3. Delete 实现
附上实验2的第一部分 https://www.cnblogs.com/JayL-zxl/p/14324297.html
附上实验2的第三部分 https://www.cnblogs.com/JayL-zxl/p/14332249.html
1. 删除算法原理
cmu这里给了演示网站 https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BPlusTree.html
关于整个删除算法的讲解这个ppthttp://courses.cms.caltech.edu/cs122/lectures-wi2018/CS122Lec11.pdf讲的比较清楚
算法描述见下表

以及下图

2 删除算法实现
2.1 第一步 : 找到包含目标key的leaf node进行删除
-
找到包含目标key的leaf node
-
如果当前是空树则立即返回
-
否则先找到要删除的key所在的page
-
随后调用
RemoveAndDeleteRecord在叶page上直接删除key值
INDEX_TEMPLATE_ARGUMENTS
void BPLUSTREE_TYPE::Remove(const KeyType &key, Transaction *transaction) {
{
// 这个专门针对于非并发的delete
Page *page = FindLeafPage(key, false);
LeafPage *leafPage = reinterpret_cast<LeafPage*>(page->GetData()); //pined leafPage
leafPage->RemoveAndDeleteRecord(key,comparator_);
-
RemoveAndDeleteRecord函数
-
这里实现越来越像Leveldb是怎么回事。。
-
利用
KeyIndex函数实现真的简单。
INDEX_TEMPLATE_ARGUMENTS
int B_PLUS_TREE_LEAF_PAGE_TYPE::RemoveAndDeleteRecord(const KeyType &key, const KeyComparator &comparator) {
int pos = KeyIndex(key, comparator);
if (pos < GetSize() && comparator(array_[pos].first, key) == 0) {
for (int j = pos + 1; j < GetSize(); j++) {
array_[j - 1] = array_[j];
}
IncreaseSize(-1);
}
return GetSize();
}
之后就是对于删除的处理,主要有两个一个是合并,一个就是redistribute。具体流程见下
2.2 Coalesce实现流程
叶子结点内关键字个数小于最小值向下执行。调用删除的核心函数CoalesceAndRedistribute
下面是CoalesceAndRedistribute的逻辑
1.如果当前结点是根节点则调用AdjustRoot(node)
这里的提示给了其实这个函数就针对两种情况
- Case1 : old_root_node是内部结点,且大小为1,表示内部结点其实已经没有key了。所以要把它的孩子更新成新的根节点
- Case2 : old_root_node是叶子结点。且大小为0,直接删了就好。
否则不需要有page被删除,则直接return flase
INDEX_TEMPLATE_ARGUMENTS
bool BPLUSTREE_TYPE::AdjustRoot(BPlusTreePage *old_root_node) {
// case 1 old_root_node (internal node) has only one size
if (!old_root_node->IsLeafPage() && old_root_node->GetSize() == 1) {
InternalPage *old_root_page = reinterpret_cast<InternalPage *>(old_root_node);
page_id_t new_root_page_id = old_root_page->adjustRootForInternal();
root_page_id_ = new_root_page_id;
UpdateRootPageId(0);
Page *new_root_page = buffer_pool_manager_->FetchPage(new_root_page_id);
BPlusTreePage *new_root = reinterpret_cast<BPlusTreePage *>(new_root_page->GetData());
new_root->SetParentPageId(INVALID_PAGE_ID);
buffer_pool_manager_->UnpinPage(new_root_page_id, true);
return true;
}
// case 2 : all elements deleted from the B+ tree
if (old_root_node->IsLeafPage() && old_root_node->GetSize() == 0) {
root_page_id_ = INVALID_PAGE_ID;
UpdateRootPageId(0);
return true;
}
return false;
}
2.否则先判断是否要进行Coalesce
这里要找兄弟结点进行合并,如果满足合并要求的话
1. 判断是否满足合并要求
这里利用一个辅助函数进行判断。如果不超过最大size就可以合并
INDEX_TEMPLATE_ARGUMENTS
template <typename N>
bool BPLUSTREE_TYPE::IsCoalesce(N *nodeL, N *nodeR) {
// maxSize consider InternalPage and LeafPage
return nodeL->GetSize() + nodeR->GetSize() <= maxSize(nodeL);
}
️ 合并函数是和直接前驱进行合并,也就是和它左边的node进行合并
2. 判断左边的page是否能进行合并
// firstly find from left
if (left_sib_index >= 0) {
page_id_t sibling_pid = parent->ValueAt(left_sib_index);
Page *sibling_page = buffer_pool_manager_->FetchPage(sibling_pid); // pined sibling_page
N *sib_node = reinterpret_cast<N *>(sibling_page->GetData());
if (IsCoalesce(node, sib_node)) {
// coalesce
// unpin node and deleted node
bool del_parent = Coalesce(&sib_node, &node, &parent, cur_index, transaction);
// unpin sibling page
buffer_pool_manager_->UnpinPage(sibling_pid, true);
// unpin parent page;
buffer_pool_manager_->UnpinPage(parent_pid, true);
if (del_parent) {
buffer_pool_manager_->DeletePage(parent_pid);
}
return false; // node is merged into sib, and already deleted
}
buffer_pool_manager_->UnpinPage(sibling_pid, false); // unpin sibling page
}
3. 否则判断右边是否能进行合并
// secondly find from right
if (right_sib_index < parent->GetSize()) {
page_id_t sibling_pid = parent->ValueAt(right_sib_index);
Page *sibling_page = buffer_pool_manager_->FetchPage(sibling_pid); // pined sibling_page
N *sib_node = reinterpret_cast<N *>(sibling_page->GetData());
if (IsCoalesce(node, sib_node)) {
// coalesce
// unpin right sib and deleted right sib
bool del_parent =
Coalesce(&node, &sib_node, &parent, cur_index, transaction);
buffer_pool_manager_->UnpinPage(node->GetPageId(), true); // unpin sibling page
buffer_pool_manager_->UnpinPage(parent_pid, true); // unpin parent page;
if (del_parent) {
buffer_pool_manager_->DeletePage(parent_pid);
}
return false; // node is merged into sib, and already deleted
}
buffer_pool_manager_->UnpinPage(sibling_pid, false); // unpin sibling page
}
4. Coalece函数的实现
实现之前先看两张图

在合并之后,父亲结点必须要更新。因为移动操作导致了之前父结点的指针发生了错误。这里会涉及到父亲结点是否需要删除的情况
具体情况见下图
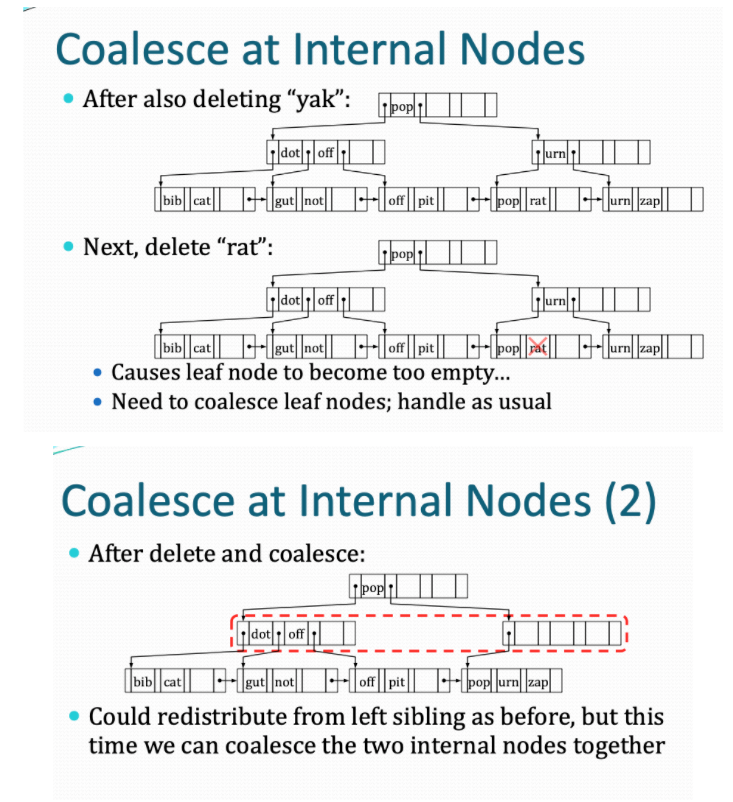
可能由于叶子结点的合并操作,导致父亲结点变成null空结点。或者说是其不满足最小结点个数要求。这样就要对父亲结点进行处理,这个时候是父亲结点也可以进行合并,这个时候原来的父亲结点就无了。合并之后的结果如下图
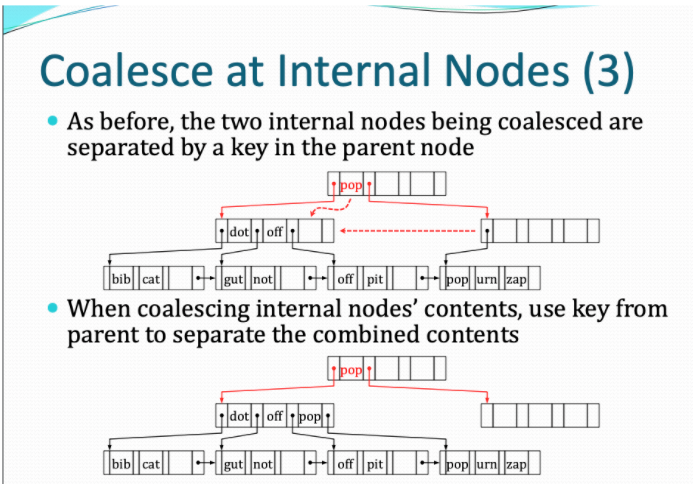
记得递归处理就好
INDEX_TEMPLATE_ARGUMENTS
template <typename N>
bool BPLUSTREE_TYPE::Coalesce(N **neighbor_node, N **node,
BPlusTreeInternalPage<KeyType, page_id_t, KeyComparator> **parent, int index,
Transaction *transaction) {
// Assume that *neighbor_node is the left sibling of *node
// Move entries from node to neighbor_node
if ((*node)->IsLeafPage()) {
LeafPage *leaf_node = reinterpret_cast<LeafPage *>(*node);
LeafPage *leaf_neighbor = reinterpret_cast<LeafPage *>(*neighbor_node);
leaf_node->MoveAllTo(leaf_neighbor);
leaf_neighbor->SetNextPageId(leaf_node->GetNextPageId());
} else {
InternalPage *internal_node = reinterpret_cast<InternalPage *>(*node);
InternalPage *internal_neighbor = reinterpret_cast<InternalPage *>(*neighbor_node);
internal_node->MoveAllTo(internal_neighbor, (*parent)->KeyAt(index), buffer_pool_manager_);
}
buffer_pool_manager_->UnpinPage((*node)->GetPageId(), true);
buffer_pool_manager_->DeletePage((*node)->GetPageId());
(*parent)->Remove(index);
// If parent is underfull, recursive operation
if ((*parent)->GetSize() < minSize(*parent)) {
return CoalesceOrRedistribute(*parent, transaction);
}
return false;
}
5. 叶子结点和内部结点对应的两个MoveAllTo函数
这个函数就不写了。实现比较简单,唯一要注意的就是对于内部结点的合并操作,要把需要删除的内部结点的叶子结点转移过去。也就是要有下面这样的一行
recipient->array_[recipient->GetSize()].first = middle_key;
3. Redistribute流程
当然也可以先看一下算法示意图。
下图是对叶子结点的的Redistribute函数
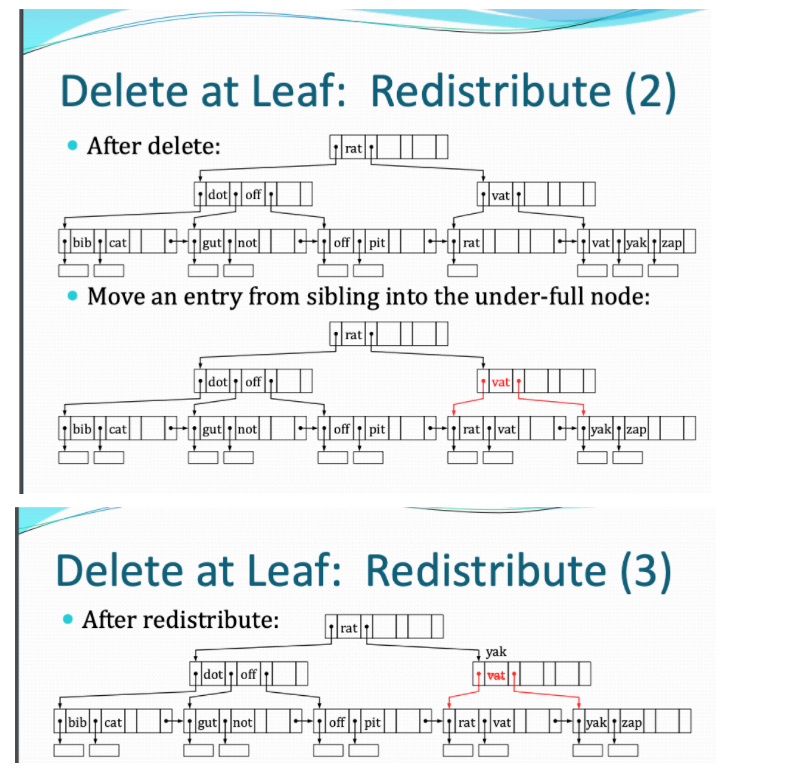
这里在移动的时候只要记得更新父亲对应index的key值就好了。
然而对于内部结点则并不是这么简单的情况了。内部结点可以直接从它的兄弟结点copy然后修改其根节点吗,这显然不合理。
对于这种情况的处理可以见下图
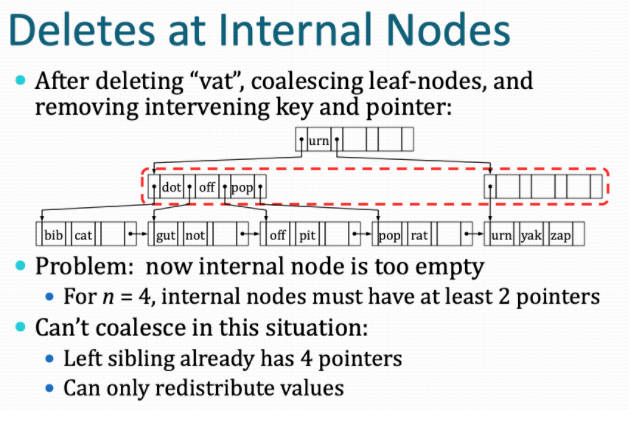
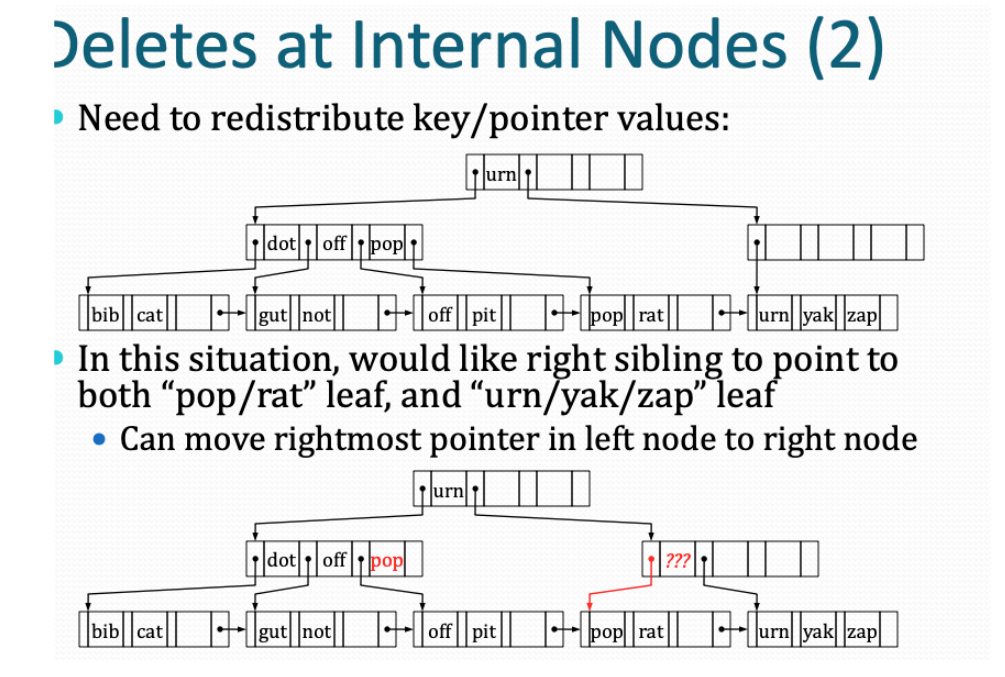

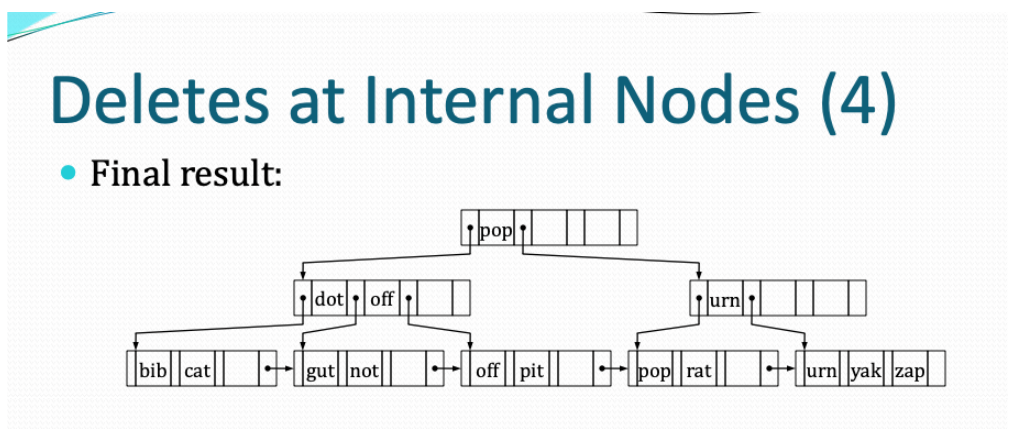
因此整个redistribute所涉及的四种情况就如下
- 向叶子结点左边借
- 向叶子结点右边借
- 内部结点左边借
- 内部结点右边借
1. 对于叶子结点向左边借的情况
好了删除算法已经实现了。首先我们可以通过test函数
cd build
make b_plus_tree_delete_test
./test/b_plus_tree_delete_test --gtest_also_run_disabled_tests
然后我们自己做一些test。这里我就拿一个例子来看
插入10、5、7、4、9得到下图是正确的
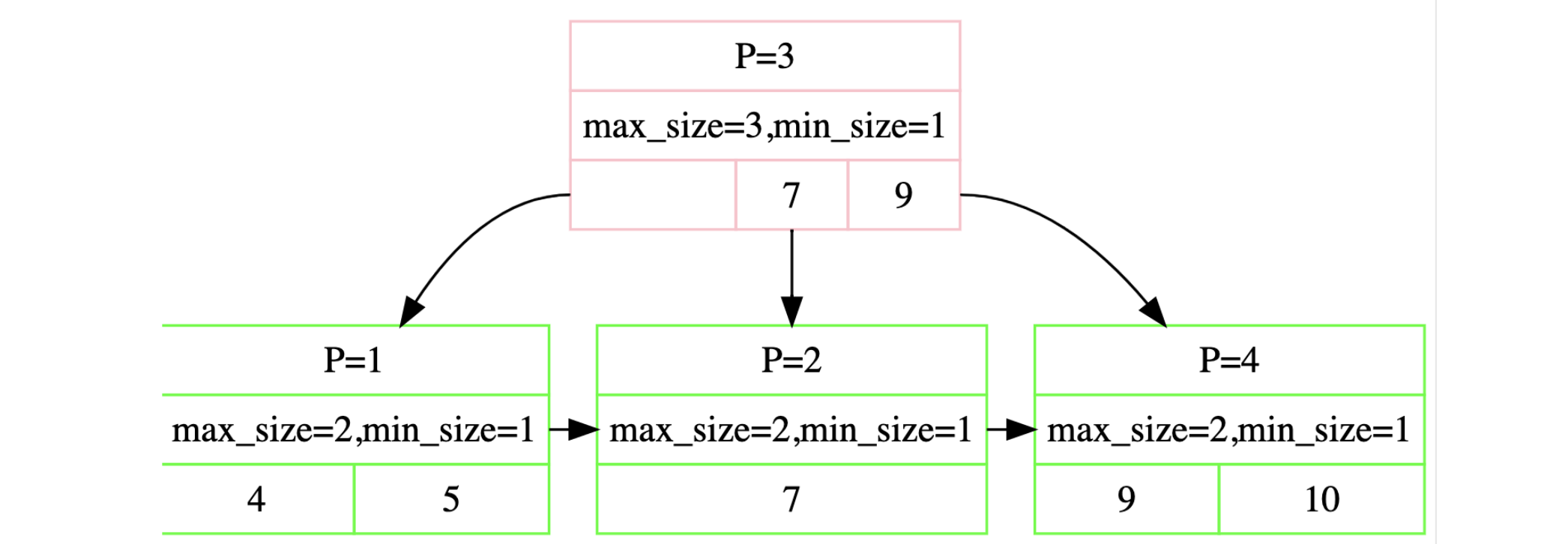
然后删除元素7
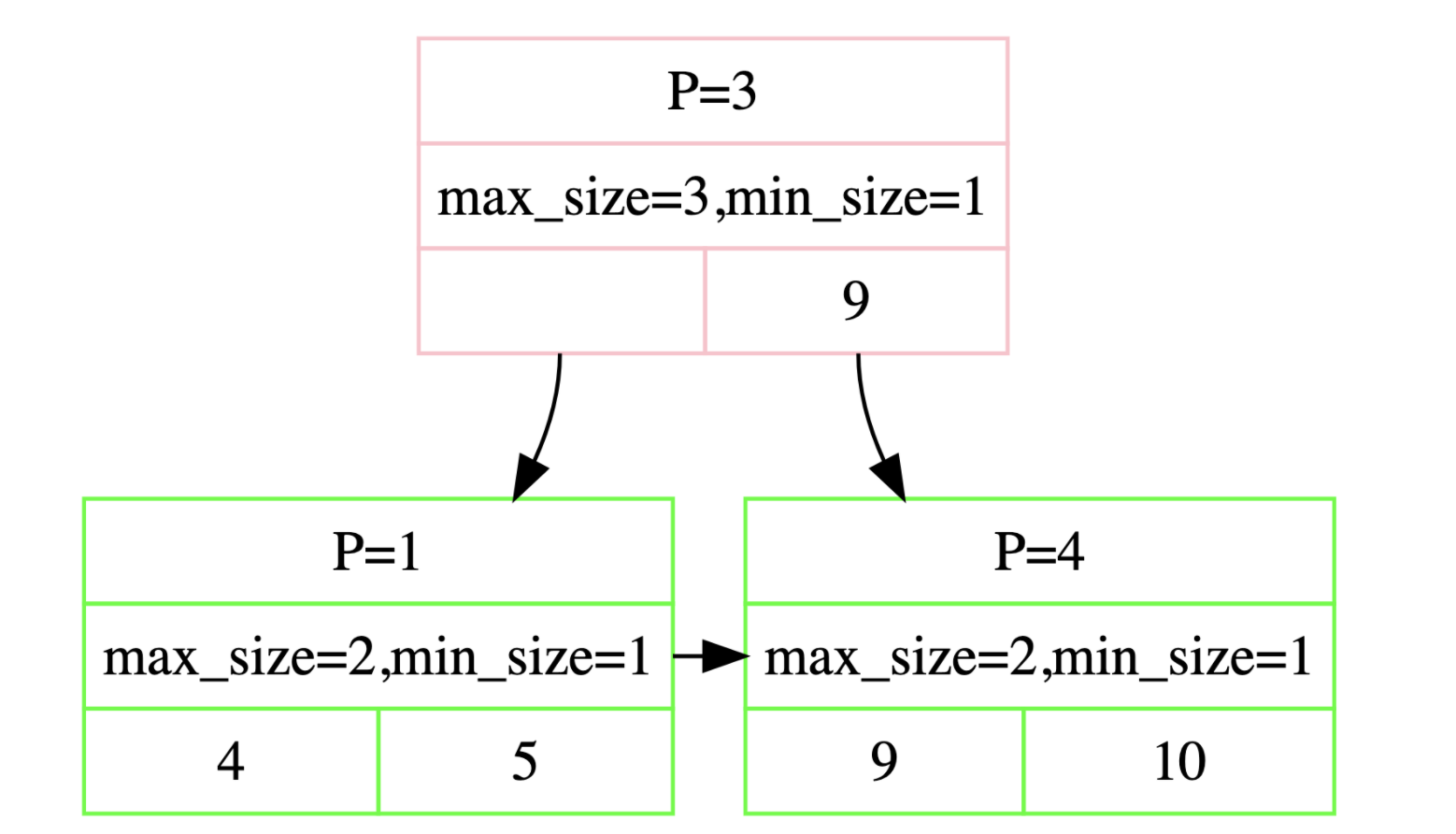
可以发现是完全正确的好了。第二部分就完成了。下面就是最后一部分对于的实现和迭代器的实现