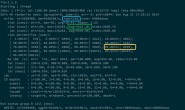
C++面向对象中的多态代码演示
//An example of using overriding techniques to demonstrate function with a polymorphism behaviour.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// abstract base class
class base
{
protected: // attribute section
int num1;
int num2;
int result;
public: // behavior section
void setVar(int n1,int n2)
{
num1 = n1;
num2 = n2;
}
virtual void op() = 0; // pure virtual function
int getresult() {return result;}
};
class add: public base // add class inherits from base class
{
public:
void op() {result = num1 + num2;}
};
//sub class inherit base class
class sub: public base
{
public:
void op() {result = num1 - num2;}
};
int main()
{
int x,y;
base *m; //pointer variable declaration of type base class
add ad; //create object1 for addition process
sub su; //create object2 for subtraction process
cout << "\nEnter two numbers seperated by space, or press Ctrl+z to Exit: ";
while(cin >> x >> y)
{
m =
m->setVar( x , y );
m->op(); //addition process, even though call is on pointer to base!
cout << "\nResult of summation = " << m->getresult();
m =
m->setVar( x , y );
m->op(); //subtraction process, even though call is on pointer to base!
cout << "\nResult of subtraction = " << m->getresult() << endl << endl;
cout << "\nEnter two numbers seperated by space or press Ctrl+z to Exit: ";
}
return 0;
}
/*program output
****************
Enter two numbers seperated by space, or press Ctrl+z to Exit: 88 9
Result of summation = 97
Result of subtraction = 79
Enter two numbers seperated by space or press Ctrl+z to Exit: ^Z
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 102.711 s
Press any key to continue.
*/