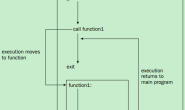
针对终结点的路由是由EndpointRoutingMiddleware和EndpointMiddleware这两个中间件协同完成的。应用在启动之前会注册若干表示终结点的Endpoint对象(具体来说是包含路由模式的RouteEndpoint对象)。如下图所示,当应用接收到请求并创建HttpContext上下文之后,EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件会根据请求的URL及其他相关信息从注册的终结点中选择匹配度最高的那个。之后被选择的终结点会以一个特性(Feature)的形式附加到当前HttpContext上下文中,EndpointMiddleware中间件最终提供这个终结点并用它来处理当前请求。[更多关于ASP.NET Core的文章请点这里]
![ASP.NET Core路由中间件[4]: EndpointRoutingMiddleware和EndpointMiddleware ASP.NET Core路由中间件[4]: EndpointRoutingMiddleware和EndpointMiddleware](https://img2020.cnblogs.com/blog/19327/202101/19327-20210107084403497-332099360.png)
目录
一、IEndpointFeature
二、EndpointRoutingMiddleware
三、EndpointMiddleware
四、注册终结点
一、IEndpointFeature
EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件选择的终结点会以特性的形式存放在当前HttpContext上下文中,这个用来封装终结点的特性通过IEndpointFeature接口表示。如下面的代码片段所示,IEndpointFeature接口通过唯一的属性Endpoint表示针对当前请求选择的终结点。我们可以调用HttpContext类型的GetEndpoint方法和SetEndpoint方法来获取与设置用来处理当前请求的终结点。
public interface IEndpointFeature { Endpoint Endpoint { get; set; } } public static class EndpointHttpContextExtensions { public static Endpoint GetEndpoint(this HttpContext context) =>context.Features.Get<IEndpointFeature>()?.Endpoint; public static void SetEndpoint(this HttpContext context, Endpoint endpoint) { var feature = context.Features.Get<IEndpointFeature>(); if (feature != null) { feature.Endpoint = endpoint; } else { context.Features.Set<IEndpointFeature>(new EndpointFeature { Endpoint = endpoint }); } } private class EndpointFeature : IEndpointFeature { public Endpoint Endpoint { get; set; } } }
二、EndpointRoutingMiddleware
EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件利用一个Matcher对象选择出与当前HttpContext上下文相匹配的终结点,然后将选择的终结点以IEndpointFeature特性的形式附加到当前HttpContext上下文中。Matcher只是一个内部抽象类型,针对终结点的选择和设置实现在它的MatchAsync方法中。如果匹配的终结点被成功选择出来,MatchAsync方法还会提取出解析出来的路由参数,然后将它们逐个添加到表示当前请求的HttpRequest对象的RouteValues属性字典中。
internal abstract class Matcher { public abstract Task MatchAsync(HttpContext httpContext); } public abstract class HttpRequest { public virtual RouteValueDictionary RouteValues { get; set; } } public class RouteValueDictionary : IDictionary<string, object>, IReadOnlyDictionary<string, object> { ... }
EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件使用的Matcher由注册的MatcherFactory服务来提供。路由系统默认使用的Matcher类型为DfaMatcher,它采用一种被称为确定有限状态自动机(Deterministic Finite Automaton,DFA)的形式从候选终结点中找到与当前请求匹配度最高的那个。由于篇幅有限,具体的细节此处不再展开介绍。DfaMatcher最终会利用DfaMatcherFactory对象间接地创建出来,DfaMatcherFactory类型派生于抽象类MatcherFactory。
internal abstract class MatcherFactory { public abstract Matcher CreateMatcher(EndpointDataSource dataSource); }
对Matcher和MatcherFactory有了基本了解之后,我们将关注点转移到EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件。如下所示的代码片段模拟了EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件的实现逻辑。我们在构造函数中注入了用于提供注册终结点的IEndpointRouteBuilder对象和用来创建Matcher对象的MatcherFactory工厂。
internal class EndpointRoutingMiddleware { private readonly RequestDelegate _next; private readonly Task<Matcher> _matcherAccessor; public EndpointRoutingMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IEndpointRouteBuilder builder, MatcherFactory factory) { _next = next; _matcherAccessor = new Task<Matcher>(CreateMatcher); Matcher CreateMatcher() { var source = new CompositeEndpointDataSource(builder.DataSources); return factory.CreateMatcher(source); } } public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext httpContext) { var matcher = await _matcherAccessor; await matcher.MatchAsync(httpContext); await _next(httpContext); } }
在实现的InvokeAsync方法中,我们只需要根据IEndpointRouteBuilder对象提供的终结点列表创建一个CompositeEndpointDataSource对象,并将其作为参数调用MatcherFactory工厂的CreateMatcher方法。该方法会返回一个Matcher对象,然后调用Matcher对象的MatchAsync方法选择出匹配的终结点,并以特性的方式附加到当前HttpContext上下文中。EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件一般通过如下所示的UseRouting扩展方法进行注册。
public static class EndpointRoutingApplicationBuilderExtensions { public static IApplicationBuilder UseRouting(this IApplicationBuilder builder); }
三、EndpointMiddleware
EndpointMiddleware中间件的职责特别明确,就是执行由EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件附加到当前HttpContext上下文中的终结点。EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件针对终结点的执行涉及如下所示的RouteOptions类型标识的配置选项。
public class RouteOptions { public bool LowercaseUrls { get; set; } public bool LowercaseQueryStrings { get; set; } public bool AppendTrailingSlash { get; set; } public IDictionary<string, Type> ConstraintMap { get; set; } public bool SuppressCheckForUnhandledSecurityMetadata { get; set; } }
配置选项RouteOptions的前三个属性与路由系统针对URL的生成有关。具体来说,LowercaseUrls属性和LowercaseQueryStrings属性决定是否会将生成的URL或者查询字符串转换成小写形式。AppendTrailingSlash属性则决定是否会为生成的URL添加后缀“/”。RouteOptions的ConstraintMap属性表示的字典与路由参数的内联约束有关,它提供了在路由模板中实现的约束字符串(如regex表示正则表达式约束)与对应约束类型(正则表达式约束类型为RegexRouteConstraint)之间的映射关系。
真正与EndpointMiddleware中间件相关的是RouteOptions的SuppressCheckForUnhandledSecurityMetadata属性,它表示目标终结点利用添加的元数据设置了一些关于安全方面的要求(主要是授权和跨域资源共享方面的要求),但是目前的请求并未经过相应的中间件处理(通过请求是否具有要求的报头判断),在这种情况下是否还有必要继续执行目标终结点。如果这个属性设置为True,就意味着EndpointMiddleware中间件根本不会做这方面的检验。如下所示的代码片段模拟了EndpointMiddleware中间件对请求的处理逻辑。
internal class EndpointMiddleware { private readonly RequestDelegate _next; private readonly RouteOptions _options; public EndpointMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, IOptions<RouteOptions> optionsAccessor) { _next = next; _options = optionsAccessor.Value; } public Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext httpContext) { var endpoint = httpContext.GetEndpoint(); if (null != endpoint) { if (!_options.SuppressCheckForUnhandledSecurityMetadata) { CheckSecurity(); } return endpoint.RequestDelegate(httpContext); } return _next(httpContext); } private void CheckSecurity(); }
我们一般调用如下所示的UseEndpoints扩展方法来注册EndpointMiddleware中间件,该方法提供了一个类型为Action<IEndpointRouteBuilder>的参数。通过前面的介绍可知,EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件会利用注入的IEndpointRouteBuilder对象来获取注册的表示终结点数据源的EndpointDataSource,所以可以通过这个方法为EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件注册终结点数据源。
public static class EndpointRoutingApplicationBuilderExtensions { public static IApplicationBuilder UseEndpoints(this IApplicationBuilder builder, Action<IEndpointRouteBuilder> configure); }
四、注册终结点
对于使用路由系统的应用程序来说,它的主要工作基本集中在针对EndpointDataSource的注册上。一般来说,当我们调用IApplicationBuilder接口的UseEndpoints扩展方法注册EndpointMiddleware中间件时,会利用提供的Action<IEndpointRouteBuilder>委托对象注册所需的EndpointDataSource对象。IEndpointRouteBuilder接口具有一系列的扩展方法,这些方法可以帮助我们注册所需的终结点。
如下所示的Map方法会根据提供的作为路由模式和处理器的RoutePattern对象与RequestDelegate对象创建一个终结点,并以ModelEndpointDataSource的形式予以注册。如下所示的代码片段还揭示了一个细节:对于作为请求处理器的RequestDelegate委托对象来说,其对应方法上标注的所有特性会以元数据的形式添加到创建的终结点上。
public static class EndpointRouteBuilderExtensions { public static IEndpointConventionBuilder Map(this IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints, RoutePattern pattern, RequestDelegate requestDelegate) { var builder = new RouteEndpointBuilder(requestDelegate, pattern, 0) { DisplayName = pattern.RawText }; var attributes = requestDelegate.Method.GetCustomAttributes(); if (attributes != null) { foreach (var attribute in attributes) { builder.Metadata.Add(attribute); } } var dataSource = endpoints.DataSources.OfType<ModelEndpointDataSource>().FirstOrDefault()?? new ModelEndpointDataSource(); endpoints.DataSources.Add(dataSource); return dataSource.AddEndpointBuilder(builder); } }
HTTP方法(Method)在RESTful API的设计中具有重要意义,几乎所有的终结点都会根据自身对资源的操作类型对请求采用HTTP方法做相应限制。如果需要为注册的终结点指定限定的HTTP方法,就可以调用如下所示的MapMethods方法。该方法会在Map方法的基础上为注册的终结点设置相应的显示名称,并针对指定的HTTP方法创建一个HttpMethodMetadata对象,然后作为元数据添加到注册的终结点上。
public static class EndpointRouteBuilderExtensions { public static IEndpointConventionBuilder MapMethods(this IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints, string pattern, IEnumerable<string> httpMethods, RequestDelegate requestDelegate) { var builder = endpoints.Map(RoutePatternFactory.Parse(pattern), requestDelegate); builder.WithDisplayName($"{pattern} HTTP: {string.Join(", ", httpMethods)}"); builder.WithMetadata(new HttpMethodMetadata(httpMethods)); return builder; } }
EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件在为当前请求筛选匹配的终结点时,针对HTTP方法的选择策略是通过IHttpMethodMetadata接口表示的元数据指定的,HttpMethodMetadata类型正是对该接口的默认实现。如下面的代码片段所示,IHttpMethodMetadata接口除了具有一个表示可接受HTTP方法列表的HttpMethods属性,还有一个布尔类型的只读属性AcceptCorsPreflight,它表示是否接受针对跨域资源共享(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing,CORS)的预检(Preflight)请求。
public interface IHttpMethodMetadata { IReadOnlyList<string> HttpMethods { get; } bool AcceptCorsPreflight { get; } } public sealed class HttpMethodMetadata : IHttpMethodMetadata { public IReadOnlyList<string> HttpMethods { get; } public bool AcceptCorsPreflight { get; } public HttpMethodMetadata(IEnumerable<string> httpMethods): this(httpMethods, acceptCorsPreflight: false) {} public HttpMethodMetadata(IEnumerable<string> httpMethods, bool acceptCorsPreflight) { HttpMethods = httpMethods.ToArray(); AcceptCorsPreflight = acceptCorsPreflight; } }
路由系统还为4种常用的HTTP方法(GET、POST、PUT和DELETE)定义了相应的方法。从如下所示的代码片段可以看出,它们最终调用的都是MapMethods方法。我们在本章开篇演示的实例中正是调用其中的MapGet方法来注册终结点的。
public static class EndpointRouteBuilderExtensions { public static IEndpointConventionBuilder MapGet(this IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints, string pattern, RequestDelegate requestDelegate) => MapMethods(endpoints, pattern, "GET", requestDelegate); public static IEndpointConventionBuilder MapPost(this IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints, string pattern, RequestDelegate requestDelegate) => MapMethods(endpoints, pattern, "POST", requestDelegate); public static IEndpointConventionBuilder MapPut(this IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints, string pattern, RequestDelegate requestDelegate) => MapMethods(endpoints, pattern, "PUT", requestDelegate); public static IEndpointConventionBuilder MapDelete(this IEndpointRouteBuilder endpoints, string pattern, RequestDelegate requestDelegate) => MapMethods(endpoints, pattern, "DELETE", requestDelegate); }
调用IApplicationBuilder接口相应的扩展方法注册EndpointRoutingMiddleware中间件和EndpointMiddleware中间件时,必须确保它们依赖的服务已经被注册到依赖注入框架之中。针对路由服务的注册可以通过调用如下所示的AddRouting扩展方法重载来完成。
public static class RoutingServiceCollectionExtensions { public static IServiceCollection AddRouting(this IServiceCollection services); public static IServiceCollection AddRouting(this IServiceCollection services, Action<RouteOptions> configureOptions); }
ASP.NET Core路由中间件[1]: 终结点与URL的映射
ASP.NET Core路由中间件[2]: 路由模式
ASP.NET Core路由中间件[3]: 终结点
ASP.NET Core路由中间件[4]: EndpointRoutingMiddleware和EndpointMiddleware
ASP.NET Core路由中间件[5]: 路由约束