机(嵌入式控制板)。下位机中根据机器人运
动学公式进行解算,将机器人速度转换为每个轮子的速度,然后通过CAN总线(或其它总线接口如RS485通信)将每个轮子的转速发送给电机驱动板控制电机转动。
而后,电机驱动板对电机转速进行闭环控制(PID控制等),并统计单位时间内接收到的编码器脉冲数,计算出轮子转速。
base_controller节点将接收到的cmd_vel速度信息转换为自定义的结构体或union类型的数据(自定义的数据类型中可以包含校验码等其它信息),并通过串口发送控制速度信息(speed_buf)或读取机器人传回的速度信息 (speed_buf_rev)。base_controller节点正确读取到底层(比如嵌入式控制板)传回的速度后进行积分,计算出机器人的估计位置和姿态,并将里程计信息和tf变换发布出去。下面的代码只是一个例子,需要完善自定义的数据结构和校验函数:
#include // C++标准库头文件
#include
#include
#include <boost/asio.hpp> // boost库头文件
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <ros/ros.h> // ros头文件
#include <std_msgs/String.h>
#include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Quaternion.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/PoseStamped.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/PolygonStamped.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Polygon.h>
#include <geometry_msgs/Point32.h>
#include <tf/tf.h>
#include <tf/transform_broadcaster.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost::asio;
/********************************回调函数***************************************/
void cmd_velCallback(const geometry_msgs::Twist &twist_aux)
{
// 在回调函数中将接收到的cmd_vel速度消息转换为自定义的结构体(或者union)类型的数据
speed_buf.vx = twist_aux.linear.x;
speed_buf.vy = twist_aux.linear.y;
speed_buf.vth = twist_aux.angular.z;
}
double x = 0.0; // 初始位置x的坐标
double y = 0.0; // 初始位置y的坐标
double th = 0.0; // 初始位置的角度
double vx = 0.0; // x方向的初始速度
double vy = 0.0; // y方向的初始速度
double vth = 0.0; // 初始角速度
double dt = 0.0; // 积分时间
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
/****************************** 配置串口 ***********************************/
io_service iosev;
serial_port sp(iosev, "/dev/ttyUSB0"); // 设置串口名称
sp.set_option(serial_port::baud_rate(115200)); // 设置波特率
sp.set_option(serial_port::flow_control(serial_port::flow_control::none)); // 设置控制方式
sp.set_option(serial_port::parity(serial_port::parity::none)); // 设置奇偶校验
sp.set_option(serial_port::stop_bits(serial_port::stop_bits::one)); // 设置停止位
sp.set_option(serial_port::character_size(8)); // 设置字母位数为8位
ros::init(argc, argv, "base_controller"); // 初始化node节点
ros::NodeHandle n;
ros::Subscriber cmd_vel_sub = n.subscribe("cmd_vel", 100, cmd_velCallback); // 订阅cmd_vel topic
ros::Publisher odom_pub = n.advertise("odom", 10); // 发布odom topic
tf::TransformBroadcaster odom_broadcaster; // 发布base_link --> odom的tf变换
ros::Publisher poly_pub = n.advertise("polygon",10); // 发布PolygonStamped信息,rviz中显示机器人边界
ros::Time current_time, last_time;
current_time = ros::Time::now();
last_time = ros::Time::now();
while(ros::ok())
{
current_time = ros::Time::now();
read(sp, buffer(speed_buf_rev)); // 从串口读取机器人速度数据
if(CRC_verify(speed_buf_rev)) // 对接收到的数据进行校验
{
vx = speed_buf_rev.vx;
vy = speed_buf_rev.vy;
vth = speed_buf_rev.vth;
// 打印接收到的机器人速度信息
ROS_INFO("vx is %2f", vx);
ROS_INFO("vy is %2f", vy);
ROS_INFO("vth is %2f", vth);
/**compute odometry in a typical way given the velocities of the robot**/
double dt = (current_time - last_time).toSec();
double delta_x = (vx * cos(th) - vy * sin(th)) * dt;
double delta_y = (vx * sin(th) + vy * cos(th)) * dt;
double delta_th = vth * dt;
x += delta_x;
y += delta_y;
th += delta_th;
/***********first, we'll publish the transform over tf*************/
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped odom_trans;
odom_trans.header.stamp = current_time;
odom_trans.header.frame_id = "odom";
odom_trans.child_frame_id = "base_link";
odom_trans.transform.translation.x = x;
odom_trans.transform.translation.y = y;
odom_trans.transform.translation.z = 0.0;
odom_trans.transform.rotation = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromYaw(th);
// send the transform
odom_broadcaster.sendTransform(odom_trans);
/*********next, we'll publish the odometry message over ROS*******/
nav_msgs::Odometry odom;
odom.header.stamp = current_time;
odom.header.frame_id = "odom";
odom.child_frame_id = "base_link";
// since all odometry is 6DOF we'll need a quaternion created from yaw
geometry_msgs::Quaternion odom_quat = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromRollPitchYaw(0,0,th);
//set the position
odom.pose.pose.position.x = x;
odom.pose.pose.position.y = y;
odom.pose.pose.position.z = 0.0;
odom.pose.pose.orientation = odom_quat;
// set the velocity
odom.twist.twist.linear.x = vx;
odom.twist.twist.linear.y = vy;
odom.twist.twist.angular.z = vth;
odom_pub.publish(odom);
/*******************publish polygon message***********************/
geometry_msgs::Point32 point[4];
// coordinates described in base_link frame
point[0].x = -0.39; point[0].y = -0.31;
point[1].x = 0.39; point[1].y = -0.31;
point[2].x = 0.39; point[2].y = 0.31;
point[3].x = -0.39; point[3].y = 0.31;
geometry_msgs::PolygonStamped poly;
poly.header.stamp = current_time;
poly.header.frame_id = "base_link"; // 多边形相对于base_link来描述
poly.polygon.points.push_back(point[0]);
poly.polygon.points.push_back(point[1]);
poly.polygon.points.push_back(point[2]);
poly.polygon.points.push_back(point[3]);
poly_pub.publish(poly);
}
else
ROS_INFO("Serial port communication failed!");
write(sp, buffer(speed_buf, buffer_length)); // 速度控制信息写入串口
last_time = current_time;
ros::spinOnce();
} // end-while
iosev.run();
}参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/21207-iHome/p/8066135.html
https://blog.csdn.net/lxiaoxiaot/article/details/6779936