通过视觉传感器赋予机械臂“眼睛”的功能,配合ATI力和力矩传感器,就可以完成机械臂“手眼”结合的能力,完成视觉抓取过程。目前测试的视觉传感器为 ZED mini双目相机,配置安装过程 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34935373/article/details/103481401 。
1.手眼标定(内参)
对于单目usb相机,可以通过ROS包usb_cam来启动相机,通过camera_calibration功能包http://wiki.ros.org/camera_calibration/完成相机内参的标定过程。本次使用的ZED双目相机,出厂的时候已经完成了内参的标定。 如果需要手动重新标定,可以通过ZED自带软件完成标定,双目不仅需要单独标定每个摄像头得到两个摄像头各自的内参矩阵和畸变参数向量,还需要要计算目标点在左右两个视图上形成的视差,首先要把该点在左右视图上两个对应的像点匹配起来。 然而,在二维空间上匹配对应点是非常耗时的,为了减少匹配搜索范围,我们可以利用极线约束使得对应点的匹配由二维搜索降为一维搜索。 而双目校正的作用:把消除畸变后的两幅图像严格地行对应,使得两幅图像的对极线恰好在同一水平线上,这样一幅图像上任意一点与其在另一幅图像上的对应点就必然具有相同的行号,只需在该行进行一维搜索即可匹配到对应点。
2.手眼标定(外参)
内参的标定是确定摄像机从三维空间到二位图像的投影关系,而外参则是确定摄像机坐标与世界坐标系之间的相对位置关系。他们之间关系为 (详情请看 视觉SLAM十四讲第五讲 相机与图像):
![]() 其中Pw为世界坐标,Pc是摄像机坐标,式中,T= (Tx,Ty,Tz),是平移向量,R = R(α,β,γ)是旋转矩阵,分别是绕摄像机坐标系z轴旋转角度为γ,绕y轴旋转角度为β,绕x轴旋转角度为α。6个参数组成(α,β,γ,Tx,Ty,Tz)为摄像机外参。
其中Pw为世界坐标,Pc是摄像机坐标,式中,T= (Tx,Ty,Tz),是平移向量,R = R(α,β,γ)是旋转矩阵,分别是绕摄像机坐标系z轴旋转角度为γ,绕y轴旋转角度为β,绕x轴旋转角度为α。6个参数组成(α,β,γ,Tx,Ty,Tz)为摄像机外参。
3.手眼标定(调包)
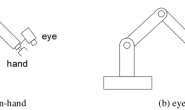
对于手眼外参标定,场景主要有以下两种,
- eye in base,眼在手外,这种场景下我们已知机械臂终端end_link与base_link、相机camera_link与识别物体object_link之间的关系,需要求解camera_link与base_link之间的变换;
- eye on hand,眼在手上,这种场景base_link和机械臂各关节joint_link、end_link已经通过URDF发布了,只需要求解camera_link与end_link之间的变换。
1. ROS也为我们提供了功能包,visp_hand2eye_calibration和ros_easy_handeye。首先测试visp_hand2eye_calibration,这个包是用来标定eye in base 眼在手外的情形。

# 安装功能包
$ sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-visp-hand2eye-calibration
# 启动测试样例
$ rosrun visp_hand2eye_calibration visp_hand2eye_calibration_client
# 启动 calibrator 节点
$ rosrun visp_hand2eye_calibration visp_hand2eye_calibration_calibrator
将会显示一些输出如下,表明安装成功,接下来就可以集成到自己的标定环境中了:
[ INFO] [1329226083.184531090]: Waiting for topics...
[ INFO] [1329226084.186233704]: 1) GROUND TRUTH:
[ INFO] [1329226084.186327570]: hand to eye transformation:
translation:
x: 0.1
y: 0.2
z: 0.3
rotation:
x: 0.96875
y: 0.0863555
z: -0.0863555
w: 0.215889
修改到自己的标定环境中:
# 启动主节点
$ roscore
# 启动 calibrator 节点
$ rosrun visp_hand2eye_calibration visp_hand2eye_calibration_calibrator
# 终端输出提示如下:
[ WARN] [1577429182.106793405]: The input topic '/camera_object' is not yet advertised
[ WARN] [1577429182.106871954]: The input topic '/world_effector' is not yet advertised
calibrator需要我们发布如下两个话题:
world_effector (visp_hand2eye_calibration/TransformArray)
- transformation between the world and the hand frame. The node expects to receive several of those transformations.
camera_object (visp_hand2eye_calibration/TransformArray)
- transformation between the camera and the object frame. The node expects to receive several of those transformations.
calibrator发布如下服务:
compute_effector_camera (visp_hand2eye_calibration/compute_effector_camera)
- Returns the hand to camera transformation result after calibration based on the data published on the subscribed topics.
compute_effector_camera_quick (visp_hand2eye_calibration/compute_effector_camera_quick)
- Returns the hand to camera transformation result after calibration. This service is not based on the data published on the subscribed topics. Instead, the transformation are passed as service parameters.
reset (visp_hand2eye_calibration/reset)
- Reset all the data published on the subscribed topics. Only new publications (transformations) will be taken into account.
总结来说就是移动机械臂采集多个点发送到:world_effector 和 camera_object 两个topic下,通过 compute_effector_camera 这个service得到变换矩阵。这位老哥写的挺好,https://blog.csdn.net/MzXuan/article/details/79177747
2. 第一种方法用到人貌似比较少,使用场景也比较局限,第二种方法基于第一种方法,这个包可以标定eye-in-hand和eye-on-base两种场景,还提供了GUI界面预期的输入为TF中发布的坐标变换。此外,还提供了一种保存和发布标定结果的方法。如下图所示,该种方法可以完成两种类型的标定。值得一提的是作者还提供了一个基于iiwa机械臂的使用例程,该例程可以在没有任何硬件的情况下使用,它使用RViz仿真的机械臂和虚拟发布的相机坐标系。 

# 进入工作目录
$ cd catkin_ws/src
# 安装例程依赖包
$ git clone https://github.com/IFL-CAMP/iiwa_stack
# 手眼标定功能包
$ git clone https://github.com/IFL-CAMP/easy_handeye
# 例程功能包
$ git clone https://github.com/marcoesposito1988/easy_handeye_demo
下载完成之后,编译iiwa包,提示CMake版本过低,但由于我们只是简单的使用一下iiwa作为仿真对象,只需要修改一下CMakeLists.txt,将cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)修改成cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.3)即可。有些包编译缺少依赖或者不通过也不太影响。启动launch文件查看是否编译成功,打开TF观察发布的关节坐标系。
 如上图所示,iiwa机械臂的机器人坐标系为iiwa_link_0和世界坐标系world重合,而末端执行器为iiwa_link_ee,iiwa_link_7坐标系就是安装标定板的位置,所以我们后面只需要修改launch文件中的坐标系名称为自己的机器人坐标系即可将手眼标定包集成到自己的项目当中。 easy_handeye_demo包中还有一个check_calibration.launch,其功能是检测标定板相对与末端执行器(或者机器人基坐标系)是否处于固定位置,以便于后面的手眼标定过程。
如上图所示,iiwa机械臂的机器人坐标系为iiwa_link_0和世界坐标系world重合,而末端执行器为iiwa_link_ee,iiwa_link_7坐标系就是安装标定板的位置,所以我们后面只需要修改launch文件中的坐标系名称为自己的机器人坐标系即可将手眼标定包集成到自己的项目当中。 easy_handeye_demo包中还有一个check_calibration.launch,其功能是检测标定板相对与末端执行器(或者机器人基坐标系)是否处于固定位置,以便于后面的手眼标定过程。
# 编译例程包
$ catkin_make -DCATKIN_WHITELIST_PACKAGES="easy_handeye_demo"
# 启动eye_in_base标定
$ roslaunch easy_handeye_demo calibrate.launch
# 启动eye_on_hand标定
$ roslaunch easy_handeye_demo calibrate.launch eye_on_hand:=true

 上图分别对应eye_on_hand和eye_in_base两种情况,其中tracking_origin表示的是相机坐标系,而tracking_marker则表示标定板的位置。因此通过矩阵计算,就可以获得相机坐标系到机器人坐标系的变换矩阵。 由于没有硬件,所以tracking_marker和tracking_origin的位置是通过手动发布的静态坐标变化得到的。可以在launch文件中看到:
上图分别对应eye_on_hand和eye_in_base两种情况,其中tracking_origin表示的是相机坐标系,而tracking_marker则表示标定板的位置。因此通过矩阵计算,就可以获得相机坐标系到机器人坐标系的变换矩阵。 由于没有硬件,所以tracking_marker和tracking_origin的位置是通过手动发布的静态坐标变化得到的。可以在launch文件中看到:
<param name="eye_on_hand" value="$(arg eye_on_hand)" />
<!-- transformations for the eye-on-base case -->
<param unless="$(arg eye_on_hand)" name="ground_truth_calibration_transformation" value="1 0 0.5 0 0 0 1" />
<param unless="$(arg eye_on_hand)" name="arbitrary_marker_placement_transformation" value="0.12 0.21 0.137 0 0 0 1" />
<!-- transformations for the eye-on-hand case -->
<param if="$(arg eye_on_hand)" name="ground_truth_calibration_transformation" value="0.12 0.21 0.137 0 0 0 1" />
<param if="$(arg eye_on_hand)" name="arbitrary_marker_placement_transformation" value="1 0 0.5 0 0 0 1" />
当想要修改该demo包用于自己的仿真机器人的时候,修改launch的如下位置中的value即可:
<arg name="robot_base_frame" value="iiwa_link_0" />
<arg name="robot_effector_frame" value="iiwa_link_ee" />
<arg name="tracking_base_frame" value="tracking_origin" />
<arg name="tracking_marker_frame" value="tracking_marker" />