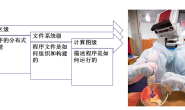
fake_ar_publisher::ARMarkerConstPtr last_msg_;
void visionCallback(const fake_ar_publisher::ARMarkerConstPtr& msg)
{
last_msg_ = msg;
ROS_INFO_STREAM(last_msg_->pose.pose);
}
这里的消息文件是:ARMarker.msg在fake_ar_publisher包里,内容如下: Header header uint32 id geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovariance pose uint32 confidence 可以看出这里先是先是通过指针找到ARMarker下的pose消息,而这里的消息类型是geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovariance,然后从官网上搜索geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovariance
 看到此消息类型的定义,这里更像是一个大的结构体,里面定义了各种消息类型,从最下面看到实际的消息定义
看到此消息类型的定义,这里更像是一个大的结构体,里面定义了各种消息类型,从最下面看到实际的消息定义
 通过这里可以理顺last_msg_->pose进行类似于对结构体的指针操作找到pose,所以写成这种形式last_msg_->pose.pose 点开geometry_msgs/Pose 可以看到内部包含了位置(xyz)和方向(xyzw) 进一步点开geometry_msgs/Point 和geometry_msgs/Quaternion 可以看到最终的消息类型 这里说一下Quaternion 有三种表示方式:旋转矩阵,欧拉角,四元数(上面定义的四元数) 到这里我们也许看到消息机制中引用的恰恰是我们熟悉的位姿格式
通过这里可以理顺last_msg_->pose进行类似于对结构体的指针操作找到pose,所以写成这种形式last_msg_->pose.pose 点开geometry_msgs/Pose 可以看到内部包含了位置(xyz)和方向(xyzw) 进一步点开geometry_msgs/Point 和geometry_msgs/Quaternion 可以看到最终的消息类型 这里说一下Quaternion 有三种表示方式:旋转矩阵,欧拉角,四元数(上面定义的四元数) 到这里我们也许看到消息机制中引用的恰恰是我们熟悉的位姿格式
 下面进入到我们的主题,取出apriltags2_ros下的类似于上面的位姿 运行
下面进入到我们的主题,取出apriltags2_ros下的类似于上面的位姿 运行 roslaunch usb_cam usb_cam-test.launch (打开usb摄像头,找到tag) roslaunch apriltags2_ros continuous_detection.launch (结合opencv,用apriltags2_ros可以实现空间tags相对于相机位姿的计算) 输入rostopic list
 通过代码发现这里的/tag_detections 是apriltag2_ros发布的主题,这里就是我们需要订阅的主题。 然后这里依然是需要找到消息文件,编写订阅节点 这里很懵逼的发现包含两个文件如下: AprilTagDetection.msg
通过代码发现这里的/tag_detections 是apriltag2_ros发布的主题,这里就是我们需要订阅的主题。 然后这里依然是需要找到消息文件,编写订阅节点 这里很懵逼的发现包含两个文件如下: AprilTagDetection.msg
 AprilTagDetectionArray.msg
AprilTagDetectionArray.msg
 这里困扰了我好久,怎么编写这里消息的订阅格式,刚开始整了两天多,断断续续的,越来越浮躁,最后索性先放了一下,找了Mastering ROS for Robotics Programming (1)书看了前面几章,然后跟着例程走了一遍,过了三天又满血复合的投入到编写节点订阅位姿的过程中。 然后对比两个msg文件发现,定义的位姿的格式不太一样 例程是geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovariance pose 这里是geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovarianceStamped pose 索性修改了一下这里的订阅格式修改成geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovariance pose 果不其然出错了,但看到下面这个错误,我恍然大悟原来detections[ ]是一个数组,需要给其指定数组位
这里困扰了我好久,怎么编写这里消息的订阅格式,刚开始整了两天多,断断续续的,越来越浮躁,最后索性先放了一下,找了Mastering ROS for Robotics Programming (1)书看了前面几章,然后跟着例程走了一遍,过了三天又满血复合的投入到编写节点订阅位姿的过程中。 然后对比两个msg文件发现,定义的位姿的格式不太一样 例程是geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovariance pose 这里是geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovarianceStamped pose 索性修改了一下这里的订阅格式修改成geometry_msgs/PoseWithCovariance pose 果不其然出错了,但看到下面这个错误,我恍然大悟原来detections[ ]是一个数组,需要给其指定数组位
 然后从AprilTagDetectionArray.msg文件和源码文件都发现了这是个数组的定义,只能说自己看的不够仔细,思维定视。 然后自己修改写出了下面订阅位姿的节点
然后从AprilTagDetectionArray.msg文件和源码文件都发现了这是个数组的定义,只能说自己看的不够仔细,思维定视。 然后自己修改写出了下面订阅位姿的节点
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "apriltags2_ros/AprilTagDetectionArray.h"
#include <iostream>
class Localizer
{
public:
Localizer(ros::NodeHandle& nh)
{
ar_sub_ = nh.subscribe<apriltags2_ros::AprilTagDetectionArray>("tag_detections", 1,
&Localizer::number_callback, this);
}
void number_callback(const apriltags2_ros::AprilTagDetectionArray::ConstPtr& msg)
{
last_msg_ = msg;
ROS_INFO_STREAM(last_msg_->detections[0].pose.pose.pose);
//ROS_INFO("the number %d ",);
//ROS_INFO("%s\n", s.data.c_str());
}
ros::Subscriber ar_sub_;
apriltags2_ros::AprilTagDetectionArrayConstPtr last_msg_;
};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv,"apriltag_detector_subscriber");
ros::NodeHandle node_obj;
Localizer localizer(node_obj);
//ros::Subscriber number_subscriber = node_obj.subscribe("tag_detections",1,number_callback);
ROS_INFO("1Vision node starting");
ros::spin();
//return 0;
}
这里输入
rostopic info /tag_detections
 看出了此话题的类型是apriltags2_ros/AprilTagDetectionArray 所以头文件写成 #include “apriltags2_ros/AprilTagDetectionArray.h” 输入
看出了此话题的类型是apriltags2_ros/AprilTagDetectionArray 所以头文件写成 #include “apriltags2_ros/AprilTagDetectionArray.h” 输入
rostopic echo /tag_detections
 这里我们看到了我们想要的position和orientation,也提示我们为什么这麽写输出流 ROS_INFO_STREAM(last_msg_->detections[0].pose.pose.pose); 通过last_msg_->detections[0]订阅到话题下的detections消息,然后通过三级的pose指针订阅到了我们想要的位姿 运行节点
这里我们看到了我们想要的position和orientation,也提示我们为什么这麽写输出流 ROS_INFO_STREAM(last_msg_->detections[0].pose.pose.pose); 通过last_msg_->detections[0]订阅到话题下的detections消息,然后通过三级的pose指针订阅到了我们想要的位姿 运行节点
rosrun apriltags2_node vision_node1
订阅到了实时的位姿输出

rqt_graph
节点图如下: