最近在做并联机器人的仿真分析,前面提到,urdf格式不支持闭链结构,因此只能用sdf格式。而ros_control控制插件并不支持sdf格式的模型,目前还没有找到好的替代方案,最终决定自己写插件,主要是按照Gazebo的官网教程来做的,现在已经有了一些进展,把初步的成果分享出来。刚开始学习编写插件,必然有许多不合理的地方,欢迎交流。
另外,评论区一位朋友分享了一个很好的博客:gaoyichao.com/Xiaotu/ 上面有官方插件教程的全部翻译,以及其它一些优质资源,这里推荐给大家。
编写模型插件
模型插件可以用来控制模型的物理属性、关节、连杆和碰撞对象等底层属性。对于机器人,我们经常用到关节的位置控制,即,控制移动关节的位移/旋转关节的角度。下面举例说明:
首先在某个目录下(例如~/Documents/)创建插件目录以及position_controller.cc 文件:
$ cd ~/Documents/
$ mkdir position_controller
$ cd position_controller/
$ gedit position_controller.cc
在 position_controller.cc 中填写以下代码
#ifndef _POSITION_PLUGIN_HH_
#define _POSITION_PLUGIN_HH_
#include <gazebo/gazebo.hh>
#include <gazebo/physics/physics.hh>
#include <gazebo/transport/transport.hh>
#include <gazebo/msgs/msgs.hh>
#include <thread>
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "ros/callback_queue.h"
#include "ros/subscribe_options.h"
#include "std_msgs/Float32.h"
namespace gazebo
{
/// \brief A plugin to control joint position.
class PositionPlugin : public ModelPlugin
{
/// \brief Constructor
public: PositionPlugin() {}
/// \brief The load function is called by Gazebo when the plugin is
/// inserted into simulation
/// \param[in] _model A pointer to the model that this plugin is
/// attached to.
/// \param[in] _sdf A pointer to the plugin's SDF element.
public: virtual void Load(physics::ModelPtr _model, sdf::ElementPtr _sdf)
{
// Safety check
if (_model->GetJointCount() == 0)
{
std::cerr << "Invalid joint count, position plugin not loaded\n";
return;
}
// Default value
double position = 0.0, p_gain, i_gain, d_gain;
// Check that the element exists, then read the value
if (_sdf->HasElement("jointname"))
joint_name_ori = _sdf->Get<std::string>("jointname");
joint_name = _model->GetScopedName() + "::" + _model->GetScopedName() + "::" + joint_name_ori;
std::cerr << "We find the joint [" <<
joint_name << "]\n";
if (_sdf->HasElement("p_gain"))
p_gain = _sdf->Get<double>("p_gain");
if (_sdf->HasElement("i_gain"))
i_gain = _sdf->Get<double>("i_gain");
if (_sdf->HasElement("d_gain"))
d_gain = _sdf->Get<double>("d_gain");
// Store the model pointer for convenience.
this->model = _model;
std::cerr << "\n The model's name is [" <<
_model->GetScopedName() << "]\n";
// Setup a P-controller, with a gain of 0.1.
this->pid = common::PID(p_gain, i_gain, d_gain);
// Apply the P-controller to the joint.
this->model->GetJointController()->SetPositionPID(
joint_name, this->pid);
// Set the joint's target position.
this->model->GetJointController()->SetPositionTarget(
joint_name, position);
// Initialize ros, if it has not already bee initialized.
if (!ros::isInitialized())
{
int argc = 0;
char **argv = NULL;
ros::init(argc, argv, joint_name_ori + "_" + "node",
ros::init_options::NoSigintHandler);
}
// Create our ROS node.
this->rosNode.reset(new ros::NodeHandle(joint_name_ori + "_" + "Handle"));
// Create a named topic, and subscribe to it.
ros::SubscribeOptions so =
ros::SubscribeOptions::create<std_msgs::Float32>(
"/" + this->model->GetName() + "/" + joint_name_ori + "/pos_cmd",
1,
boost::bind(&PositionPlugin::OnRosMsg, this, _1),
ros::VoidPtr(), &this->rosQueue);
this->rosSub = this->rosNode->subscribe(so);
// Spin up the queue helper thread.
this->rosQueueThread =
std::thread(std::bind(&PositionPlugin::QueueThread, this));
}
/// \brief Set the position of the joint
/// \param[in] _pos New target position
public: void SetPosition(const double &_pos)
{
// Set the joint's target velocity.
this->model->GetJointController()->SetPositionTarget(
joint_name, _pos);
}
/// \brief Handle an incoming message from ROS
/// \param[in] _msg A float value that is used to set the position
/// of the joint.
public: void OnRosMsg(const std_msgs::Float32ConstPtr &_msg)
{
this->SetPosition(_msg->data);
}
/// \brief ROS helper function that processes messages
private: void QueueThread()
{
static const double timeout = 0.01;
while (this->rosNode->ok())
{
this->rosQueue.callAvailable(ros::WallDuration(timeout));
}
}
/// \brief Pointer to the model.
private: physics::ModelPtr model;
/// \brief Pointer to the joint.
private: physics::JointPtr joint;
/// \brief A PID controller for the joint.
private: common::PID pid;
/// \brief A node use for ROS transport
private: std::unique_ptr<ros::NodeHandle> rosNode;
/// \brief A ROS subscriber
private: ros::Subscriber rosSub;
/// \brief A ROS callbackqueue that helps process messages
private: ros::CallbackQueue rosQueue;
/// \brief A thread the keeps running the rosQueue
private: std::thread rosQueueThread;
public: std::string joint_name, joint_name_ori;
};
// Tell Gazebo about this plugin, so that Gazebo can call Load on this plugin.
GZ_REGISTER_MODEL_PLUGIN(PositionPlugin)
}
#endif
注释已经比较全了,下面逐步分析代码:
#ifndef _POSITION_PLUGIN_HH_
#define _POSITION_PLUGIN_HH_
#include <gazebo/gazebo.hh>
#include <gazebo/physics/physics.hh>
#include <gazebo/transport/transport.hh>
#include <gazebo/msgs/msgs.hh>
#include <thread>
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "ros/callback_queue.h"
#include "ros/subscribe_options.h"
#include "std_msgs/Float32.h"
namespace gazebo
{
/// \brief A plugin to control joint position.
class PositionPlugin : public ModelPlugin
{
引用头文件。从 ModelPlugin 继承一个插件类,命名为 PositionPlugin。
/// \brief Constructor
public: PositionPlugin() {}
初始化所创建的插件类类
/// \brief The load function is called by Gazebo when the plugin is
/// inserted into simulation
/// \param[in] _model A pointer to the model that this plugin is
/// attached to.
/// \param[in] _sdf A pointer to the plugin's SDF element.
public: virtual void Load(physics::ModelPtr _model, sdf::ElementPtr _sdf)
{
利用Load函数加载模型以及sdf文件的标签元素,这些参数是插件作用于模型的桥梁。
// Safety check
if (_model->GetJointCount() == 0)
{
std::cerr << "Invalid joint count, position plugin not loaded\n";
return;
}
安全检查,检测是否读取到关节。如果模型不存在<joint>关节标签,将停止初始化,以免报错。
// Default value
double position = 0.0, p_gain, i_gain, d_gain;
// Check that the element exists, then read the value
if (_sdf->HasElement("jointname"))
joint_name_ori = _sdf->Get<std::string>("jointname");
joint_name = _model->GetScopedName() + "::" + _model->GetScopedName() + "::" + joint_name_ori;
std::cerr << "We find the joint [" <<
joint_name << "]\n";
if (_sdf->HasElement("p_gain"))
p_gain = _sdf->Get<double>("p_gain");
if (_sdf->HasElement("i_gain"))
i_gain = _sdf->Get<double>("i_gain");
if (_sdf->HasElement("d_gain"))
d_gain = _sdf->Get<double>("d_gain");
定义初始位置,接下来读取sdf文件元素参数的值。包括关节名<jointname>、pid参数等。这些参数需要在sdf文件调用插件时进行定义。
// Store the model pointer for convenience.
this->model = _model;
std::cerr << "\n The model's name is [" <<
_model->GetScopedName() << "]\n";
// Setup a P-controller, with a gain of 0.1.
this->pid = common::PID(p_gain, i_gain, d_gain);
// Apply the P-controller to the joint.
this->model->GetJointController()->SetPositionPID(
joint_name, this->pid);
// Set the joint's target position.
this->model->GetJointController()->SetPositionTarget(
joint_name, position);
存储模型,并通过 GetJointController() 方法设置pid参数和初始位置。
// Initialize ros, if it has not already bee initialized.
if (!ros::isInitialized())
{
int argc = 0;
char **argv = NULL;
ros::init(argc, argv, joint_name_ori + "_" + "node",
ros::init_options::NoSigintHandler);
}
检测ros是否初始化,如果没有,初始化ros。
// Create our ROS node.
this->rosNode.reset(new ros::NodeHandle(joint_name_ori + "_" + "Handle"));
// Create a named topic, and subscribe to it.
ros::SubscribeOptions so =
ros::SubscribeOptions::create<std_msgs::Float32>(
"/" + this->model->GetName() + "/" + joint_name_ori + "/pos_cmd",
1,
boost::bind(&PositionPlugin::OnRosMsg, this, _1),
ros::VoidPtr(), &this->rosQueue);
this->rosSub = this->rosNode->subscribe(so);
// Spin up the queue helper thread.
this->rosQueueThread =
std::thread(std::bind(&PositionPlugin::QueueThread, this));
}
创建ROS节点与话题,话题名称为/MODELNAME/JOINTNAME/pos_cmd的形式,当然也可以根据需求进行更改。
/// \brief Set the position of the joint
/// \param[in] _pos New target position
public: void SetVelocity(const double &_pos)
{
// Set the joint's target velocity.
this->model->GetJointController()->SetPositionTarget(
joint_name, _pos);
}
定义位置控制函数,方法和初始化时一样,只不过位置参数是从ros话题传入的。
/// \brief Handle an incoming message from ROS
/// \param[in] _msg A float value that is used to set the position
/// of the joint.
public: void OnRosMsg(const std_msgs::Float32ConstPtr &_msg)
{
this->SetVelocity(_msg->data);
}
ros消息订阅者回调函数,一旦接收到消息,就将消息传入位置控制函数。
/// \brief ROS helper function that processes messages
private: void QueueThread()
{
static const double timeout = 0.01;
while (this->rosNode->ok())
{
this->rosQueue.callAvailable(ros::WallDuration(timeout));
}
}
利用rosQueue.callAvailable来处理队列消息。
/// \brief Pointer to the model.
private: physics::ModelPtr model;
/// \brief Pointer to the joint.
private: physics::JointPtr joint;
/// \brief A PID controller for the joint.
private: common::PID pid;
/// \brief A node use for ROS transport
private: std::unique_ptr<ros::NodeHandle> rosNode;
/// \brief A ROS subscriber
private: ros::Subscriber rosSub;
/// \brief A ROS callbackqueue that helps process messages
private: ros::CallbackQueue rosQueue;
/// \brief A thread the keeps running the rosQueue
private: std::thread rosQueueThread;
public: std::string joint_name, joint_name_ori;
};
定义上面用到的所有变量。
// Tell Gazebo about this plugin, so that Gazebo can call Load on this plugin.
GZ_REGISTER_MODEL_PLUGIN(PositionPlugin)
}
#endif
利用 GZ_REGISTER_MODEL_PLUGIN 在Gazebo中注册插件。
编译插件
在插件文件夹下新建CMakeLists.txt文件:
$ gedit ~/Documents/position_controller/CMakeLists.txt
在文件中填写以下内容:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8 FATAL_ERROR)
find_package(roscpp REQUIRED)
find_package(std_msgs REQUIRED)
include_directories(${roscpp_INCLUDE_DIRS})
include_directories(${std_msgs_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# Find Gazebo
find_package(gazebo REQUIRED)
include_directories(${GAZEBO_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${GAZEBO_LIBRARY_DIRS})
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} ${GAZEBO_CXX_FLAGS}")
# Build our plugin
add_library(position_controller SHARED position_controller.cc)
target_link_libraries(position_controller ${GAZEBO_LIBRARIES} ${roscpp_LIBRARIES})
接下来创建build目录并编译代码:
$ mkdir ~/Documents/position_controller/build
$ cd ~/Documents/position_controller/build
$ cmake ../
$ make
编译完成后,将会在 build 目录下生成一个共享库 libposition_controller.so。为了能够在Gazebo中插入该库,我们需要将库的路径添加到环境变量 GAZEBO_PLUGIN_PATH 中。我们打开 ~/.bashrc 文件:
gedit ~/.bashrc
在文件末尾添加以下代码并保存,重新打开终端使环境变量加载生效。
export GAZEBO_PLUGIN_PATH=${GAZEBO_PLUGIN_PATH}:~/Documents/position_controller/build/
下载示例模型并编写world文件
从以下连接下载示例sdf模型,是两个内外嵌套、可以沿轴线移动的圆柱体。将model.config和model.sdf两个文件放置在 ~/.gazebo/models/pos_control_model 目录下(因为 ~/.gazebo/models/ 目录在Gazebo默认环境变量中,可以直接加载)。
在终端中输入以下命令以创建一个世界文件,也可以在已有的世界文件中直接进行加载:
$ cd ~/Documents/position_controller
$ gedit pos_control_model.world
pos_control_world.world 的内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<sdf version="1.6">
<world name="pos_control_world">
<!-- 环境光 -->
<include>
<uri>model://sun</uri>
</include>
<!-- 地面 -->
<include>
<uri>model://ground_plane</uri>
</include>
<!-- A testing model -->
<model name='pos_control_model'>
<include>
<uri>model://pos_control_model</uri>
</include>
<joint name="fixed to ground" type="fixed">
<parent>world</parent>
<child>pos_control_model::link_0</child>
</joint>
<!-- Attach the plugin to this model -->
<plugin name="position_controller" filename="libposition_controller.so">
<jointname>joint_0</jointname>
<!-- PID gain for controller -->
<p_gain>1e3</p_gain>
<i_gain>0.0</i_gain>
<d_gain>10.0</d_gain>
</plugin>
</model>
</world>
</sdf>
其中这一部分:
<!-- A testing model -->
<model name='pos_control_model'>
<include>
<uri>model://pos_control_model</uri>
</include>
加载了刚才下载的模型。
这一部分:
<!-- Attach the plugin to this model -->
<plugin name="position_controller" filename="libposition_controller.so">
<jointname>joint_0</jointname>
<!-- PID gain for controller -->
<p_gain>1e3</p_gain>
<i_gain>0</i_gain>
<d_gain>10</d_gain>
</plugin>
声明了刚刚编写的控制插件。并定义了所需控制的关节名称和pid参数,这里我们先随意指定pid参数,具体应用时可以再做调整。
使用插件
先从终端中启动ROS主机:
$ roscore
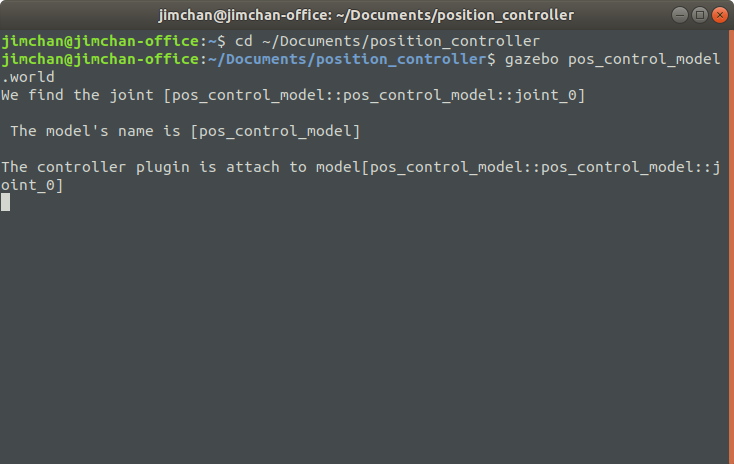
新开一个终端,从gazebo中运行model_push.world文件:
$ cd ~/Documents/position_controller
$ gazebo pos_control_model.world
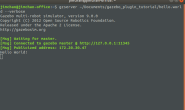
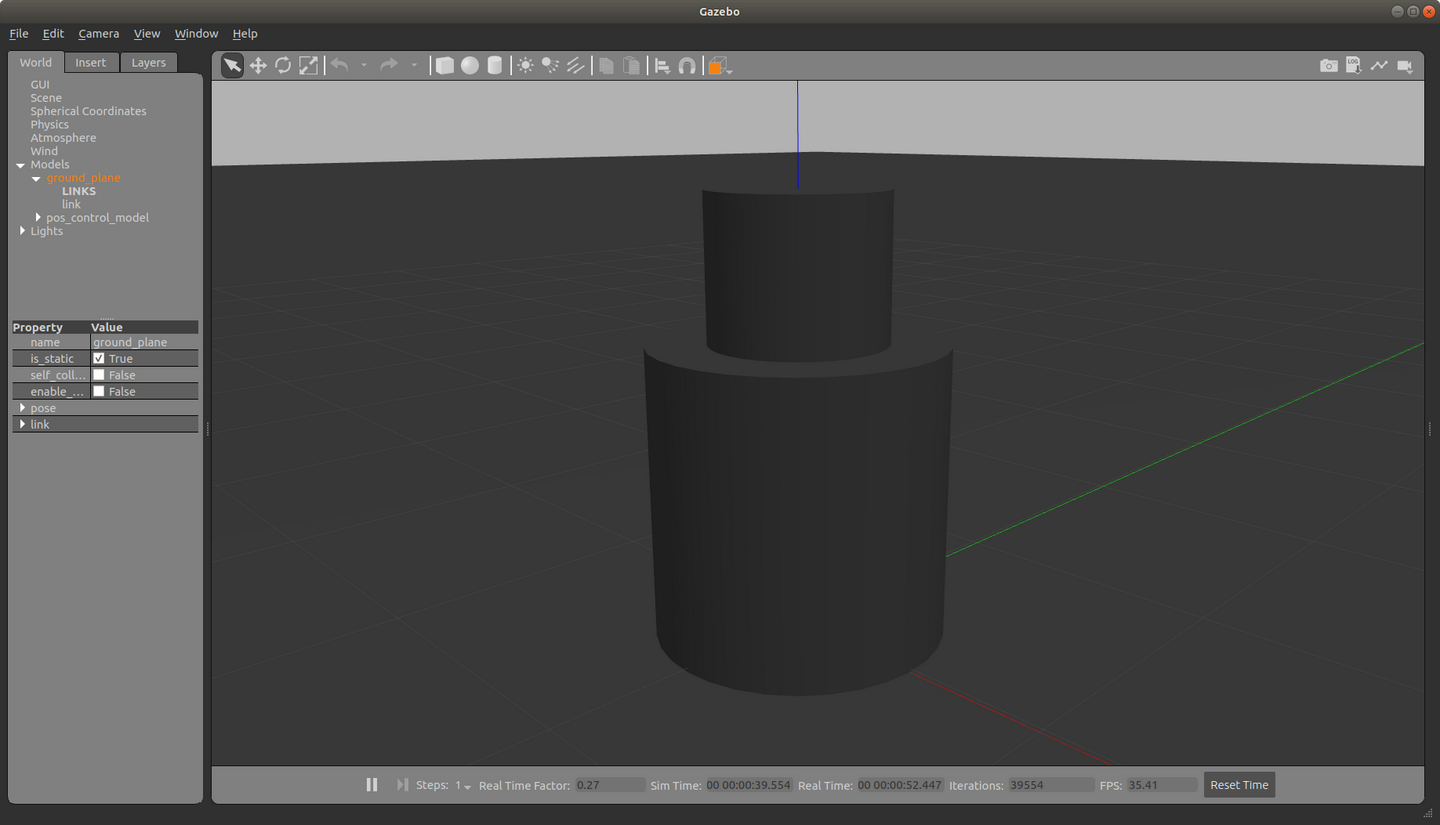
从终端消息中我们可以看到插件被成功加载了!
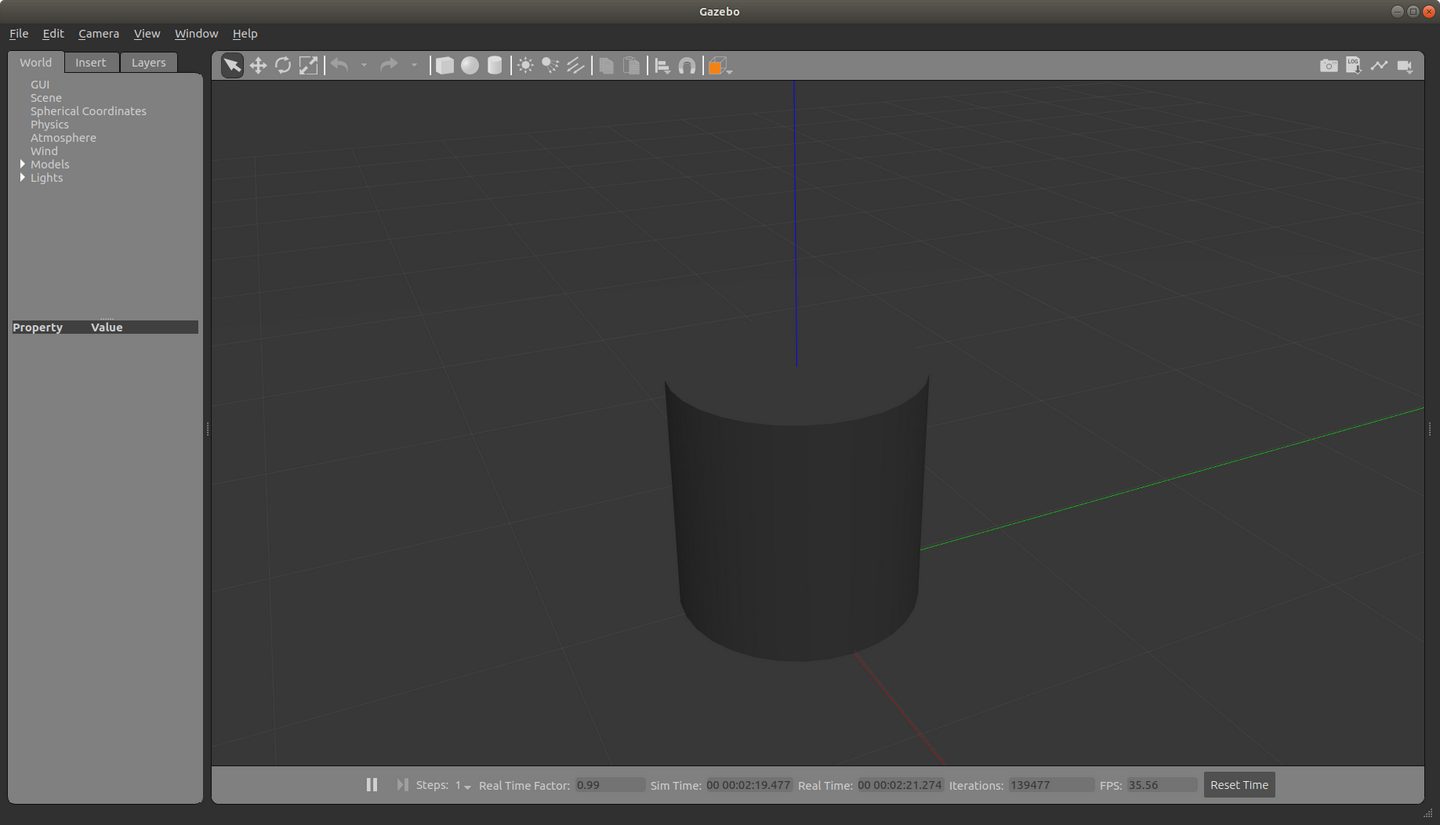
并成功启动gazebo,显示出了模型,是一个圆柱体:
接下来再新建一个终端,用rostopic查询话题:
$ rostopic list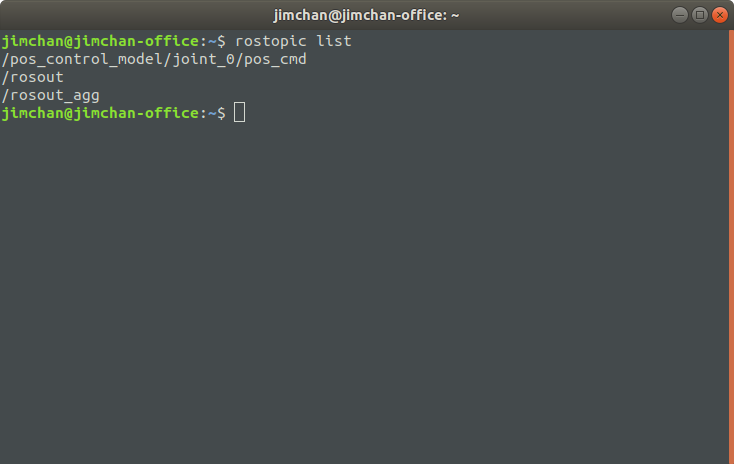
可以看到,位置控制的话题/pos_control_model/joint_0/pos_cmd 已经成功发布了。这就意味着,我们可以向这个话题发布消息来进行位置控制。利用rostopic进行消息发布演示如下:
$ rostopic pub /pos_control_model/joint_0/pos_cmd std_msgs/Float32 "data: 0.5"
我们向话题发布浮点型数据0.5,观察gazebo仿真界面,可以看到模型中的一个小圆柱向上移动了0.5。用这种方法同样可以控制旋转关节的运动。
Gazebo API
关于Gazebo的插件开发,官方提供了详细的API接口,包括Gazebo仿真中所用到的各种类的定义以及成员函数。 我们在进行插件开发时,可以直接到网站上查询:
总结
本文实现了一个非常简单的PID位置控制插件。实际上,只要用一定的C++编程基础,参考Gazebo提供的接口,就可以编写出功能更加丰富的插件,亦可以在已有插件的基础上根据自身的需求进行改进,适合于想要在Gazebo仿真上进行深层次研究的朋友们。
参考资料
[1] 对插件编写有参考价值的一个回答:
Surprising tutorial behavior when using model->SetLinearVel. Also, where can I learn more?
[2] 官方插件库使用说明: