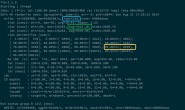
C++演示在不同的范围内不冲突使用同名变量的范例
// An example of using the same variable declarations in different scopes in C++ without conflicts
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class abc //Class declaration statement, you can use struct, and union also.
{
public:
int x; //Variable declaration within class.
abc():x(10){} //Constructor to intialize data members.
};
namespace def //Namespace declaration statement.
{
int x = 20;//Variable declaration within def space.
}
int getx() //Function return its local variable.
{
int x = 30; //Variable declaration within function space.
return x;
}
int x = 40; //Global space variable declaration.
int main()
{
int x = 50;//Local space variable declaration within main function.
abc a;
cout << "Scope within class abc: x = " << a.x
<< "\nScope within namespace def: x = " << def::x
<< "\nScope within function getx: x = " << getx()
<< "\nScope within global scope : x = " << ::x
<< "\nScope within local main function: x = " << x;
{
int x = 60; //Local scope variable declaration within segment of code
cout << "\nScope within local code block: x = " << x;
}
cout<<endl<<endl;//Send two new line to the screen
return 0;
}
/*Program Output:
Scope within class abc: x = 10
Scope within namespace def: x = 20
Scope within function getx: x = 30
Scope within global scope : x = 40
Scope within local main function: x = 50
Scope within local code block: x = 60
*/