一、什么是神经网络
神经网络是一种以人脑为模型的机器学习,简单地说就是创造一个人工神经网络,通过一种算法允许计算机通过合并新的数据来学习。 以人脑中的神经网络为启发,历史上出现过很多不同版本最著名的算法是1980年的 backpropagation
1、多层向前神经网络(Multilayer Feed-Forward Neural Network)
多层向前神经网络由以下部分组成:输入层(input layer), 隐藏层 (hidden layers), 输入层 (output layers)

- 每层由单元(units)组成
- 输入层(input layer)是由训练集的实例特征向量传入
- 经过连接结点的权重(weight)传入下一层,一层的输出是下一层的输入
- 隐藏层的个数可以是任意的,输入层有一层,输出层有一层
- 每个单元(unit)也可以被称作神经结点,根据生物学来源定义
- 以上成为2层的神经网络(输入层不算)
- 一层中加权的求和,然后根据非线性方程转化输出
- 作为多层向前神经网络,理论上,如果有足够多的隐藏层(hidden layers) 和足够大的训练集, 可以模拟出任何方程
神经网络结构
- 使用神经网络训练数据之前,必须确定神经网络的层数,以及每层单元的个数
- 特征向量在被传入输入层时通常被先标准化(normalize)到0和1之间 (为了加速学习过程)
- 离散型变量可以被编码成每一个输入单元对应一个特征值可能赋的值
比如:特征值A可能取三个值(a0, a1, a2), 可以使用3个输入单元来代表A。
如果A=a0, 那么代表a0的单元值就取1, 其他取0;
如果A=a1, 那么代表a1de单元值就取1,其他取0,以此类推
- 神经网络即可以用来做分类(classification)问题,也可以解决回归(regression)问题,对于分类问题,如果是2类,可以用一个输出单元表示(0和1分别代表2类) 如果多余2类,每一个类别用一个输出单元表示 所以输入层的单元数量通常等于类别的数量
- 没有明确的规则来设计最好有多少个隐藏层,一般根据实验测试和误差,以及准确度来实验并改进
交叉验证
目的是得到可靠稳定的模型,具体做法是拿出大部分数据进行建模,留小部分样本用刚刚建立的模型进行预测,并求出这小部分样本预测的误差,记录它们的平方和,这个过程一直进行,直到所有的样本都恰好被预测了一次,交叉验证在克服过拟合问题上非常有效。常用的方法有:10折交叉验证、Holdout验证、留一验证

Backpropagation算法
BP算法是一种有监督式的学习算法,其主要思想是:输入学习样本,使用反向传播算法对网络的权值和偏差进行反复的调整训练,使输出的向量与期望向量尽可能地接近,当网络输出层的误差平方和小于指定的误差时训练完成,保存网络的权值和偏差。具体步骤如下: 1、初始化权重(weights)和偏向(bias): 随机初始化在-1到1之间,或者-0.5到0.5之间,每个单元有一个偏向 2、对于每一个训练实例X,执行以下步骤: (1)由输入层向前传送

![]()
其中
I~j~:本单元输出(非线性转化前)
w~ij~:每个单元之间的连接权重
O~i~:上一单元输出
θ~j~:偏向

非线性转化函数(激活函数),对本单元输出值进行非线性转化后作为下一单元输入
 (2)根据误差(error)反向传送
(2)根据误差(error)反向传送
- 对于输出层:
![]()
- 对于隐藏层:
![]()
- 权重更新:
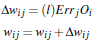
Errj:用于更新偏向
Oj:为输出的值
Tj:为标签的值
- 偏向更新
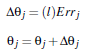
l:学习率
(3) 终止条件
- 权重的更新低于某个阈值
- 预测的错误率低于某个阈值
- 达到预设一定的循环次数
二、代码
神经网络搭建
import numpy as np
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
def tanh_deriv(x):
return 1.0 - np.tanh(x) * np.tanh(x)
def logistic(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def logistic_derivative(x):
return logistic(x) * (1 - logistic(x))
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, layers, activation='tanh'):
"""
:param layers: 一个列表类型,列表里面至少要有两个值,即至少要有输入层和输出层
:param activation: 激活函数,"logistic" 或者 "tanh"
"""
if activation == 'logistic':
self.activation = logistic
self.activation_deriv = logistic_derivative
elif activation == 'tanh':
self.activation = tanh
self.activation_deriv = tanh_deriv
self.weights = []
# 初始化权重
for i in range(1, len(layers) - 1):
self.weights.append((2 * np.random.random((layers[i - 1] + 1, layers[i] + 1)) - 1) * 0.25)
self.weights.append((2 * np.random.random((layers[i] + 1, layers[i + 1])) - 1) * 0.25)
def fit(self, X, y, learning_rate=0.2, epochs=10000):
X = np.atleast_2d(X)
temp = np.ones([X.shape[0], X.shape[1] + 1])
temp[:, 0:-1] = X # adding the bias unit to the input layer
X = temp
y = np.array(y)
for k in range(epochs):
i = np.random.randint(X.shape[0])
a = [X[i]]
for l in range(len(self.weights)): # going forward network, for each layer
a.append(self.activation(np.dot(a[l], self.weights[
l]))) # Computer the node value for each layer (O_i) using activation function
error = y[i] - a[-1] # Computer the error at the top layer
deltas = [
error * self.activation_deriv(a[-1])] # For output layer, Err calculation (delta is updated error)
# Staring backprobagation
for l in range(len(a) - 2, 0, -1): # we need to begin at the second to last layer
# Compute the updated error (i,e, deltas) for each node going from top layer to input layer
deltas.append(deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T) * self.activation_deriv(a[l]))
deltas.reverse()
for i in range(len(self.weights)):
layer = np.atleast_2d(a[i])
delta = np.atleast_2d(deltas[i])
self.weights[i] += learning_rate * layer.T.dot(delta)
def predict(self, x):
x = np.array(x)
temp = np.ones(x.shape[0] + 1)
temp[0:-1] = x
a = temp
for l in range(0, len(self.weights)):
a = self.activation(np.dot(a, self.weights[l]))
return a
利用神经网络实现手写数字识别
每个图片大小为8×8 ,识别数字:0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from NeuralNetwork import NeuralNetwork
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.data
y = digits.target
X -= X.min() # normalize the values to bring them into the range 0-1
X /= X.max()
# 由于图片大小为8*8,因此输入层为64,中间层100,输出层为10
nn = NeuralNetwork([64, 100, 10], 'logistic')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y) # 分离训练集测试集
labels_train = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_train)
labels_test = LabelBinarizer().fit_transform(y_test)
print("start fitting")
nn.fit(X_train, labels_train, epochs=3000)
predictions = []
for i in range(X_test.shape[0]):
o = nn.predict(X_test[i] )
predictions.append(np.argmax(o))
print(confusion_matrix(y_test,predictions))
print(classification_report(y_test,predictions))
结果:
[[41 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 42 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 2]
[ 0 0 48 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 1 0 47 0 1 0 4 0 1]
[ 0 2 0 0 35 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 44 0 0 0 1]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 1 47 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 50 0 0]
[ 0 9 0 1 0 2 0 0 25 6]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 37]]
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 41
1 0.78 0.91 0.84 46
2 1.00 1.00 1.00 48
3 0.98 0.87 0.92 54
4 1.00 0.95 0.97 37
5 0.90 0.98 0.94 45
6 0.98 0.98 0.98 48
7 0.91 1.00 0.95 50
8 1.00 0.58 0.74 43
9 0.79 0.97 0.87 38
avg / total 0.93 0.92 0.92 450