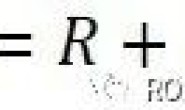本章的理论内容已经总结到了SLAM14讲学习笔记(九)单目稠密重建、深度滤波器详解与补充(纠正第13讲 建图 中的错误),这章的内容在关键的深度滤波器的地方犯了一些错误,我将其标了出来。本文没有理论知识,对理论知识不够了解的,请点击上面的链接。 本章的代码难点主要在于两点: 第一:通过极线匹配之后,如何通过三角测量算出两点的深度来。在ch7中,调用opencv的函数来三角化的。而这章是自己写的,是通过建立二元线性方程组,然后通过克莱默法则求解的。(见下面的注释) 第二:深度滤波器的均值与方差的更新过程,难以与书上的理论步骤匹配。(因为书上高博犯错了,标错了一个咖马角,还写错了贝塔与贝塔撇的关系)
因为这一节的内容不像第9讲设计前端(代码详述),或者第10讲的后端1(代码详述)(主要难点在于工程项目的架构上),这章的代码内容只相当于是一个小程序,因此我不再传到github上,而是直接复制粘贴到下面:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
#include <boost/timer.hpp>
// for sophus
#include <sophus/se3.h>
using Sophus::SE3;
// for eigen
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
using namespace Eigen;
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace cv;
/**********************************************
* 本程序演示了单目相机在已知轨迹下的稠密深度估计
* 使用极线搜索 + NCC 匹配的方式,与书本的 13.2 节对应
* 请注意本程序并不完美,你完全可以改进它——我其实在故意暴露一些问题。
***********************************************/
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// parameters
const int boarder = 20; // 边缘宽度,检测一个点是否在图像边框内时将用到这个宽度;另外极线匹配时也将用到
const int width = 640; // 宽度
const int height = 480; // 高度
const double fx = 481.2f; // 相机内参
const double fy = -480.0f;
const double cx = 319.5f;
const double cy = 239.5f;
const int ncc_window_size = 2; // NCC 取的窗口半宽度
const int ncc_area = (2*ncc_window_size+1)*(2*ncc_window_size+1); // NCC窗口面积
const double min_cov = 0.1; // 收敛判定:最小方差
const double max_cov = 10; // 发散判定:最大方差
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// 重要的函数
// 从 REMODE 数据集读取数据
bool readDatasetFiles(
const string& path,
vector<string>& color_image_files,
vector<SE3>& poses
);
// 根据新的图像更新深度估计
bool update(
const Mat& ref,
const Mat& curr,
const SE3& T_C_R,
Mat& depth, //新来的图像的深度
Mat& depth_cov //对应的方差(即不确定性)
);
// 极线搜索
bool epipolarSearch(
const Mat& ref,
const Mat& curr,
const SE3& T_C_R,
const Vector2d& pt_ref,
const double& depth_mu,
const double& depth_cov,
Vector2d& pt_curr
);
// 更新深度滤波器
bool updateDepthFilter(
const Vector2d& pt_ref,
const Vector2d& pt_curr,
const SE3& T_C_R,
Mat& depth, //系统所维护的深度滤波器
Mat& depth_cov //对应的方差
);
// 计算 NCC 评分
double NCC( const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const Vector2d& pt_ref, const Vector2d& pt_curr );
// 双线性灰度插值
inline double getBilinearInterpolatedValue( const Mat& img, const Vector2d& pt ) {
uchar* d = & img.data[ int(pt(1,0))*img.step+int(pt(0,0)) ];
double xx = pt(0,0) - floor(pt(0,0));
double yy = pt(1,0) - floor(pt(1,0));
return (( 1-xx ) * ( 1-yy ) * double(d[0]) +
xx* ( 1-yy ) * double(d[1]) +
( 1-xx ) *yy* double(d[img.step]) +
xx*yy*double(d[img.step+1]))/255.0;
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
// 一些小工具
// 显示估计的深度图
void plotDepth( const Mat& depth );
// 像素到相机坐标系
inline Vector3d px2cam ( const Vector2d px ) {
return Vector3d (
(px(0,0) - cx)/fx,
(px(1,0) - cy)/fy,
1
);
}
// 相机坐标系到像素
inline Vector2d cam2px ( const Vector3d p_cam ) {
return Vector2d (
p_cam(0,0)*fx/p_cam(2,0) + cx,
p_cam(1,0)*fy/p_cam(2,0) + cy
);
}
// 检测一个点是否在图像边框内,本节中设置边缘宽度为20
inline bool inside( const Vector2d& pt ) {
return pt(0,0) >= boarder && pt(1,0)>=boarder
&& pt(0,0)+boarder<width && pt(1,0)+boarder<=height;
}
// 显示极线匹配
void showEpipolarMatch( const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const Vector2d& px_ref, const Vector2d& px_curr );
// 显示极线
void showEpipolarLine( const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const Vector2d& px_ref, const Vector2d& px_min_curr, const Vector2d& px_max_curr );
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
//代码的目的是估计“参考帧”(第一帧)的像素深度!
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
if ( argc != 2 )
{
cout<<"Usage: dense_mapping path_to_test_dataset"<<endl;
return -1;
}
// 从数据集读取数据
vector<string> color_image_files;
vector<SE3> poses_TWC;
//将路径值传入readDatasetFiles中,以传参的形式将相对完整的路径和位姿传出来
bool ret = readDatasetFiles( argv[1], color_image_files, poses_TWC );
if ( ret==false )
{
cout<<"Reading image files failed!"<<endl;
return -1;
}
cout<<"read total "<<color_image_files.size()<<" files."<<endl;
// 第一张图
Mat ref = imread( color_image_files[0], 0 ); // gray-scale image
SE3 pose_ref_TWC = poses_TWC[0];//以第一帧图像的位姿作为参考,作为TWR,建立世界坐标系与参考图像坐标系的变换关系
double init_depth = 3.0; // 深度初始值
double init_cov2 = 3.0; // 方差初始值
Mat depth( height, width, CV_64F, init_depth ); // 深度图, 64F代表每一个像素点元素占64位浮点数,通道数为1
Mat depth_cov( height, width, CV_64F, init_cov2 ); // 深度图方差
for ( int index=1; index<color_image_files.size(); index++ )
{
cout<<"*** loop "<<index<<" ***"<<endl;
Mat curr = imread( color_image_files[index], 0 );
if (curr.data == nullptr) continue;
SE3 pose_curr_TWC = poses_TWC[index];
SE3 pose_T_C_R = pose_curr_TWC.inverse() * pose_ref_TWC; // 坐标转换关系: T_C_W * T_W_R = T_C_R ,得到当前图像与参考图像(即第一帧)之间的坐标变换
//通过当前图像更新深度滤波器,参数分别为参考图像(第一帧),当前图像,两者之间的位姿变换,深度、以及深度的方差(即不确定性的方差)
//在此函数中调用updateDepthFilte来更新滤波器
update( ref, curr, pose_T_C_R, depth, depth_cov );
//显示一下深度图(这个深度图不是通过RGBD相机拍摄的,而是通过三角测量以及深度滤波器的方式算出每个像素点的深度的)
plotDepth( depth );
imshow("image", curr);
waitKey(1);
}
cout<<"estimation returns, saving depth map ..."<<endl;
imwrite( "depth.png", depth );
cout<<"done."<<endl;
return 0;
}
//通过这个文件读取色彩文件
bool readDatasetFiles(
const string& path,
vector< string >& color_image_files,
std::vector<SE3>& poses
)
{
ifstream fin( path+"/first_200_frames_traj_over_table_input_sequence.txt");
if ( !fin ) return false;
while ( !fin.eof() )
{
// 数据格式:图像文件名 tx, ty, tz, qx, qy, qz, qw ,注意是 TWC 而非 TCW
string image;
fin>>image;
double data[7];
for ( double& d:data ) fin>>d;
//把图像文件名和路径拼在一起,返回引用的实参中的color_image_files字符串型的数组中
color_image_files.push_back( path+string("/images/")+image );
poses.push_back(
SE3( Quaterniond(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]),
Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2]))
);
if ( !fin.good() ) break;
}
return true;
}
// 对整个深度图进行更新
bool update(const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const SE3& T_C_R, Mat& depth, Mat& depth_cov )
{
//为加快速度,采用openMP并行编程,下面的boarder是指:只算图的边框内的值
#pragma omp parallel for
for ( int x=boarder; x<width-boarder; x++ )
#pragma omp parallel for
for ( int y=boarder; y<height-boarder; y++ )
{
// 遍历每个像素,检查深度方差图中的值是否已经收敛或发散
if ( depth_cov.ptr<double>(y)[x] < min_cov || depth_cov.ptr<double>(y)[x] > max_cov ) // 深度已收敛或发散
continue;
// 在极线上搜索 (x,y) 的匹配
Vector2d pt_curr;
//搜索后将找到的对应像素坐标,返回到pt_curr当中
bool ret = epipolarSearch (
ref,
curr,
T_C_R,
Vector2d(x,y),
depth.ptr<double>(y)[x],
sqrt(depth_cov.ptr<double>(y)[x]),
pt_curr
);
if ( ret == false ) // 匹配失败
continue;
// 取消该注释以显示匹配
showEpipolarMatch( ref, curr, Vector2d(x,y), pt_curr );
// 匹配成功,更新深度图
updateDepthFilter( Vector2d(x,y), pt_curr, T_C_R, depth, depth_cov );
}
}
// 极线搜索
// 方法见书 13.2 13.3 两节
bool epipolarSearch(
const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr,
const SE3& T_C_R, const Vector2d& pt_ref,
const double& depth_mu, const double& depth_cov,
Vector2d& pt_curr )
{
//把参考帧的像素坐标系下的原待匹配点转换到参考帧的归一化相机坐标系下
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam( pt_ref );
//归一化处理??
f_ref.normalize();
//从参考帧的归一化相机坐标系下,按照之前估计的深度分布的均值,转换到相机坐标系下
Vector3d P_ref = f_ref*depth_mu; // 参考帧的 P 向量
//参考帧相机坐标系下的待匹配点左乘Tcr得到current帧下的相机坐标系,再变换至current的帧的像素坐标系下
Vector2d px_mean_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*P_ref ); // 按深度均值投影的像素
//确定最小深度值和最大深度值,两个点连线在第二帧的投影即为所要搜寻的极线范围
//至于这里为什么是3,见书的337页,“以均值为中心,左右各取3西格玛作为半径,从而确定深度的范围
double d_min = depth_mu-3*depth_cov, d_max = depth_mu+3*depth_cov;
if ( d_min<0.1 ) d_min = 0.1;
//之前的px_mean_curr为均值深度估计的像素坐标,下面是用最大深度和最小深度估计的像素坐标
Vector2d px_min_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*(f_ref*d_min) ); // 按最小深度投影的像素
Vector2d px_max_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*(f_ref*d_max) ); // 按最大深度投影的像素
//确定一条向量,作为极线的方向
Vector2d epipolar_line = px_max_curr - px_min_curr; // 极线(线段形式)
Vector2d epipolar_direction = epipolar_line; // 极线方向
epipolar_direction.normalize();
double half_length = 0.5*epipolar_line.norm(); // 极线线段的半长度
if ( half_length>100 ) half_length = 100; // 我们不希望搜索太多东西
// 取消此句注释以显示极线(线段)
showEpipolarLine( ref, curr, pt_ref, px_min_curr, px_max_curr );
// 在极线上搜索,以深度均值点为中心,左右各取半长度
//best_ncc作为NCC的一个初始的值,之后依次计算极线上各点的NCC值,保存极线上的最大NCC值;
double best_ncc = -1.0;
//类似的,保存最大NCC的值对应的像素坐标
Vector2d best_px_curr;
for ( double l=-half_length; l<=half_length; l+=0.7 ) // l+=sqrt(2)
{
Vector2d px_curr = px_mean_curr + l*epipolar_direction; // 待匹配点,均值加长度*方向
if ( !inside(px_curr) )
continue;
// 计算待匹配点与参考帧的 NCC
//依次传入四个参数:参考帧图像,当前帧图像,参考帧像素坐标系下的待匹配点坐标,当前帧像素坐标系下的待匹配点坐标
double ncc = NCC( ref, curr, pt_ref, px_curr );
if ( ncc>best_ncc )
{
best_ncc = ncc;
best_px_curr = px_curr;
}
}
if ( best_ncc < 0.85f ) // 只相信 NCC 很高的匹配
return false;
//将搜索到的最佳的像素坐标返回
pt_curr = best_px_curr;
return true;
}
double NCC (
const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr,
const Vector2d& pt_ref, const Vector2d& pt_curr
)
{
// 零均值-归一化互相关
// 先算均值
double mean_ref = 0, mean_curr = 0;
vector<double> values_ref, values_curr; // 参考帧和当前帧的均值
for ( int x=-ncc_window_size; x<=ncc_window_size; x++ )
for ( int y=-ncc_window_size; y<=ncc_window_size; y++ )
{
//依次累加窗口内的值,得到参考帧中极线上某个点所在块内的灰度值之和
double value_ref = double(ref.ptr<uchar>( int(y+pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(x+pt_ref(0,0)) ])/255.0;
mean_ref += value_ref;
//依次累加窗口内的值,得到当前帧中极线上的对应点所在块内的灰度值之和,注意这里用的是双线性插值法
double value_curr = getBilinearInterpolatedValue( curr, pt_curr+Vector2d(x,y) );
mean_curr += value_curr;
values_ref.push_back(value_ref);
values_curr.push_back(value_curr);
}
//除以面积,这才得到了均值
mean_ref /= ncc_area;
mean_curr /= ncc_area;
// 计算 Zero mean NCC
double numerator = 0, demoniator1 = 0, demoniator2 = 0;
for ( int i=0; i<values_ref.size(); i++ )
{
//下面两行即NCC公式的分子
double n = (values_ref[i]-mean_ref) * (values_curr[i]-mean_curr);
numerator += n;
//下面两行即NCC的分母中根号下的两项
demoniator1 += (values_ref[i]-mean_ref)*(values_ref[i]-mean_ref);
demoniator2 += (values_curr[i]-mean_curr)*(values_curr[i]-mean_curr);
}
return numerator / sqrt( demoniator1*demoniator2+1e-10 ); // 防止分母出现零
}
bool updateDepthFilter(
const Vector2d& pt_ref,
const Vector2d& pt_curr,
const SE3& T_C_R,
Mat& depth,
Mat& depth_cov
)
{
// 我是一只喵
// 不知道这段还有没有人看(有人看!而且还做了笔记)
// 用三角化计算深度 根据极线搜索,确定了两帧图像对应的匹配点(即分别是形参中的pt_ref和pt_curr)
SE3 T_R_C = T_C_R.inverse();
//把参考帧的像素坐标变换到参考帧的归一化相机坐标系下
Vector3d f_ref = px2cam( pt_ref );
//模长变为1,因为之后算西格玛的时候,要用到它
f_ref.normalize();
//把当前帧的像素坐标变换到当前帧的归一化相机坐标系下
Vector3d f_curr = px2cam( pt_curr );
f_curr.normalize();
// 方程
// d_ref * f_ref = d_cur * ( R_RC * f_cur ) + t_RC 即书P153页 7.24公式
// => [ f_ref^T f_ref, -f_ref^T f_cur ] [d_ref] = [f_ref^T t]
// [ f_cur^T f_ref, -f_cur^T f_cur ] [d_cur] = [f_cur^T t]
// 二阶方程用克莱默法则求解并解之
//克莱默法则是先算齐次行列式的值D,然后用常数项b依次替换掉i列,算行列式Di,Di/D即为xi的值
Vector3d t = T_R_C.translation();
Vector3d f2 = T_R_C.rotation_matrix() * f_curr;
//重点来了:
//s1*x1=s2*R*x2+t,移项得到s1*x1-s2*R*x2=t (1)
//(1)两边同乘x1的转置x1T,得s1*x1T*x1-s2*x1T*R*x2=x1T*t (2) 注意"T"指的是转置的意思
//(1)两边同乘(R*x2)T,得s1*(R*x2)T*x1-s2*((R*x2)T)*R*x2=(R*x2)T * t (3)
//因此接下来的A[]就是存放未知数为s1和s2的线性方程组的系数矩阵,b存放方程组右端的两个常数
Vector2d b = Vector2d ( t.dot ( f_ref ), t.dot ( f2 ) );
double A[4];
A[0] = f_ref.dot ( f_ref );
A[2] = f_ref.dot ( f2 );
A[1] = -A[2];
A[3] = - f2.dot ( f2 );
//d就是系数矩阵的行列式
double d = A[0]*A[3]-A[1]*A[2];
//线性方程组求出的两个深度值
Vector2d lambdavec =
Vector2d ( A[3] * b ( 0,0 ) - A[1] * b ( 1,0 ),
-A[2] * b ( 0,0 ) + A[0] * b ( 1,0 )) /d;
//xm=s1*x1
Vector3d xm = lambdavec ( 0,0 ) * f_ref;
//xn=s2*R*x2+t
Vector3d xn = t + lambdavec ( 1,0 ) * f2;
//其实xm和xn应该是相等的,相加除以2,减小二者的误差
Vector3d d_esti = ( xm+xn ) / 2.0; // 三角化算得的深度向量
double depth_estimation = d_esti.norm(); // 深度值
// 计算不确定性(以一个像素为误差)
//获取参考帧下的某点(本函数传入的第一个形参)的相机坐标系下的点
Vector3d p = f_ref*depth_estimation;
//得到书326页13.7公式的a
Vector3d a = p - t;
//得到两个向量的模长长度(因为想要通过 “a向量*b向量=a的模长*b的模长*cos(a,b)”来计算cos值)
double t_norm = t.norm();
double a_norm = a.norm();
//得到13.7公式中的阿尔法、贝塔,注意第一个f_ref已经归一化过了(即“f_ref.normalize();”),模长是1
double alpha = acos( f_ref.dot(t)/t_norm );
double beta = acos( -a.dot(t)/(a_norm*t_norm));
//由于高博书中的错误,这里其实应该是double beta_prime = beta - atan(1/fx);得到贝塔撇
double beta_prime = beta + atan(1/fx);
//书中的咖马,也应该是下面的那个咖马
double gamma = M_PI - alpha - beta_prime;
double p_prime = t_norm * sin(beta_prime) / sin(gamma);
double d_cov = p_prime - depth_estimation;
double d_cov2 = d_cov*d_cov;
// 高斯融合,即13.6公式
double mu = depth.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ];
double sigma2 = depth_cov.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ];
double mu_fuse = (d_cov2*mu+sigma2*depth_estimation) / ( sigma2+d_cov2);
double sigma_fuse2 = ( sigma2 * d_cov2 ) / ( sigma2 + d_cov2 );
//更新系统现有的状态量
depth.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ] = mu_fuse;
depth_cov.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ] = sigma_fuse2;
return true;
}
// 后面这些太简单我就不注释了(其实是因为懒)
void plotDepth(const Mat& depth)
{
imshow( "depth", depth*0.4 );
waitKey(1);
}
void showEpipolarMatch(const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const Vector2d& px_ref, const Vector2d& px_curr)
{
Mat ref_show, curr_show;
cv::cvtColor( ref, ref_show, CV_GRAY2BGR );
cv::cvtColor( curr, curr_show, CV_GRAY2BGR );
cv::circle( ref_show, cv::Point2f(px_ref(0,0), px_ref(1,0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0,0,250), 2);
cv::circle( curr_show, cv::Point2f(px_curr(0,0), px_curr(1,0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0,0,250), 2);
imshow("ref", ref_show );
imshow("curr", curr_show );
waitKey(1);
}
void showEpipolarLine(const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const Vector2d& px_ref, const Vector2d& px_min_curr, const Vector2d& px_max_curr)
{
Mat ref_show, curr_show;
cv::cvtColor( ref, ref_show, CV_GRAY2BGR );
cv::cvtColor( curr, curr_show, CV_GRAY2BGR );
cv::circle( ref_show, cv::Point2f(px_ref(0,0), px_ref(1,0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0,255,0), 2);
cv::circle( curr_show, cv::Point2f(px_min_curr(0,0), px_min_curr(1,0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0,255,0), 2);
cv::circle( curr_show, cv::Point2f(px_max_curr(0,0), px_max_curr(1,0)), 5, cv::Scalar(0,255,0), 2);
cv::line( curr_show, Point2f(px_min_curr(0,0), px_min_curr(1,0)), Point2f(px_max_curr(0,0), px_max_curr(1,0)), Scalar(0,255,0), 1);
imshow("ref", ref_show );
imshow("curr", curr_show );
waitKey(1);
}