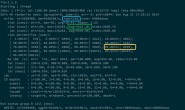
本示例演示了用户定义的类如何能够重载运算符
// complex.cs
using System;
public struct Complex
{
public int real;
public int imaginary;
public Complex(int real, int imaginary)
{
this.real = real;
this.imaginary = imaginary;
}
// 声明要重载的运算符 (+)、
// 可相加的类型(两个 Complex 对象)以及
// return type (Complex):
public static Complex operator +(Complex c1, Complex c2)
{
return new Complex(c1.real + c2.real, c1.imaginary + c2.imaginary);
}
// 重写 ToString 方法,从而以适当的格式显示复数:
public override string ToString()
{
return(String.Format("{0} + {1}i", real, imaginary));
}
public static void Main()
{
Complex num1 = new Complex(2,3);
Complex num2 = new Complex(3,4);
// 通过重载的加号运算符
// 将两个 Complex 对象(num1 和 num2)相加:
Complex sum = num1 + num2;
// 使用重写的 ToString 方法打印数字以及相加得到的和:
Console.WriteLine("First complex number: {0}",num1);
Console.WriteLine("Second complex number: {0}",num2);
Console.WriteLine("The sum of the two numbers: {0}",sum);
}
}
代码2
// dbbool.cs
using System;
public struct DBBool
{
// 三个可能的 DBBool 值:
public static readonly DBBool dbNull = new DBBool(0);
public static readonly DBBool dbFalse = new DBBool(-1);
public static readonly DBBool dbTrue = new DBBool(1);
// 为 dbFalse、dbNull、dbTrue 存储 -1、0、1 的私有字段:
int value;
// 私有构造函数。值参数必须为 -1、0 或 1:
DBBool(int value)
{
this.value = value;
}
// 从 bool 到 DBBool 的隐式转换。将 true 映射为
// DBBool.dbTrue,将 false 映射为 DBBool.dbFalse:
public static implicit operator DBBool(bool x)
{
return x? dbTrue: dbFalse;
}
// 从 DBBool 到 bool 的显式转换。如果
// 给定的 DBBool 为 dbNull,则引发异常;否则返回
// true 或 false:
public static explicit operator bool(DBBool x)
{
if (x.value == 0) throw new InvalidOperationException();
return x.value > 0;
}
// 相等运算符。如果任何一个操作数为 dbNull,则返回 dbNull;
// 否则返回 dbTrue 或 dbFalse:
public static DBBool operator ==(DBBool x, DBBool y)
{
if (x.value == 0 || y.value == 0) return dbNull;
return x.value == y.value? dbTrue: dbFalse;
}
// 不等运算符。如果任何一个操作数为
// dbNull,则返回 dbNull;否则返回 dbTrue 或 dbFalse:
public static DBBool operator !=(DBBool x, DBBool y)
{
if (x.value == 0 || y.value == 0) return dbNull;
return x.value != y.value? dbTrue: dbFalse;
}
// 逻辑非运算符。如果操作数为
// dbFalse,则返回 dbTrue;如果操作数为 dbNull,则返回 dbNull;如果
// 操作数为 dbTrue,则返回 dbFalse:
public static DBBool operator !(DBBool x)
{
return new DBBool(-x.value);
}
// 逻辑“与”运算符。如果任何一个操作数为
// dbFalse,则返回 dbFalse;如果任何一个操作数为 dbNull,则返回 dbNull;否则,返回 dbTrue:
public static DBBool operator &(DBBool x, DBBool y)
{
return new DBBool(x.value < y.value? x.value: y.value);
}
// 逻辑“或”运算符。如果任何一个操作数为
// dbTrue,则返回 dbTrue;如果任何一个操作数为 dbNull,则返回 dbNull;否则,返回 dbFalse:
public static DBBool operator |(DBBool x, DBBool y)
{
return new DBBool(x.value > y.value? x.value: y.value);
}
// 绝对真运算符。如果操作数为
// dbTrue,则返回 true,否则返回 false:
public static bool operator true(DBBool x)
{
return x.value > 0;
}
// 绝对假运算符。如果操作数为
// dbFalse,则返回 true,否则返回 false:
public static bool operator false(DBBool x)
{
return x.value < 0;
}
// 重载从 DBBool 到 string 的转换:
public static implicit operator string(DBBool x)
{
return x.value > 0 ? "dbTrue"
: x.value < 0 ? "dbFalse"
: "dbNull";
}
// 重写 Object.Equals(object o) 方法:
public override bool Equals(object o)
{
try
{
return (bool) (this == (DBBool) o);
}
catch
{
return false;
}
}
// 重写 Object.GetHashCode() 方法:
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return value;
}
// 重写 ToString 方法以便将 DBBool 转换为 string:
public override string ToString()
{
switch (value)
{
case -1:
return "DBBool.False";
case 0:
return "DBBool.Null";
case 1:
return "DBBool.True";
default:
throw new InvalidOperationException();
}
}
}
class Test
{
static void Main()
{
DBBool a, b;
a = DBBool.dbTrue;
b = DBBool.dbNull;
Console.WriteLine( "!{0} = {1}", a, !a);
Console.WriteLine( "!{0} = {1}", b, !b);
Console.WriteLine( "{0} & {1} = {2}", a, b, a & b);
Console.WriteLine( "{0} | {1} = {2}", a, b, a | b);
// 调用真运算符以确定 DBBool 变量的
// 布尔值:
if (b)
Console.WriteLine("b is definitely true");
else
Console.WriteLine("b is not definitely true");
}
}