@[toc]
一、简介
PCL中总结了几种需要进行点云滤波处理的情况,这几种情况如下:
(1)点云数据密度不规则需要平滑。
(2)因为遮挡等问题造成离群点需要去除。
(3)大量数据需要进行下采样( Downsample)。
(4)噪音数据需要去除。
对应的方法如下:
(1)按具体给定的规则限制过滤去除点。
(2)通过常用滤波算法修改点的部分属性。
(3)对数据进行下采样,
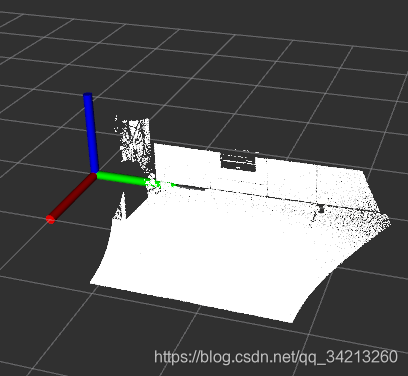
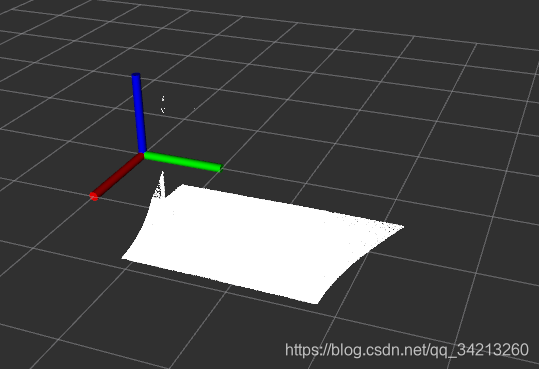
原始测试点云
二、点云提取滤波器
2.1 直通滤波器
- 去除掉在用户指定某一维度上的指定范围内(或外)部的点。
#include
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
//直通滤波器
template
void myPassThroughFilter(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_){
// Create the filtering object
pcl::PassThrough pass;
pass.setInputCloud(inPC_);
pass.setFilterFieldName("z");// 滤波字段设置为z轴方向
pass.setFilterLimits(0.0, 1.0);
// pass.setFilterLimitsNegative (true); //设置保留范围内还是过滤掉范围内, 默认为flase。true为过滤掉范围内的,flase为过滤掉范围外的
pass.filter(*outPC_);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
myPassThroughFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// 转换成ROS格式并发布,用RVIZ查看点云
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_filtered, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
2.2 根据点云的索引提取点云(点云分割)
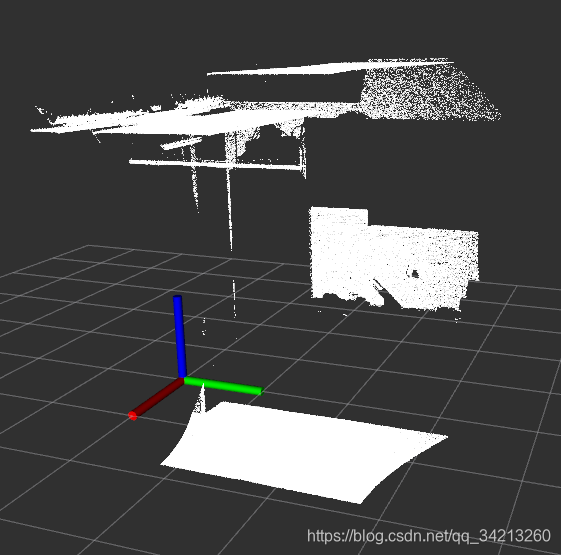
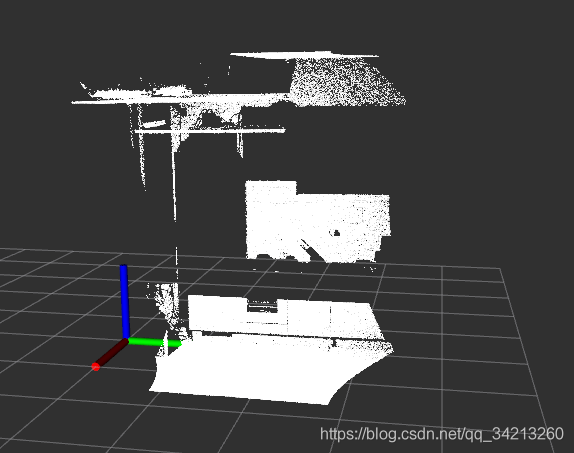
基于某一分割算法提取点云中的一个子集。这里以平面分割算法为例:
#include
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
template
void extractPlanarPC(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_){
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients ());
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices ());
// Create the segmentation object
pcl::SACSegmentation seg; //创建分割对象
// Optional
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true); //设置对估计模型参数进行优化处理
// Mandatory
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);//设置分割模型类别
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC); //设置用RANSAC方法
seg.setMaxIterations (100);//设置最大迭代次数
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.02); //判断是否为模型内点的距离阀值
seg.setInputCloud (inPC_);
seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);
//创建提取器
pcl::ExtractIndices extractor;
extractor.setInputCloud(inPC_);
extractor.setIndices(inliers);
// 提取平面点
extractor.setNegative(false); // If set to true, you can extract point clouds outside the specified index
extractor.filter(*outPC_);
// 提取剩余的点
extractor.setNegative(true); // If set to true, you can extract point clouds outside the specified index
extractor.filter(*inPC_);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
// myPassThroughFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
myVoxelGridFilter(cloud,cloud);
// myStatisticFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// myRadiusFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// myPlanarFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// 提取所有平面
int nr_points=cloud->points.size (); int i=0;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_plane_all(new pcl::PointCloud);
while(cloud->points.size () > 0.1 * nr_points){
extractPlanarPC(cloud,cloud_filtered);
*cloud_plane_all+=*cloud_filtered;
i++;
}
std::cout<<i<<std::endl;
// 转换成ROS格式并发布,用RVIZ查看点云
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_plane_all, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
2.3 条件滤波器
因为直通滤波一次只能对某个坐标轴的范围进行滤波。假如想限制两个轴以上的范围,直通滤波就无能为力了。而条件滤波(condition removal filter)正好可以解决这个问题,条件滤波相比于直通滤波优点就是一次可以对多个轴的范围进行划定限制。
#include
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/conditional_removal.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
template
void myConditionFilter(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_){
// 创建条件定义对象 //条件与
typename pcl::ConditionAnd::Ptr condition_add(new pcl::ConditionAnd());
//为条件定义对象添加比较算子
condition_add->addComparison (typename pcl::FieldComparison::ConstPtr (new
pcl::FieldComparison ("z", pcl::ComparisonOps::GT, 0.0))); //添加在Z字段上大于0的比较算子
condition_add->addComparison (typename pcl::FieldComparison::ConstPtr (new
pcl::FieldComparison ("z", pcl::ComparisonOps::LT, 0.8))); //添加在Z字段上小于0.8的比较算子
// 也可以是条件或 pcl::ConditionOr
typename pcl::ConditionOr::Ptr condition_or(new pcl::ConditionOr());
condition_or->addComparison (typename pcl::FieldComparison::ConstPtr (new
pcl::FieldComparison ("x", pcl::ComparisonOps::GT, 0.8))); //添加在x字段上大于0.8的比较算子
condition_or->addComparison (typename pcl::FieldComparison::ConstPtr (new
pcl::FieldComparison ("x", pcl::ComparisonOps::LT, 0.0))); //添加在x字段上小于0.0的比较算子
// 两个条件合并 此时 condition_or || condition_add
// condition_or->addCondition(condition_add);
// 或者 condition_add && condition_or
// condition_add->addCondition(condition_or);
// build the filter 创建滤波器并用条件定义对象初始化
pcl::ConditionalRemoval condrem;
condrem.setCondition (condition_add);
condrem.setInputCloud (inPC_);
condrem.setKeepOrganized(true); //设置保持点云的结构
// apply filter
condrem.filter (*outPC_);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
myConditionFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// 转换成ROS格式并发布,用RVIZ查看点云
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_filtered, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
condrem.setCondition (condition_add);
condrem.setCondition (condition_or);
// 两个条件合并 此时 condition_or || condition_add
condition_or->addCondition(condition_add);
condrem.setCondition (condition_or);
// condition_add && condition_or
condition_add->addCondition(condition_or);
condrem.setCondition (condition_add);
- 参数含义
pcl::ComparisonOps::LE //小于等于 LE = less equal pcl::ComparisonOps::GT //大于 GT = Greater than pcl::ComparisonOps::LT //小于 pcl::ComparisonOps::EQ //相等还可以对曲率进行限制

2.4 任意多边形内部点云提取
#include
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/crop_hull.h>
#include <pcl/surface/concave_hull.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
template
void myConvexHullFilter(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_){
/*设置滤波的边框点*/
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr boundingbox_ptr (new pcl::PointCloud);
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(2, 2, 0));
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(2, -2,0 ));
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(-2, 2,0 ));
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(-2, -2,0 ));
boundingbox_ptr->push_back(pcl::PointXYZ(0, 0,1.5 ));
/*求上面给出的这个边框点集的凸包*/
pcl::ConvexHull hull; //创建凸包对象
hull.setInputCloud(boundingbox_ptr);
hull.setDimension(3); /*设置凸包维度,也可以是2D*/
std::vector polygons; /*用于保存凸包顶点*/
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr surface_hull (new pcl::PointCloud); /*用于描绘凸包形状*/
hull.reconstruct(*surface_hull, polygons); // 计算凸包
pcl::CropHull bb_filter;//创建凸包滤波器对象
bb_filter.setDim(3); /*设置维度要和前面的维度相同*/
bb_filter.setInputCloud(inPC_);
bb_filter.setHullIndices(polygons); /*封闭多边形顶点*/
bb_filter.setHullCloud(surface_hull); /*封闭多边形形状*/
bb_filter.filter(*outPC_); /*结果保存到objects*/
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
myConvexHullFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// 转换成ROS格式并发布,用RVIZ查看点云
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_filtered, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
三、点云降采样
3.1 体素降采样
使用体素化网格方法实现下采样,即减少点的数量,减少点云数据,并同时保存点云的形状特征。在提高配准,曲面重建,形状识别等算法速度中非常实用,PCL实现的VoxelGrid类通过输入的点云数据创建一个三维体素栅格,然后每个体素内用体素中所有点的重心来近似显示体素中其他点,这样该体素内所有点都用一个重心点最终表示。对于所有体素处理后得到的过滤后的点云。这种方法比用体素中心逼近的方法更慢,但是对于采样点对应曲面的表示更为准确。
#include
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
template
void myVoxelGridFilter(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_)
{
pcl::VoxelGrid downSampleFilter;
downSampleFilter.setInputCloud (inPC_);
downSampleFilter.setLeafSize (0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f);//设置滤波时创建的体素体积为1cm的立方体
downSampleFilter.filter (*outPC_);//执行滤波处理,存储输出
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
// myPassThroughFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
myVoxelGridFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_filtered, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
3.2 随机降采样
从指定点云中随机抽取出固定数量的点,每次执行提取的点都不同,但数量一样
#include
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/random_sample.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
template
void myRandomFilter(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_){
pcl::RandomSample Random_Sample;
Random_Sample.setSample(1000);
Random_Sample.setInputCloud(inPC_);
Random_Sample.filter(*outPC_);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
myRandomFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// 转换成ROS格式并发布,用RVIZ查看点云
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_filtered, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
3.3 均匀降采样
#include
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/uniform_sampling.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
template
void myUniformFilter(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_){
pcl::UniformSampling unisam;
//设置滤波时创建的半径球体
unisam.setRadiusSearch(0.01f) ;
unisam.setInputCloud(inPC_);
unisam.filter(*outPC_);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
myUniformFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// 转换成ROS格式并发布,用RVIZ查看点云
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_filtered, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
四、移除离群点
4.1 统计滤波器StatisticalOutlierRemoval
使用统计分析技术,从一个点云数据中集中移除测量噪声点(也就是离群点)比如:激光扫描通常会产生密度不均匀的点云数据集,另外测量中的误差也会产生稀疏的离群点,使效果不好。估计局部点云特征(例如采样点处法向量或曲率变化率)的运算复杂,这会导致错误的数值,反过来就会导致点云配准等后期的处理失败。
解决办法:每个点的邻域进行一个统计分析,并修剪掉一些不符合一定标准的点,稀疏离群点移除方法基于在输入数据中对点到临近点的距离分布的计算,对每一个点,计算它到它的所有临近点的平均距离,,假设得到的结果是一个高斯分布,其形状是由均值和标准差决定,平均距离在标准范围之外的点,可以被定义为离群点并可从数据中去除。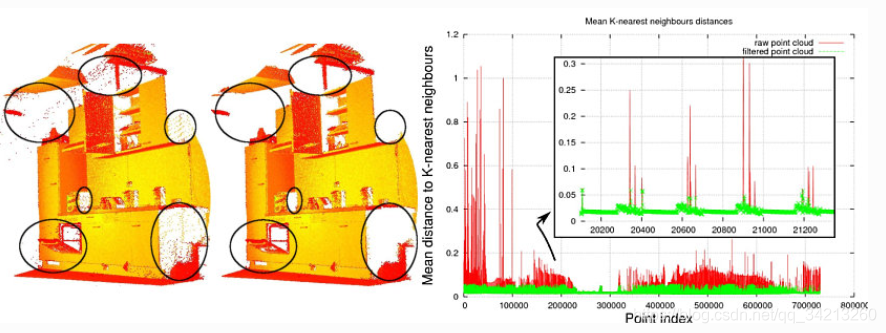
#include
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
template
void myStatisticFilter(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_){
// Create the filtering object
// 创建滤波器,对每个点分析的临近点的个数设置为50 ,并将标准差的倍数设置为1 这意味着如果一
//个点的距离超出了平均距离一个标准差以上,则该点被标记为离群点,并将它移除,存储起来
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval StatisticFilter_;
StatisticFilter_.setInputCloud (inPC_);
StatisticFilter_.setMeanK (50); //设置在进行统计时考虑查询点临近点数
StatisticFilter_.setStddevMulThresh (1.0);//设置判断是否为离群点的阀值
StatisticFilter_.setNegative (true);//默认为flase。true为保留离群点,flase为过滤掉离群点
StatisticFilter_.filter (*outPC_);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
// myPassThroughFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// myVoxelGridFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
myStatisticFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// 转换成ROS格式并发布,用RVIZ查看点云
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_filtered, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
4.2 半径滤波器
- 原理
用户指定每个索引必须在指定半径内的邻居至少有N个。例如,如果指定了1个邻居,则只会从点云中删除黄色点。如果指定了2个邻居,则黄色和绿色点将从点云中删除。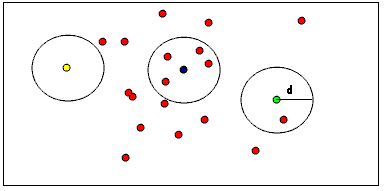
#include
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/radius_outlier_removal.h>
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
template
void myRadiusFilter(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_){
// Create the filtering object
pcl::RadiusOutlierRemoval outrem;
// build the filter
outrem.setInputCloud(inPC_);
outrem.setRadiusSearch(0.8);//设置半径为0.8的范围内找临近点
outrem.setMinNeighborsInRadius (2);//设置查询点的邻域点集数小于2的删除
// apply filter
outrem.filter (*outPC_); //执行条件滤波 在半径为0.8 在此半径内必须要有两个邻居点,此点才会保存
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
// myPassThroughFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// myVoxelGridFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// myStatisticFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
myRadiusFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// 转换成ROS格式并发布,用RVIZ查看点云
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_filtered, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}
五、点云投影
5.1 使用参数化模型投影点云
所有点云都会被投影到指定模型上。例如:投影到平面模型上
#include
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h> //模型系数头文件
#include <pcl/filters/project_inliers.h> //投影滤波类头文件
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointType;
template
void myPlanarFilter(typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr inPC_, typename pcl::PointCloud::Ptr outPC_){
// Create a set of planar coefficients with X=Y=0,Z=1
// 填充ModelCoefficients的值,使用ax+by+cz+d=0平面模型,其中 a=b=d=0,c=1 也就是X——Y平面
//定义模型系数对象,并填充对应的数据
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients ());
coefficients->values.resize (4);
coefficients->values[0] = coefficients->values[1] = 0;
coefficients->values[2] = 1.0;
coefficients->values[3] = 0;
// 创建ProjectInliers对象,使用ModelCoefficients作为投影对象的模型参数
pcl::ProjectInliers proj; //创建投影滤波对象
proj.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE); //设置对象对应的投影模型
proj.setInputCloud (inPC_); //设置输入点云
proj.setModelCoefficients (coefficients); //设置模型对应的系数
proj.filter (*outPC_); //投影结果存储
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "PCL_test_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher PC_pub= nh.advertise("outPC", 1);// 发布点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 pubPC_msg;
// 过滤前点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 保存过滤后点云
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取点云
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("/home/qian/test.pcd", *cloud) == -1)//打开点云文件
{
PCL_ERROR("Couldn't read file test_pcd.pcd\n");
return (-1);
}
// myPassThroughFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// myVoxelGridFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// myStatisticFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// myRadiusFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
myPlanarFilter(cloud,cloud_filtered);
// 转换成ROS格式并发布,用RVIZ查看点云
pcl::toROSMsg(*cloud_filtered, pubPC_msg);
pubPC_msg.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
pubPC_msg.header.frame_id = "map";
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
PC_pub.publish(pubPC_msg);
rate.sleep();
}
return 0;
}