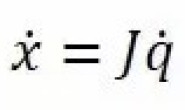我先上下结果图吧,效果勉强还行,在这里我只训练了行人,官网的weights是coco数据集训练的,有80类;

1、YOLOV3目标检测
关于yolov3的原理我在这里就不解释了,可谷歌学术自行阅读,说实话yolov3的效果着实不错,但是源码是C的,不依赖其他任何库,看的云里雾里,在这里我用的darknet训练的,利用tensorflow+keras进行测试的;
关于tensorflow+keras版本yolov3,可参照
1 https://github.com/qqwweee/keras-yolo3
测试
(1)获取训练好的权重
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
(2)转换 Darknet YOLO 模型为 Keras 模型
python convert.py yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights model_data/yolo.h5
转换过程如图

(3)运行目标检测测试代码
python yolo.py
此时即可看到目标检测的效果
2、卡尔曼滤波追踪
关于卡尔曼滤波的理论这里不打算讲了,就是那个5个基本的公式,这里直接给出公式:
公式1:X(k|k-1) = FX(k-1 | k-1) + BU(k) + W(k)
公式2:P(k|k-1) = FP(k-1|k-1)F’ + Q(k)
公式3:X(k|k) = X(k|k-1) + Kg(k)[Z(k) – AX(k|k-1)
公式4:Kg(k) = P(k|k-1)A’/{AP(k|k-1)A’ + R} //卡尔曼增益
公式5:P(k|k) = (1- Kg(k) H) P(k|k-1)
另外,Z(k) = HX(k) + V,Z是测量值,X是系统值,W是过程噪声,V是测量噪声,H是测量矩阵,A是转移矩阵,Q是W的协方差,R是V的协方差,X(k|k-1)是估计值;X(k|k)是X(k|k-1)的最优估计值,即滤波估计值;P(k|k-1)是估计值误差方差
矩阵,P(k|k)是滤波误差方差矩阵。
下面给出Python版本的卡尔曼滤波小程序:
'''
File name : kalman_filter.py
File Description : Kalman Filter Algorithm Implementation
Author : Srini Ananthakrishnan
Date created : 07/14/2017
Date last modified: 07/16/2017
Python Version : 2.7
'''
# Import python libraries
import numpy as np
class KalmanFilter(object):
"""Kalman Filter class keeps track of the estimated state of
the system and the variance or uncertainty of the estimate.
Predict and Correct methods implement the functionality
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kalman_filter
Attributes: None
"""
def __init__(self):
"""Initialize variable used by Kalman Filter class
Args:
None
Return:
None
"""
self.dt = 0.005 # delta time
self.A = np.array([[1, 0], [0, 1]]) # matrix in observation equations
self.u = np.zeros((2, 1)) # previous state vector
# (x,y) tracking object center
self.b = np.array([[0], [255]]) # vector of observations
self.P = np.diag((3.0, 3.0)) # covariance matrix
self.F = np.array([[1.0, self.dt], [0.0, 1.0]]) # state transition mat
self.Q = np.eye(self.u.shape[0]) # process noise matrix
self.R = np.eye(self.b.shape[0]) # observation noise matrix
self.lastResult = np.array([[0], [255]])
def predict(self):
"""Predict state vector u and variance of uncertainty P (covariance).
where,
u: previous state vector
P: previous covariance matrix
F: state transition matrix
Q: process noise matrix
Equations:
u'_{k|k-1} = Fu'_{k-1|k-1}
P_{k|k-1} = FP_{k-1|k-1} F.T + Q
where,
F.T is F transpose
Args:
None
Return:
vector of predicted state estimate
"""
# Predicted state estimate
self.u = np.round(np.dot(self.F, self.u))
# Predicted estimate covariance
self.P = np.dot(self.F, np.dot(self.P, self.F.T)) + self.Q
self.lastResult = self.u # same last predicted result
return self.u
def correct(self, b, flag):
"""Correct or update state vector u and variance of uncertainty P (covariance).
where,
u: predicted state vector u
A: matrix in observation equations
b: vector of observations
P: predicted covariance matrix
Q: process noise matrix
R: observation noise matrix
Equations:
C = AP_{k|k-1} A.T + R
K_{k} = P_{k|k-1} A.T(C.Inv)
u'_{k|k} = u'_{k|k-1} + K_{k}(b_{k} - Au'_{k|k-1})
P_{k|k} = P_{k|k-1} - K_{k}(CK.T)
where,
A.T is A transpose
C.Inv is C inverse
Args:
b: vector of observations
flag: if "true" prediction result will be updated else detection
Return:
predicted state vector u
"""
if not flag: # update using prediction
self.b = self.lastResult
else: # update using detection
self.b = b
C = np.dot(self.A, np.dot(self.P, self.A.T)) + self.R
K = np.dot(self.P, np.dot(self.A.T, np.linalg.inv(C)))
self.u = np.round(self.u + np.dot(K, (self.b - np.dot(self.A,
self.u))))
self.P = self.P - np.dot(K, np.dot(C, K.T))
self.lastResult = self.u
return self.u
3、匈牙利匹配算法
匈牙利算法原理可参考这篇博客,写的还不错
https://blog.csdn.net/jingshushu1995/article/details/80411325
下面我给出我的卡尔曼滤波之后的匈牙利匹配算法的代码
欢迎大家自己做修改,代码规范 并不好,勉强能够学习一下,后面我会再进行修改。谢谢赞赏
'''
File name : tracker.py
File Description : Tracker Using Kalman Filter & Hungarian Algorithm
Date created : 07/14/2017
Date last modified: 07/16/2017
Python Version : 2.7
'''
# Import python libraries
import numpy as np
from kalman_filter import KalmanFilter
from common import dprint
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment
class Track(object):
"""Track class for every object to be tracked
Attributes:
None
"""
def __init__(self, prediction, trackIdCount):
"""Initialize variables used by Track class
Args:
prediction: predicted centroids of object to be tracked
trackIdCount: identification of each track object
Return:
None
"""
self.track_id = trackIdCount # identification of each track object
self.KF = KalmanFilter() # KF instance to track this object
self.prediction = np.asarray(prediction) # predicted centroids (x,y)
self.skipped_frames = 0 # number of frames skipped undetected
self.trace = [] # trace path
class Tracker(object):
"""Tracker class that updates track vectors of object tracked
Attributes:
None
"""
def __init__(self, dist_thresh, max_frames_to_skip, max_trace_length,
trackIdCount):
"""Initialize variable used by Tracker class
Args:
dist_thresh: distance threshold. When exceeds the threshold,
track will be deleted and new track is created
max_frames_to_skip: maximum allowed frames to be skipped for
the track object undetected
max_trace_lenght: trace path history length
trackIdCount: identification of each track object
Return:
None
"""
self.dist_thresh = dist_thresh
self.max_frames_to_skip = max_frames_to_skip
self.max_trace_length = max_trace_length
self.tracks = []
self.trackIdCount = trackIdCount
def Update(self, detections):
"""Update tracks vector using following steps:
- Create tracks if no tracks vector found
- Calculate cost using sum of square distance
between predicted vs detected centroids
- Using Hungarian Algorithm assign the correct
detected measurements to predicted tracks
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hungarian_algorithm
- Identify tracks with no assignment, if any
- If tracks are not detected for long time, remove them
- Now look for un_assigned detects
- Start new tracks
- Update KalmanFilter state, lastResults and tracks trace
Args:
detections: detected centroids of object to be tracked
Return:
None
"""
# Create tracks if no tracks vector found
if (len(self.tracks) == 0):
for i in range(len(detections)):
track = Track(detections[i], self.trackIdCount)
self.trackIdCount += 1
self.tracks.append(track)
# Calculate cost using sum of square distance between
# predicted vs detected centroids
N = len(self.tracks)
M = len(detections)
cost = np.zeros(shape=(N, M)) # Cost matrix
for i in range(len(self.tracks)):
for j in range(len(detections)):
try:
diff = self.tracks[i].prediction - detections[j]
distance = np.sqrt(diff[0][0]*diff[0][0] +
diff[1][0]*diff[1][0])
cost[i][j] = distance
except:
pass
# Let's average the squared ERROR
cost = (0.5) * cost
# Using Hungarian Algorithm assign the correct detected measurements
# to predicted tracks
assignment = []
for _ in range(N):
assignment.append(-1)
row_ind, col_ind = linear_sum_assignment(cost)
for i in range(len(row_ind)):
assignment[row_ind[i]] = col_ind[i]
# Identify tracks with no assignment, if any
un_assigned_tracks = []
for i in range(len(assignment)):
if (assignment[i] != -1):
# check for cost distance threshold.
# If cost is very high then un_assign (delete) the track
if (cost[i][assignment[i]] > self.dist_thresh):
assignment[i] = -1
un_assigned_tracks.append(i)
pass
else:
self.tracks[i].skipped_frames += 1
# If tracks are not detected for long time, remove them
del_tracks = []
for i in range(len(self.tracks)):
if (self.tracks[i].skipped_frames > self.max_frames_to_skip):
del_tracks.append(i)
if len(del_tracks) > 0: # only when skipped frame exceeds max
for id in del_tracks:
if id < len(self.tracks):
del self.tracks[id]
del assignment[id]
else:
dprint("ERROR: id is greater than length of tracks")
# Now look for un_assigned detects
un_assigned_detects = []
for i in range(len(detections)):
if i not in assignment:
un_assigned_detects.append(i)
# Start new tracks
if(len(un_assigned_detects) != 0):
for i in range(len(un_assigned_detects)):
track = Track(detections[un_assigned_detects[i]],
self.trackIdCount)
self.trackIdCount += 1
self.tracks.append(track)
# Update KalmanFilter state, lastResults and tracks trace
for i in range(len(assignment)):
self.tracks[i].KF.predict()
if(assignment[i] != -1):
self.tracks[i].skipped_frames = 0
self.tracks[i].prediction = self.tracks[i].KF.correct(
detections[assignment[i]], 1)
else:
self.tracks[i].prediction = self.tracks[i].KF.correct(
np.array([[0], [0]]), 0)
if(len(self.tracks[i].trace) > self.max_trace_length):
for j in range(len(self.tracks[i].trace) -
self.max_trace_length):
del self.tracks[i].trace[j]
self.tracks[i].trace.append(self.tracks[i].prediction)
self.tracks[i].KF.lastResult = self.tracks[i].prediction
4、整体代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Class definition of YOLO_v3 style detection model on image and video
"""
from tracker import Tracker
import copy
import colorsys
import os
from timeit import default_timer as timer
import cv2
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.models import load_model
from keras.layers import Input
from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
from yolo3.model import yolo_eval, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body
from yolo3.utils import letterbox_image
import os
from keras.utils import multi_gpu_model
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
"model_path": 'model_data/yolov3.h5',
"anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"classes_path": 'model_data/coco_classes.txt',
"score" : 0.3,
"iou" : 0.45,
"model_image_size" : (416, 416),
"gpu_num" : 1,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults) # set up default values
self.__dict__.update(kwargs) # and update with user overrides
self.class_names = self._get_class()
self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
self.sess = K.get_session()
self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
def _get_class(self):
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def _get_anchors(self):
anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
def generate(self):
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# Load model, or construct model and load weights.
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
num_classes = len(self.class_names)
is_tiny_version = num_anchors==6 # default setting
try:
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
except:
self.yolo_model = tiny_yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//2, num_classes) \
if is_tiny_version else yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//3, num_classes)
self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path) # make sure model, anchors and classes match
else:
assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
num_anchors/len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
np.random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
np.random.shuffle(self.colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
np.random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
# Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
if self.gpu_num>=2:
self.yolo_model = multi_gpu_model(self.yolo_model, gpus=self.gpu_num)
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
len(self.class_names), self.input_image_shape,
score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
return boxes, scores, classes
def detect_image(self, image):
start = timer()
centers=[]
if self.model_image_size != (None, None):
assert self.model_image_size[0]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
assert self.model_image_size[1]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size)))
else:
new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32),
image.height - (image.height % 32))
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size)
image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
#print(image_data.shape)
image_data /= 255.
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={
self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
K.learning_phase(): 0
})
#print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/FiraMono-Medium.otf',
size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300
for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
predicted_class = self.class_names[c]
box = out_boxes[i]
score = out_scores[i]
number=len(out_boxes)
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
if c==0:
top, left, bottom, right = box
center=(int ((left+right)//2),int((top+bottom)//2))
b=np.array([[(left+right)//2],[(top+bottom)//2]])
centers.append(b)
top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
#print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom))
if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
else:
text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
# My kingdom for a good redistributable image drawing library.
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle(
[left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
outline=self.colors[c])
draw.rectangle(
[tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
fill=self.colors[c])
#draw.rectangle(
#[tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
#fill=self.colors[c])
draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
del draw
end = timer()
#print(end - start)
return image,centers,number
def close_session(self):
self.sess.close()
def detect_video(yolo, video_path, output_path=""):
vid = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
if not vid.isOpened():
raise IOError("Couldn't open webcam or video")
video_FourCC = int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FOURCC))
video_fps = vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
video_size = (int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),
int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
isOutput = True if output_path != "" else False
if isOutput:
#print("!!! TYPE:", type(output_path), type(video_FourCC), type(video_fps), type(video_size))
out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, video_FourCC, video_fps, video_size)
accum_time = 0
curr_fps = 0
fps = "FPS: ??"
prev_time = timer()
tracker = Tracker(160, 30, 6, 100)
# Variables initialization
skip_frame_count = 0
track_colors = [(255, 0, 0), (0, 255, 0), (0, 0, 255), (255, 255, 0),
(0, 255, 255), (255, 0, 255), (255, 127, 255),
(127, 0, 255), (127, 0, 127)]
pause = False
while True:
return_value, frame = vid.read()
print(frame.shape)
image = Image.fromarray(frame)
image,centers,number = yolo.detect_image(image)
print(image.size)
result = np.asarray(image)
curr_time = timer()
exec_time = curr_time - prev_time
prev_time = curr_time
accum_time = accum_time + exec_time
curr_fps = curr_fps + 1
if accum_time > 1:
accum_time = accum_time - 1
fps = "FPS: " + str(curr_fps)
curr_fps = 0
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
#cv2.putText(result, text=fps, org=(3, 15), fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,fontScale=0.50, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=2)
cv2.putText(result, str(number), (20, 40), font, 1, (0, 0, 255), 5)
#for k in range(len(centers)):
#cv2.circle(frame, centers[k], 3, (255, 255, 0), 3)
#cv2.imshow("xiao",frame)
#cv2.waitKey(100000)
############################################################################################
#print(len(centers))
#for i in range(len(centers)):
#print(centers[i])
#cv2.waitKey(0)
if (len(centers) > 0):
# Track object using Kalman Filter
tracker.Update(centers)
# For identified object tracks draw tracking line
# Use various colors to indicate different track_id
for i in range(len(tracker.tracks)):
if (len(tracker.tracks[i].trace) > 1):
for j in range(len(tracker.tracks[i].trace) - 1):
# Draw trace line
x1 = tracker.tracks[i].trace[j][0][0]
y1 = tracker.tracks[i].trace[j][1][0]
x2 = tracker.tracks[i].trace[j + 1][0][0]
y2 = tracker.tracks[i].trace[j + 1][1][0]
clr = tracker.tracks[i].track_id % 9
cv2.line(result, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x2), int(y2)),
track_colors[clr], 4)
#x3 = tracker.tracks[i].track_id
#cv2.putText(result,str(tracker.tracks[j].track_id),(int(x1),int(y1)),font,track_colors[j],3)
#cv2.circle(result,(int(x1),int(y1)),3,track_colors[j],3)
# Display the resulting tracking frame
cv2.imshow('Tracking', result)
###################################################
cv2.namedWindow("result", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("result", result)
if isOutput:
out.write(result)
if cv2.waitKey(100) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
yolo.close_session()