.
简单描述一下自己通过学习nifi和查看源码,然后自己通过nifi的体现很基础的实现自己的业务的处理器开发。
适合刚入门的看,有nifi基础的,可以跳过!
目录
一、 获取一个json文件的文本信息.
1.Json文档的输入端,需要一个GenerateFlowFile处理器,做如下配置:
2.拖拽自己实现的处理器
3.使用PutFile
二、合并文本的内容
1.Json文档的输入端
2.拖拽自己实现的处理器
3.使用PutFile
4.整体的流程图如下所示:
三、给一个文件内容添加头信息
1.Json文档的输入端
2.拖拽自己实现的处理器
3.使用PutFile
4.整体的流程图如下所示
一、 获取一个json文件的文本信息.
假定我们需要在一段json文件中,获取json串中的某个key所对应的value的值,那么在nifi的架子上,该如何操作呐?共分为三步:
1.Json文档的输入端,需要一个GenerateFlowFile处理器,做如下配置:
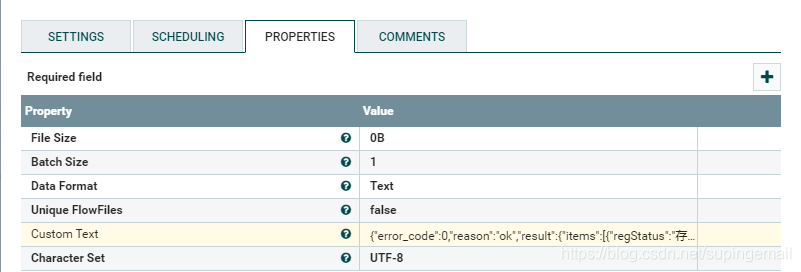
Custom text 存放的是目标json串.json如下所示:{“error_code”:0,”reason”:”ok”,”result”:{“items”:[{“regStatus”:”存续”,”estiblishTime”:1495555200000,”regCapital”:””,”pencertileScore”:4902,”type”:1,”legalPersonName”:”温旭颖”,”toco”:2,”legalPersonId”:2051255554,”name”:”陕西蜂窝科技股份有限公司”,”logo”:””,”alias”:”蜂窝科技”,”id”:3053414776,”category”:”723″,”personType”:1,”base”:”han”},{“regStatus”:”注销”,”estiblishTime”:1473264000000,”regCapital”:””,”pencertileScore”:3860,”type”:1,”legalPersonName”:”常青”,”toco”:8,”legalPersonId”:1911055314,”name”:”陕西蜂窝科技股份有限公司”,”logo”:””,”alias”:”蜂窝科技”,”id”:2958332903,”category”:”721″,”personType”:1,”base”:”xj”}],”total”:18}}
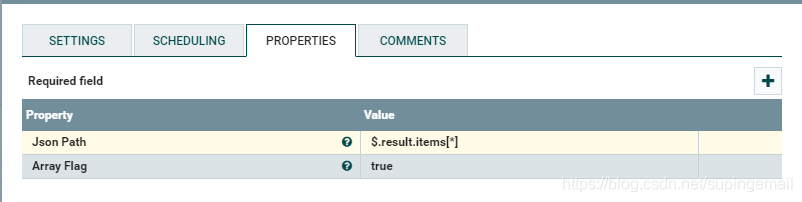
2.拖拽自己实现的处理器
根据要求配置好自己的json_path的路径,这样方便获取数据.如: $.result.items[*]
自己处理器的主要代码是:
@Tags({"first-example:fetch value from json string"})
@SideEffectFree
@CapabilityDescription("fetch value from json string.")
public class FirstProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
private List<PropertyDescriptor> properties;
private Set<Relationship> relationships;
private final String arrayFlag="true";
/**
* json路径.
*/
public static final PropertyDescriptor JSON_PATH = new PropertyDescriptor.Builder()
.name("Json Path")
.required(true)
.description("json path value,such as:$.test")
.addValidator(StandardValidators.NON_EMPTY_VALIDATOR)
.build();
/**
* json路径.
*/
public static final PropertyDescriptor ARRAY_FLAG = new PropertyDescriptor.Builder()
.name("Array Flag")
.required(true)
.description("mark if the input json is array or not")
.addValidator(StandardValidators.NON_EMPTY_VALIDATOR)
.allowableValues("true", "false")
.defaultValue("false")
.build();
/**
* 成功标识.
*/
public static final Relationship SUCCESS = new Relationship.Builder()
.name("SUCCESS")
.description("Succes relationship")
.build();
@Override
public Set<Relationship> getRelationships(){
return relationships;
}
@Override
public List<PropertyDescriptor> getSupportedPropertyDescriptors(){
return properties;
}
/**
* 初始化配置
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void init(final ProcessorInitializationContext context){
List<PropertyDescriptor> properties = new ArrayList<>();
properties.add(JSON_PATH);
properties.add(ARRAY_FLAG);
this.properties = Collections.unmodifiableList(properties);
Set<Relationship> relationships = new HashSet<>();
relationships.add(SUCCESS);
this.relationships = Collections.unmodifiableSet(relationships);
}
@Override
public void onTrigger(final ProcessContext context, final ProcessSession session) throws ProcessException {
final AtomicReference<String> value = new AtomicReference<>();
FlowFile flowfile = session.get();
session.read(flowfile, new InputStreamCallback() {
@Override
public void process(InputStream in) throws IOException {
try{
String json =IOUtils.toString(in, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
String flag = context.getProperty(ARRAY_FLAG).getValue();
if (flag.equalsIgnoreCase(arrayFlag)){
List<Object> dataList = JsonPath.read(json, context.getProperty(JSON_PATH).getValue());
if (ObjectUtils.allNotNull(dataList)){
StringBuilder all = new StringBuilder("[");
int total = 0;
for (Object object : dataList) {
LinkedHashMap<String,Object> dataMap = (LinkedHashMap<String, Object>) object;
Set<String> keys = dataMap.keySet();
int count = 0;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("{");
for (String key :keys ) {
if (count==keys.size()-1){
builder.append("\""+key+"\":\""+dataMap.get(key)+"\"");
}else{
builder.append("\""+key+"\":\""+dataMap.get(key)+"\",");
}
count++;
}
if (total==dataList.size()-1){
builder.append("}");
}else {
builder.append("},");
}
total++;
all.append(builder.toString());
builder.reverse();
}
all.append("]");
value.set(all.toString());
}
}else {
String result = JsonPath.read(json, context.getProperty(JSON_PATH).getValue());
value.set(result);
}
}catch(Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
getLogger().error("failed to read json string.");
}
}
});
//Write the results to an attribute
String results = value.get();
if(results != null && !results.isEmpty()){
String flag = context.getProperty(ARRAY_FLAG).getValue();
if (flag.equalsIgnoreCase(arrayFlag)){
Map<String,String> data=new HashMap<>(16);
data.put(NiFiConstant.MATCH_ATTR,value.toString());
flowfile = session.putAllAttributes(flowfile,data);
}else {
flowfile = session.putAttribute(flowfile, NiFiConstant.MATCH_ATTR, results);
}
}
//To write the results back out ot flow file
flowfile = session.write(flowfile, new OutputStreamCallback() {
@Override
public void process(OutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.write(value.get().getBytes());
}
});
session.transfer(flowfile, SUCCESS);
}
}
要指明是不是一个json array ,因为jsonobject 和jsonarray 的解析和接收对象是不一样的。
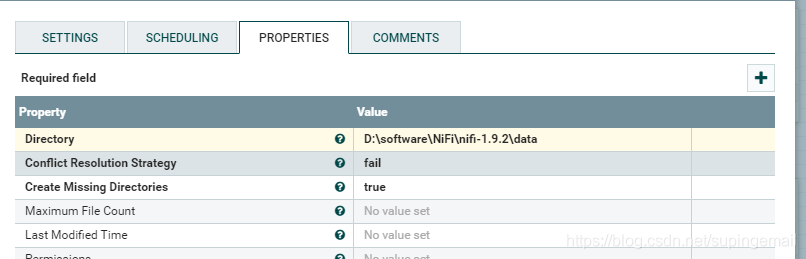
3.使用PutFile
指定处理完成之后,文件的输出地址:
4.整个的流程图如下:
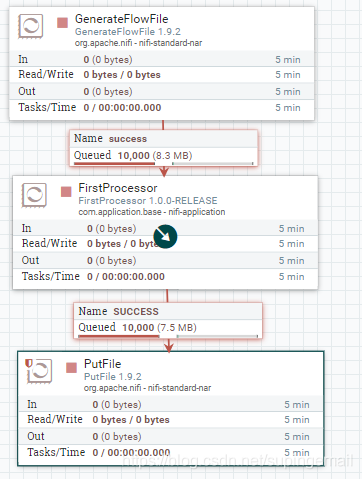
直接上代码,按照图所示来操作,就可以看见对应的文件输出到目录里了。
二、合并文本的内容
假定我们需要在把一个文本内容拼接上另外一个文本内容,那么在nifi的架子上,该如何操作呐?共分为三步:
1.Json文档的输入端
需要一个GenerateFlowFile处理器,做如下配置:
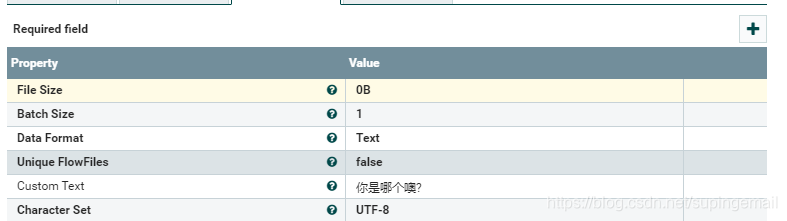
Custom text 存放的是操作的文本内容,如下所示: 你是哪个 ?
2.拖拽自己实现的处理器
根据要求配置好自己的input value的值,这样就可以将a中的文本内容进行拼接:

代码实现如下:
@Tags({"second-example:Combine two sentences!"})
@SeeAlso({})
@SideEffectFree
@CapabilityDescription("merge two content to one together")
@ReadsAttributes({@ReadsAttribute(attribute="", description="")})
@WritesAttributes({@WritesAttribute(attribute="", description="")})
public class SecondProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
/**
* 属性描述对象集合
*/
private List<PropertyDescriptor> descriptors;
/**
* 关联关系集合
*/
private Set<Relationship> relationships;
/**
* 文件设置.
*/
private static final String FILE_NAME = "out-";
private static final String FILE_SUFFIX = ".txt";
public static final PropertyDescriptor INPUT_VALUE = new PropertyDescriptor.Builder()
.name("INPUT_VALUE")
.displayName("INPUT VALUE")
.description("input value for operating")
.required(true)
//非空验证
.addValidator(StandardValidators.NON_EMPTY_VALIDATOR)
.build();
public static final Relationship RELATIONSHIP_SUCCESS = new Relationship.Builder()
.name("sucess")
.description("example relationship uccess")
.build();
public static final Relationship RELATIONSHIP_FAILURE = new Relationship.Builder()
.name("failure")
.description("example relationship failure")
.build();
public static final PropertyDescriptor CHARSET = new PropertyDescriptor.Builder()
.name("character-set")
.displayName("Character Set")
.required(true)
.defaultValue("UTF-8")
.addValidator(StandardValidators.CHARACTER_SET_VALIDATOR)
.build();
@Override
protected void init(final ProcessorInitializationContext context) {
final List<PropertyDescriptor> descriptors = new ArrayList<PropertyDescriptor>();
descriptors.add(INPUT_VALUE);
descriptors.add(CHARSET);
this.descriptors = Collections.unmodifiableList(descriptors);
final Set<Relationship> relationships = new HashSet<Relationship>();
relationships.add(RELATIONSHIP_SUCCESS);
relationships.add(RELATIONSHIP_FAILURE);
this.relationships = Collections.unmodifiableSet(relationships);
}
@Override
public Set<Relationship> getRelationships() {
return this.relationships;
}
@Override
public final List<PropertyDescriptor> getSupportedPropertyDescriptors() {
return descriptors;
}
@OnScheduled
public void onScheduled(final ProcessContext context) {
getLogger().info("Processor-Name"+context.getName());
Map<PropertyDescriptor, String> dataMap = context.getProperties();
for (Map.Entry<PropertyDescriptor, String> entry : dataMap.entrySet()) {
getLogger().info("key="+entry.getKey().toString()+",value="+entry.getValue());
}
}
@Override
public void onTrigger(final ProcessContext context, final ProcessSession session) throws ProcessException {
FlowFile flowFile = session.get();
if ( flowFile == null ) {
return;
}
final AtomicReference<String> value = new AtomicReference<>();
session.read(flowFile, new InputStreamCallback() {
@Override
public void process(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
try{
String inputVal = IOUtils.toString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
//utf8 的设置
final Charset charset = Charset.forName(context.getProperty(CHARSET).getValue());
getLogger().info("得到字符集结果是:"+charset.name());
String current = new String(context.getProperty(INPUT_VALUE).getValue().getBytes(charset),StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
String result = "处理结果:" + inputVal + current;
//以 utf8 的方式把流信息写出去.
getLogger().info("处理得到的结果是:"+result);
value.set(result);
}catch(Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
getLogger().error("failed to read input string!");
}
}
});
String results = value.get();
if(results != null && !results.isEmpty()){
flowFile = session.putAttribute(flowFile, NiFiConstant.MATCH_ATTR, results);
}
//写入文件信息.
flowFile = session.write(flowFile, new OutputStreamCallback() {
@Override
public void process(OutputStream outputStream) throws IOException {
getLogger().info("写出的消息是:"+value.get());
byte[] content = value.get().getBytes();
//远程的输出流
outputStream.write(content);
//重新定义本地输出流.
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(FILE_NAME+uuid()+FILE_SUFFIX));
outputStream.write(content);
}
});
session.transfer(flowFile, RELATIONSHIP_SUCCESS);
}
/**
* 产生一个32位的GUID
* @return
*/
public String uuid() {
return getIdentifier().replace("-", "").toUpperCase();
}
}
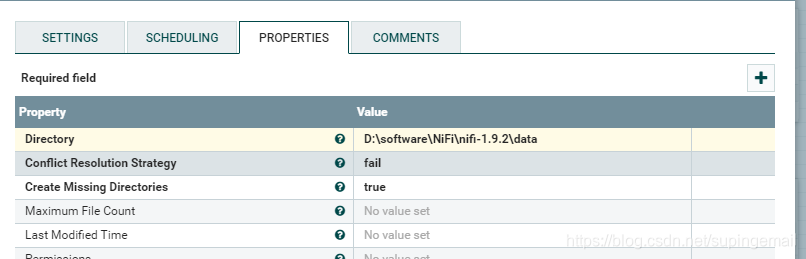
3.使用PutFile
指定处理完成之后,文件的输出地址:.
4.整体的流程图如下所示:
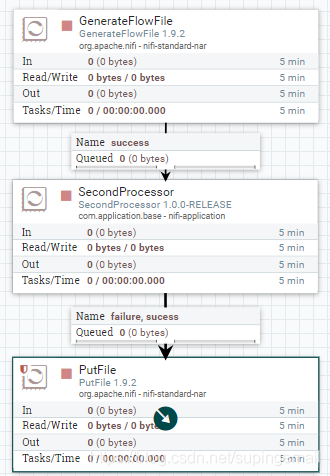
如此就可以完成两个文本内容的拼接并输出的操作。
三、给一个文件内容添加头信息
假定我们需要在把一个文件内部的内容拼接上另外一个文本内容,那么在nifi的架子上,该如何操作呐?共分为三步:
1.Json文档的输入端
需要一个GenerateFlowFile处理器,做如下配置:
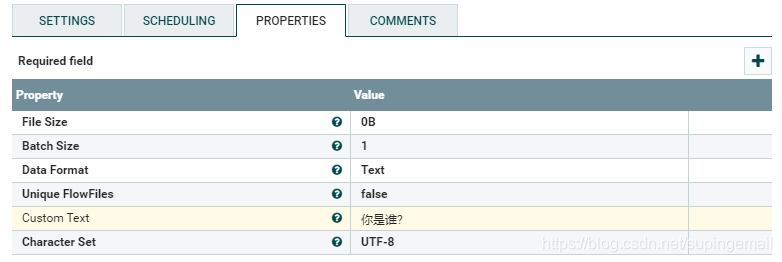
注意file size 和字符集的设置。Custom text 存放的是操作的文本内容,如下所示:你是谁?
2.拖拽自己实现的处理器
根据要求配置好自己的文件的绝对路径的值,这样就可以将a中的文本内容进行拼接
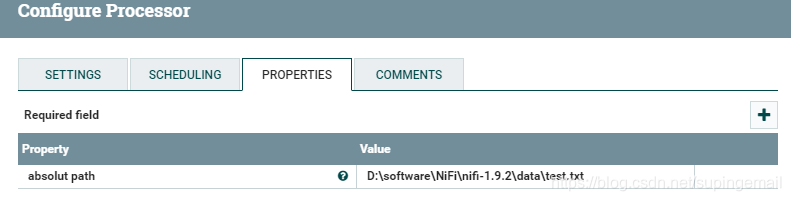
需要一个绝对的文件路径,具体代码如下:
@Tags({"third-example:deal with content!"})
@SeeAlso({})
@SideEffectFree
@CapabilityDescription("add prefix to given content.")
@ReadsAttributes({@ReadsAttribute(attribute="", description="")})
@WritesAttributes({@WritesAttribute(attribute="", description="")})
public class ThirdProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
/**
* 属性描述对象集合
*/
private List<PropertyDescriptor> descriptors;
/**
* 关联关系集合
*/
private Set<Relationship> relationships;
/**
* 文件设置.
*/
private static final String FILE_NAME = "combine-";
private static final String FILE_SUFFIX = ".txt";
public static final PropertyDescriptor ABSOLUTE_PATH = new PropertyDescriptor.Builder()
.name("ABSOLUTE_PATH")
.displayName("ABSOLUT PATH")
.description("input file path for operating")
.required(true)
//非空验证
.addValidator(StandardValidators.NON_EMPTY_VALIDATOR)
.build();
public static final Relationship SHIP_SUCCESS = new Relationship.Builder()
.name("sucess")
.description("example relationship uccess")
.build();
public static final Relationship SHIP_FAILURE = new Relationship.Builder()
.name("failure")
.description("example relationship failure")
.build();
public static final PropertyDescriptor CHARSET = new PropertyDescriptor.Builder()
.name("character-set")
.displayName("Character Set")
.required(true)
.defaultValue("UTF-8")
.addValidator(StandardValidators.CHARACTER_SET_VALIDATOR)
.build();
@Override
protected void init(final ProcessorInitializationContext context) {
final List<PropertyDescriptor> descriptors = new ArrayList<PropertyDescriptor>();
descriptors.add(ABSOLUTE_PATH);
descriptors.add(CHARSET);
this.descriptors = Collections.unmodifiableList(descriptors);
final Set<Relationship> ships = new HashSet<Relationship>();
ships.add(SHIP_SUCCESS);
ships.add(SHIP_FAILURE);
this.relationships = Collections.unmodifiableSet(ships);
}
@Override
public Set<Relationship> getRelationships() {
return this.relationships;
}
@Override
public final List<PropertyDescriptor> getSupportedPropertyDescriptors() {
return descriptors;
}
@OnScheduled
public void onScheduled(final ProcessContext context) {
getLogger().info("Processor-Name"+context.getName());
Map<PropertyDescriptor, String> dataMap = context.getProperties();
for (Map.Entry<PropertyDescriptor, String> entry : dataMap.entrySet()) {
getLogger().info("key="+entry.getKey().toString()+",value="+entry.getValue());
}
}
@Override
public void onTrigger(final ProcessContext context, final ProcessSession session) throws ProcessException {
FlowFile flowFile = session.get();
if ( flowFile == null ) {
return;
}
final AtomicReference<String> value = new AtomicReference<>();
//utf8 的设置
final Charset charset = Charset.forName(context.getProperty(CHARSET).getValue());
session.read(flowFile, new InputStreamCallback() {
@Override
public void process(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
try{
String headerDesc = IOUtils.toString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
String filePath = context.getProperty(ABSOLUTE_PATH).getValue();
InputStreamReader inRd = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath),charset);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(inRd);
String line=null;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
while (null!=(line=reader.readLine())){
getLogger().info("文件信息是:"+line);
builder.append(headerDesc+new String(line.getBytes(charset),StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name())+"\n\t");
}
//以 utf8 的方式把流信息写出去.
getLogger().info("处理得到的结果是:"+builder.toString());
value.set(builder.toString());
}catch(Exception ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
getLogger().error("failed to read input string!");
}
}
});
String results = value.get();
if(results != null && !results.isEmpty()){
flowFile = session.putAttribute(flowFile, NiFiConstant.MATCH_ATTR, results);
}
//写入文件信息.
flowFile = session.write(flowFile, new OutputStreamCallback() {
@Override
public void process(OutputStream outputStream) throws IOException {
getLogger().info("写出的消息是:"+value.get());
byte[] content = value.get().getBytes();
//远程的输出流
outputStream.write(content);
//重新定义本地输出流.
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(FILE_NAME+uuid()+FILE_SUFFIX));
outputStream.write(content);
}
});
session.transfer(flowFile, SHIP_SUCCESS);
}
/**
* 产生一个32位的GUID
* @return
*/
public String uuid() {
return getIdentifier().replace("-", "").toUpperCase();
}
}
3.使用PutFile
指定处理完成之后,文件的输出地址
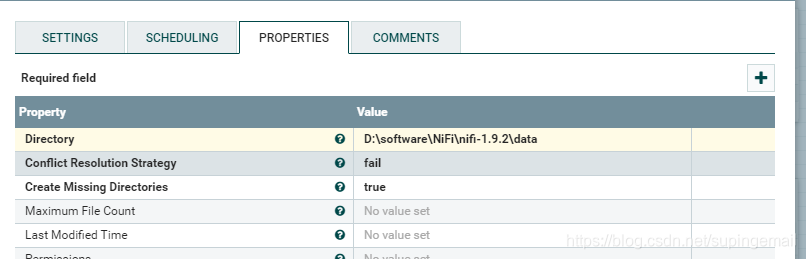
4.整体的流程图如下所示
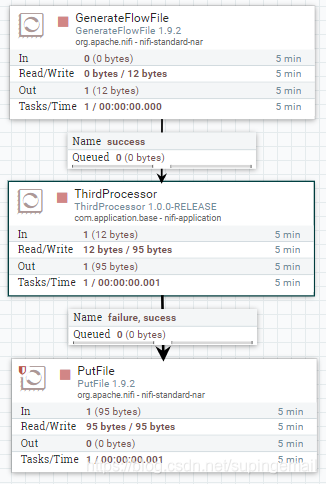
如此挨个执行,不报错的情况下,就可以看见执行的结果了。
本文只是一个简单描述下如何基于nifi框架,来实现自己的业务逻辑,下一篇我就复杂使用下,看看如何操作。
如有不明白的,请微信搜索公众号 :codingba ,我会一一解答。