项目目标
由于大气运动极为复杂,影响天气的因素较多,而人们认识大气本身运动的能力极为有限,因此天气预报水平较低,预报员在预报实践中,每次预报的过程都极为复杂,需要综合分析,并预报各气象要素,比如温度、降水等。本项目需要训练一个二分类模型,来预测在给定天气因素下,城市是否下雨。
数据说明
本数据包含了来自澳大利亚多个气候站的日常共15W的数据,项目随机抽取了1W条数据作为样本。特征如下:
| 特征 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Date | 观察日期 |
| Location | 获取该信息的气象站的名称 |
| MinTemp | 以摄氏度为单位的低温度 |
| MaxTemp | 以摄氏度为单位的高温度 |
| Rainfall | 当天记录的降雨量,单位为mm |
| Evaporation | 到早上9点之前的24小时的A级蒸发量(mm) |
| Sunshine | 白日受到日照的完整小时 |
| WindGustDir | 在到午夜12点前的24小时中的强风的风向 |
| WindGustSpeed | 在到午夜12点前的24小时中的强风速(km/h) |
| WindDir9am | 上午9点时的风向 |
| WindDir3pm | 下午3点时的风向 |
| WindSpeed9am | 上午9点之前每个十分钟的风速的平均值(km/h) |
| WindSpeed3pm | 下午3点之前每个十分钟的风速的平均值(km/h) |
| Humidity9am | 上午9点的湿度(百分比) |
| Humidity3am | 下午3点的湿度(百分比) |
| Pressure9am | 上午9点平均海平面上的大气压(hpa) |
| Pressure3pm | 下午3点平均海平面上的大气压(hpa) |
| Cloud9am | 上午9点的天空被云层遮蔽的程度,0表示完全晴朗的天空,而8表示它完全是阴天 |
| Cloud3pm | 下午3点的天空被云层遮蔽的程度 |
| Temp9am | 上午9点的摄氏度温度 |
| Temp3pm | 下午3点的摄氏度温度 |
项目过程
-处理缺失值
-删除与预测无关的特征
-随机抽样
-对分类变量进行编码
-处理异常值
-数据归一化
-训练模型
-模型预测
项目代码(Jupyter)
import pandas as pd import numpy as np
读取数据 探索数据
weather = pd.read_csv("weather.csv", index_col=0) weather.head() weather.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> Int64Index: 142193 entries, 0 to 142192 Data columns (total 20 columns): # Column Non-Null Count Dtype --- ------ -------------- ----- 0 MinTemp 141556 non-null float64 1 MaxTemp 141871 non-null float64 2 Rainfall 140787 non-null float64 3 Evaporation 81350 non-null float64 4 Sunshine 74377 non-null float64 5 WindGustDir 132863 non-null object 6 WindGustSpeed 132923 non-null float64 7 WindDir9am 132180 non-null object 8 WindDir3pm 138415 non-null object 9 WindSpeed9am 140845 non-null float64 10 WindSpeed3pm 139563 non-null float64 11 Humidity9am 140419 non-null float64 12 Humidity3pm 138583 non-null float64 13 Pressure9am 128179 non-null float64 14 Pressure3pm 128212 non-null float64 15 Cloud9am 88536 non-null float64 16 Cloud3pm 85099 non-null float64 17 Temp9am 141289 non-null float64 18 Temp3pm 139467 non-null float64 19 RainTomorrow 142193 non-null object dtypes: float64(16), object(4) memory usage: 22.8+ MB
删除与预测无关的特征
weather.drop(["Date", "Location"],inplace=True, axis=1)
删除缺失值,重置索引
weather.dropna(inplace=True)
weather.index = range(len(weather))
1.WindGustDir WindDir9am WindDir3pm 属于定性数据中的无序数据——OneHotEncoder
2.Cloud9am Cloud3pm 属于定性数据中的有序数据——OrdinalEncoder
3.RainTomorrow 属于标签变量——LabelEncoder
为了简便起见,WindGustDir WindDir9am WindDir3pm 三个风向中只保留第一个最强风向
weather_sample.drop(["WindDir9am", "WindDir3pm"], inplace=True, axis=1)
编码分类变量
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder,OrdinalEncoder,LabelEncoder print(np.unique(weather_sample["RainTomorrow"])) print(np.unique(weather_sample["WindGustDir"])) print(np.unique(weather_sample["Cloud9am"])) print(np.unique(weather_sample["Cloud3pm"]))
['No' 'Yes'] ['E' 'ENE' 'ESE' 'N' 'NE' 'NNE' 'NNW' 'NW' 'S' 'SE' 'SSE' 'SSW' 'SW' 'W' 'WNW' 'WSW'] [0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.] [0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.]
# 查看样本不均衡问题,较轻微 weather_sample["RainTomorrow"].value_counts()
No 7750 Yes 2250 Name: RainTomorrow, dtype: int64
# 编码标签 weather_sample["RainTomorrow"] = pd.DataFrame(LabelEncoder().fit_transform(weather_sample["RainTomorrow"]))
# 编码Cloud9am Cloud3pm oe = OrdinalEncoder().fit(weather_sample["Cloud9am"].values.reshape(-1, 1)) weather_sample["Cloud9am"] = pd.DataFrame(oe.transform(weather_sample["Cloud9am"].values.reshape(-1, 1))) weather_sample["Cloud3pm"] = pd.DataFrame(oe.transform(weather_sample["Cloud3pm"].values.reshape(-1, 1)))
# 编码WindGustDir ohe = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False) ohe.fit(weather_sample["WindGustDir"].values.reshape(-1, 1)) WindGustDir_df = pd.DataFrame(ohe.transform(weather_sample["WindGustDir"].values.reshape(-1, 1)), columns=ohe.get_feature_names())
WindGustDir_df.tail()

合并数据
weather_sample_new = pd.concat([weather_sample,WindGustDir_df],axis=1) weather_sample_new.drop(["WindGustDir"], inplace=True, axis=1) weather_sample_new

调整列顺序,将数值型变量与分类变量分开,便于数据归一化
Cloud9am = weather_sample_new.iloc[:,12] Cloud3pm = weather_sample_new.iloc[:,13] weather_sample_new.drop(["Cloud9am"], inplace=True, axis=1) weather_sample_new.drop(["Cloud3pm"], inplace=True, axis=1) weather_sample_new["Cloud9am"] = Cloud9am weather_sample_new["Cloud3pm"] = Cloud3pm RainTomorrow = weather_sample_new["RainTomorrow"] weather_sample_new.drop(["RainTomorrow"], inplace=True, axis=1) weather_sample_new["RainTomorrow"] = RainTomorrow weather_sample_new.head()

为了防止数据归一化受到异常值影响,在此之前先处理异常值
# 观察数据异常情况 weather_sample_new.describe([0.01,0.99])
因为数据归一化只针对数值型变量,所以将两者进行分离
# 对数值型变量和分类变量进行切片 weather_sample_mv = weather_sample_new.iloc[:,0:14] weather_sample_cv = weather_sample_new.iloc[:,14:33]
盖帽法处理异常值
## 盖帽法处理数值型变量的异常值 def cap(df,quantile=[0.01,0.99]): for col in df: # 生成分位数 Q01,Q99 = df[col].quantile(quantile).values.tolist() # 替换异常值为指定的分位数 if Q01 > df[col].min(): df.loc[df[col] < Q01, col] = Q01 if Q99 < df[col].max(): df.loc[df[col] > Q99, col] = Q99 cap(weather_sample_mv) weather_sample_mv.describe([0.01,0.99])

数据归一化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler weather_sample_mv = pd.DataFrame(StandardScaler().fit_transform(weather_sample_mv)) weather_sample_mv

重新合并数据
weather_sample = pd.concat([weather_sample_mv, weather_sample_cv], axis=1)
weather_sample.head()

划分特征与标签
X = weather_sample.iloc[:,:-1]
y = weather_sample.iloc[:,-1]
print(X.shape) print(y.shape)
(10000, 32) (10000,)
创建模型与交叉验证
from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, recall_score
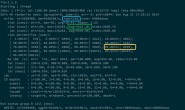
for kernel in ["linear","poly","rbf"]: accuracy = cross_val_score(SVC(kernel=kernel), X, y, cv=5, scoring="accuracy").mean() print("{}:{}".format(kernel,accuracy))
linear:0.8564 poly:0.8532 rbf:0.8531000000000001