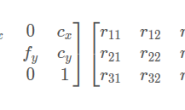本文借鉴很多这个链接的内容,之后加了一些新的注释。
目录
Camera类
camera.h
camera.cpp
Frame类
frame.h
frame.cpp
MapPoint类
mappoint.h
mappoint.cpp
Map类
map.h
map.cpp
Config类
config.h
config.cpp
Camera类
高博:Camera 类存储相机的内参和外参,并完成相机坐标系、像素坐标系、和世界坐标系之间的坐标变换。当然,在世界坐标系中你需要一个相机的(变动的)外参,我们以参数的形式传入。
camera.h
#ifndef CAMERA_H
#define CAMERA_H
#include "myslam/common_include.h"
namespace myslam
{
// Pinhole RGBD camera model
class Camera
{
public:
//定义指向自身的指针,构造时如下使用:
//Camera::Ptr camera_=New(Camera);
typedef std::shared_ptr<Camera> Ptr;
//相机内参
float fx_, fy_, cx_, cy_, depth_scale_; // Camera intrinsics
//构造函数需要先读取数据,depth_scale有初值
Camera();
Camera ( float fx, float fy, float cx, float cy, float depth_scale=0 ) :
fx_ ( fx ), fy_ ( fy ), cx_ ( cx ), cy_ ( cy ), depth_scale_ ( depth_scale )
{}
// coordinate transform: world, camera, pixel
// 世界,相机,像素三坐标系转换,涉及世界坐标系都有外参T_c_w,像素对外需要深度
Vector3d world2camera( const Vector3d& p_w, const SE3& T_c_w );
Vector3d camera2world( const Vector3d& p_c, const SE3& T_c_w );
Vector2d camera2pixel( const Vector3d& p_c );
Vector3d pixel2camera( const Vector2d& p_p, double depth=1 );
Vector3d pixel2world ( const Vector2d& p_p, const SE3& T_c_w, double depth=1 );
Vector2d world2pixel ( const Vector3d& p_w, const SE3& T_c_w );
};
}
#endif // CAMERA_H
camera.cpp
#include "myslam/camera.h"
//5.1.2最后有之间转化的内容梳理
//定义工作空间,自然你要是用opencv,工作空间要加cv
namespace myslam
{
Camera::Camera()
{
}
//世界to相机:w_to_c变换矩阵乘世界坐标系的点位置
Vector3d Camera::world2camera ( const Vector3d& p_w, const SE3& T_c_w )
{
return T_c_w*p_w;
}
//相机to世界:c_to_w变换矩阵乘相机坐标系的点位置
Vector3d Camera::camera2world ( const Vector3d& p_c, const SE3& T_c_w )
{
return T_c_w.inverse() *p_c;
}
//相机to坐标系:书中公式5.5,p_c虽然是3*1矩阵,但如下输出没问题,和p_c(n)一样
Vector2d Camera::camera2pixel ( const Vector3d& p_c )
{
return Vector2d (
fx_ * p_c ( 0,0 ) / p_c ( 2,0 ) + cx_,
fy_ * p_c ( 1,0 ) / p_c ( 2,0 ) + cy_
);
}
//和上面相反
Vector3d Camera::pixel2camera ( const Vector2d& p_p, double depth )
{
return Vector3d (
( p_p ( 0,0 )-cx_ ) *depth/fx_,
( p_p ( 1,0 )-cy_ ) *depth/fy_,
depth
);
}
//︿( ̄︶ ̄)︿
Vector2d Camera::world2pixel ( const Vector3d& p_w, const SE3& T_c_w )
{
return camera2pixel ( world2camera ( p_w, T_c_w ) );
}
//︿( ̄︶ ̄)︿
Vector3d Camera::pixel2world ( const Vector2d& p_p, const SE3& T_c_w, double depth )
{
return camera2world ( pixel2camera ( p_p, depth ), T_c_w );
}
}
Frame类
高博:由于 Frame 类是基本数据单元,在许多地方会用到它,但现在初期设计阶段,我们还不清楚以后可能新加的内容。所以这里的 Frame 类只提供基本的数据存储和接口。如果之后有新增的内容,我们就继续往里添加。
frame.h
#ifndef FRAME_H
#define FRAME_H
#include "myslam/common_include.h"
#include "myslam/camera.h"
namespace myslam
{
// forward declare
class MapPoint;
class Frame
{
public:
typedef std::shared_ptr<Frame> Ptr;
unsigned long id_; // id of this frame
double time_stamp_; // when it is recorded
SE3 T_c_w_; // transform from world to camera
Camera::Ptr camera_; // Pinhole RGBD Camera model
Mat color_, depth_; // color and depth image
public: // data members
Frame();//师哥说一个类中同一函数可以有多种构造方式
Frame( long id, double time_stamp=0, SE3 T_c_w=SE3(), Camera::Ptr camera=nullptr, Mat color=Mat(), Mat depth=Mat() );
//~函数取反,是析构函数,详见https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15267341/article/details/78585570
~Frame();
// factory function 创建帧
static Frame::Ptr createFrame();
// find the depth in depth map//color图中找对应像素的深度
double findDepth( const cv::KeyPoint& kp );
// Get Camera Center取得光心
Vector3d getCamCenter() const;
// check if a point is in this frame 判断一个点是否在该帧内
bool isInFrame( const Vector3d& pt_world );
};
}
#endif // FRAME_H
frame.cpp
#include "myslam/frame.h"
namespace myslam
{
//同一函数不同定义方式
Frame::Frame()
: id_(-1), time_stamp_(-1), camera_(nullptr)
{
}
Frame::Frame ( long id, double time_stamp, SE3 T_c_w, Camera::Ptr camera, Mat color, Mat depth )
: id_(id), time_stamp_(time_stamp), T_c_w_(T_c_w), camera_(camera), color_(color), depth_(depth)
{
}
Frame::~Frame()
{
}
//这里注意下,由factory_id++一个数去构造Frame对象时,调用的是默认构造函数,由于默认构造函数全都有默认值,所以就是按坑填,先填第一个id_,
//所以也就是相当于创建了一个只有ID号的空白帧。
Frame::Ptr Frame::createFrame()
{
static long factory_id = 0;
return Frame::Ptr( new Frame(factory_id++) );
}
//注意看这个函数参数类型是cv::KeyPoint&,所以也就是color图已经detect出keypoint了,去寻找depth
double Frame::findDepth ( const cv::KeyPoint& kp )
{
int x = cvRound(kp.pt.x);
int y = cvRound(kp.pt.y);
//这个还是.ptr模板函数定位像素值的方法,记住用法
ushort d = depth_.ptr<ushort>(y)[x];
if ( d!=0 )
{
//除以比例尺之后return
return double(d)/camera_->depth_scale_;
}
//某个点没采集到深度值(过远)
else
{
// check the nearby points
int dx[4] = {-1,0,1,0};
int dy[4] = {0,-1,0,1};
for ( int i=0; i<4; i++ )
{
d = depth_.ptr<ushort>( y+dy[i] )[x+dx[i]];
if ( d!=0 )
{
return double(d)/camera_->depth_scale_;
}
}
}
//如果还没有,就返回-1.0,表示访问失败
return -1.0;
}
// T_c_w_.inverse()求出来的平移部分就是R^(-1)*(-t),也就是相机坐标系下的(0,0,0)在世界坐标系下的坐标,也就是相机光心的世界坐标
// 实验了以下程序结果为 1\n 3\n 4\n
// int main(int argc,char** argv)
// {
// Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector ( M_PI/4, Eigen::Vector3d ( 0,0,1 ) );
// Eigen::Isometry3d T=Eigen::Isometry3d::Identity(); // 虽然称为3d,实质上是4*4的矩阵
// T.rotate ( rotation_vector ); // 按照rotation_vector进行旋转
// T.pretranslate ( Eigen::Vector3d ( 1,3,4 ) ); // 把平移向量设成(1,3,4)
// cout << "translation = \n"<<T.translation()<<endl;
// return 0;
// }
Vector3d Frame::getCamCenter() const
{
return T_c_w_.inverse().translation();
}
bool Frame::isInFrame ( const Vector3d& pt_world )
{
Vector3d p_cam = camera_->world2camera( pt_world, T_c_w_ );
//这步是取得Z值,Z为相机和物体实际距离,小于0直接return false
if ( p_cam(2,0)<0 )
return false;
Vector2d pixel = camera_->world2pixel( pt_world, T_c_w_ );
//xy值都大于0并且小于color图的行列
return pixel(0,0)>0 && pixel(1,0)>0
&& pixel(0,0)<color_.cols
&& pixel(1,0)<color_.rows;
}
}
MapPoint类
高博:MapPoint 表示路标点。我们将估计它的世界坐标,并且我们会拿当前帧提取到的特征点与地图中的路标点匹配,来估计相机的运动,因此还需要存储它对应的描述子。此外,我们会记录一个点被观测到的次数和被匹配到的次数,作为评价它的好坏程度的指标。
mappoint.h
#ifndef MAPPOINT_H
#define MAPPOINT_H
namespace myslam
{
class Frame;
class MapPoint
{
public:
typedef shared_ptr<MapPoint> Ptr;
unsigned long id_; // ID
Vector3d pos_; // Position in world
Vector3d norm_; // Normal of viewing direction 视向法线?
Mat descriptor_; // Descriptor for matching
int observed_times_; // being observed by feature matching algo.
int correct_times_; // being an inliner in pose estimation
MapPoint();
MapPoint( long id, Vector3d position, Vector3d norm );
// factory function
static MapPoint::Ptr createMapPoint();
};
}
#endif // MAPPOINT_H
mappoint.cpp
#include "myslam/common_include.h"
#include "myslam/mappoint.h"
namespace myslam
{
MapPoint::MapPoint()
: id_(-1), pos_(Vector3d(0,0,0)), norm_(Vector3d(0,0,0)), observed_times_(0), correct_times_(0)
{
}
MapPoint::MapPoint ( long id, Vector3d position, Vector3d norm )
: id_(id), pos_(position), norm_(norm), observed_times_(0), correct_times_(0)
{
}
//创造零点
MapPoint::Ptr MapPoint::createMapPoint()
{
static long factory_id = 0;
return MapPoint::Ptr(
new MapPoint( factory_id++, Vector3d(0,0,0), Vector3d(0,0,0) )
);
}
Map类
高博:Map 类管理着所有的路标点,并负责添加新路标、删除不好的路标等工作。VO 的匹配过程只需要和 Map 打交道即可。当然 Map 也会有很多操作,但现阶段我们只定义主要的数据结构。
map.h
#ifndef MAP_H
#define MAP_H
#include "myslam/common_include.h"
#include "myslam/frame.h"
#include "myslam/mappoint.h"
namespace myslam
{
class Map
{
public:
typedef shared_ptr<Map> Ptr;
unordered_map<unsigned long, MapPoint::Ptr > map_points_; // all landmarks
unordered_map<unsigned long, Frame::Ptr > keyframes_; // all key-frames
Map() {}
void insertKeyFrame( Frame::Ptr frame );
void insertMapPoint( MapPoint::Ptr map_point );
};
}
#endif // MAP_H
map.cpp
#include "myslam/map.h"
namespace myslam
{
void Map::insertKeyFrame ( Frame::Ptr frame )
{
cout<<"Key frame size = "<<keyframes_.size()<<endl;
//可能是这个意思,我还在思考。。原理上应该是关键帧里没有,那么插入
//根据帧的id去找这个帧的位置(序号)看是否与关键帧最后一位相等
if ( keyframes_.find(frame->id_) == keyframes_.end() )
{
//如果相等,则以pair形式插入该帧,该pair包括id和frame
keyframes_.insert( make_pair(frame->id_, frame) );
}
else
{
keyframes_[ frame->id_ ] = frame;
}
}
void Map::insertMapPoint ( MapPoint::Ptr map_point )
{
//地图点的插入
if ( map_points_.find(map_point->id_) == map_points_.end() )
{
map_points_.insert( make_pair(map_point->id_, map_point) );
}
else
{
map_points_[map_point->id_] = map_point;
}
}
Config类
高博:Config 类负责参数文件的读取,并在程序任意地方都可随时提供参数的值。所以我们把 Config 写成单件模式(Singleton)。它只有一个全局对象,当我们设置参数文件时,创建该对象并读取参数文件,随后就可以在任意地方访问参数值,最后在程序结束时自动销毁(~函数?)。
config.h
#ifndef CONFIG_H
#define CONFIG_H
#include "myslam/common_include.h"
namespace myslam
{
class Config
{
private:
static std::shared_ptr<Config> config_;
cv::FileStorage file_;
Config () {} // private constructor makes a singleton
public:
~Config(); // close the file when deconstructing
// set a new config file
static void setParameterFile( const std::string& filename );
// access the parameter values
template< typename T >
static T get( const std::string& key )
{
return T( Config::config_->file_[key] );
}
};
}
#endif // CONFIG_H
config.cpp
#include "myslam/config.h"
namespace myslam
{
void Config::setParameterFile( const std::string& filename )
{
if ( config_ == nullptr )
config_ = shared_ptr<Config>(new Config);//没有config则构建
config_->file_ = cv::FileStorage( filename.c_str(), cv::FileStorage::READ );
if ( config_->file_.isOpened() == false ) //文件无法打开则报错
{
std::cerr<<"parameter file "<<filename<<" does not exist."<<std::endl;
config_->file_.release();
return;
}
}
Config::~Config()
{
if ( file_.isOpened() )
file_.release();//释放file
}
//这里就是全局指针
shared_ptr<Config> Config::config_ = nullptr;
}