题目:
输入一棵二元查找树,将该二元查找树转换成一个排序的双向链表。
要求不能创建任何新的结点,只调整指针的指向。
   10
  / /
  6  14
 / / / /
4  8 12 16
 转换成双向链表
4=6=8=10=12=14=16。
 
 首先我们定义的二元查找树 节点的数据结构如下:
struct BSTreeNode
{
int m_nValue; // value of node
BSTreeNode *m_pLeft; // left child of node
BSTreeNode *m_pRight; // right child of node
};
算法思想:
在二元查找树对应的有序双向链表中,
节点的左指针指向二元查找树中对应节点的左子树中最大节点
节点的右指针指向二元查找树中对应节点的右子树中最小节点
根据上述思想,以树的根节点为分界点,生成两个单向链表:
单链表1:根节点的左子树转换成一个左指针连接成的单向链表;该链表中只能有左指针,如果得到的是右指针,则转换成对应的左指针。
单链表2:根节点的右子树转换成一个右指针链接成的单向链表;该链表中只能有右指针,如果得到的是左指针,则转换成对应的右指针。
双向链表的左右指针转换关系:
p->m_pLeft = q  等价于 q->m_pRight =
p->m_pRight = q 等价于 q->m_pLeft =
然后在分别将上述两个单向链表补充完整,最终形成一个双向链表。
程序源码:
tree.h
/********************************
tree.h : 定义树的头文件
********************************/
#ifndef __TREE_H__
#define __TREE_H__
typedef int ElemType;
struct BSTreeNode{
ElemType m_nValue;
struct BSTreeNode *m_pLeft;
struct BSTreeNode *m_pRight;
};
typedef struct BSTreeNode *pBSTreeNode;
typedef struct BSTreeNode *pSearchTree;
pSearchTree Insert(ElemType x,pSearchTree T);
void InOrderTree(pSearchTree T);
void PrintList(pBSTreeNode pHead);
void TreeToList(pSearchTree pT);
pBSTreeNode DList(pSearchTree pRoot);
#endif
tree.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "tree.h"
extern pBSTreeNode phead;
extern int root_val;
// 打印双向链表
void PrintList(pBSTreeNode pHead)
{
if (NULL == pHead)
{
return;
}
printf("\n%11s: ","List");
pBSTreeNode p = pHead;
do
{
printf("%d, ", p->m_nValue);
p = p->m_pRight;
}while(p != NULL);
printf("\n");
}
//判断节点是否为叶子节点
int IsLeafNode(pBSTreeNode pNode)
{
if (NULL == pNode)
return 0;
if ((NULL == pNode->m_pLeft) && (NULL == pNode->m_pRight))
return 1;
return 0;
}
//判断节点属于根节点的左子树还是右子树
int IsLTreeNode(pBSTreeNode pNode)
{
if (NULL == pNode)
return 0;
return ((pNode->m_nValue < root_val)? 1:0);
}
/*创建新节点*/
pBSTreeNode NewNode(ElemType x)
{
pBSTreeNode new_node;
new_node = (pBSTreeNode)malloc(sizeof(struct BSTreeNode));
if ( NULL == new_node){
printf("malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}else{
new_node->m_nValue = x;
new_node->m_pLeft = new_node->m_pRight = NULL;
}
return new_node;
}
/*在二叉树中插入节点*/
pSearchTree Insert(ElemType x, pSearchTree T)
{
if (NULL == T)
{
T = NewNode(x); //创建新节点
}
else {
if ( x < T->m_nValue){ //如果新插入的节点小于当前节点,则插入其左节点
T->m_pLeft = Insert(x, T->m_pLeft);
}
else{
if ( x > T->m_nValue){
T->m_pRight = Insert(x, T->m_pRight);//如果大于当前节点,则插入其右节点
}
else{
printf("x is already exsited\n"); //不允许重复节点
}
}
}
return T;
}
/*中序遍历二叉树*/
void InOrderTree(pSearchTree T)
{
if (NULL != T)
{
InOrderTree(T->m_pLeft);
printf("%d, ", T->m_nValue);
InOrderTree(T->m_pRight);
}
}
/**********************************************
查找节点在双向链表中对应的左指针指向的节点
以该节点为根节点的左子树中最大的节点
*********************************************/
pBSTreeNode FindLeft(pSearchTree pT)
{
pBSTreeNode p;
if (NULL == pT){
return NULL;
}
if ( NULL == pT->m_pRight){ //如果当前节点不存在右节点,则当前节点就是所找节点
return pT;
}
else{
p = FindLeft(pT->m_pRight);
}
return p;
}
/******************************************
查找节点在双向链表中对应的右指针指向的节点
以该节点为根节点的右子树中最小的节点
*******************************************/
pBSTreeNode FindRight(pSearchTree pT)
{
pBSTreeNode p;
if (NULL == pT){
return NULL;
}
if (NULL == pT->m_pLeft){ //如果当前节点不存在左节点,则当前节点即为所找节点
return pT;
}
else{
p = FindRight(pT->m_pLeft);
}
return p;
}
/**********************************************
以根节点为分界,生成两个单向链表。
比根节点小的节点,生成用左指针连接而成的单链表
比根节点大的节点,生成用右指针链接而成的单链表
***********************************************/
void TreeToList(pSearchTree pT)
{
pSearchTree L,R;
if (NULL == pT)
return ;
L = pT->m_pLeft; //先保存当前节点的左右子树
R = pT->m_pRight;
pT->m_pLeft = FindLeft(pT->m_pLeft); //查找当前节点在双向链表中左指针指向的节点
/***********************************************
如果查找到的节点非空而且属于根节点的右子树,则进行如下处理:
1.将左指针指向改为右指针指向;
2.删除左指针,避免结构中出现环
************************************************/
if (pT->m_pLeft && !IsLTreeNode(pT->m_pLeft)){
pT->m_pLeft->m_pRight = pT; //将左指针指向改为对应的右指针指向
pT->m_pLeft = NULL; //删除左指针
}
pT->m_pRight = FindRight(pT->m_pRight); //查找当前节点在双向链表中右指针指向的节点
/***********************************************
如果查找到的节点非空而且属于根节点的左子树,则进行如下处理
1.将右指针指向改为左指针指向;
2.删除右指针,避免结构中出现环
************************************************/
if ( pT->m_pRight && IsLTreeNode(pT->m_pRight)){
pT->m_pRight->m_pLeft = pT; //将右指针指向改为对应的左指针指向
pT->m_pRight = NULL; //删除右指针
}
TreeToList(L);
TreeToList(R);
}
/****************************************
将根节点连接的两个单向链表生成一个双向链表
函数返回双向链表的头结点
*****************************************/
pBSTreeNode DList(pBSTreeNode pT)
{
if (NULL == pT)
{
return NULL;
}
pBSTreeNode p = pT;
pBSTreeNode q = p->m_pLeft;
/*补齐左指向的单向链表的右指向*/
while (q != NULL){
q->m_pRight = p;
p = q;
q = p->m_pLeft;
}
phead = p;
p = pT;
q = p->m_pRight;
/*补齐右指向的单向链表的左指向*/
while ( q != NULL){
q->m_pLeft = p;
p = q;
q = p->m_pRight;
}
return phead;
}
main.c
/****************************************
author: Rita Huang
date: 2012.12.06
desc: 由二元查找树生成有序双向链表
算法思想:
在二元查找树对应的有序双向链表中,
节点的左指针指向二元查找树中对应节点的左子树中最大节点
节点的右指针指向二元查找树中对应节点的右子树中最小节点
根据上述思想,
1)先将根节点的左子树转换成一个左指针连接成的单向链表;
2)将根节点的右子树转换成一个右指针链接成的单向链表;
3)再分别将上述两个单向链表补充完整,最终形成一个双向链表。
***************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "tree.h"
pBSTreeNode phead; //生成的双向链表的头结点
int root_val = 0; //二元查找树根节点的值
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
int c;
pSearchTree T;
T = NULL;
fp = freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
if (NULL == fp){
printf("open file in.txt failed\n");
exit(0);
}
while ( scanf("%d",&c) != EOF ){
T = Insert(c,T);
}
fclose(stdin);
printf("InOrderTree: ");
InOrderTree(T);
printf("\n");
if ( NULL != T )
root_val = T->m_nValue; //获取二元查找树根节点的值
TreeToList(T); /*二元查找树转换为两个单向链表*/
phead=DList(T); /*两个单向链表生成一个双向链表*/
PrintList(phead);
return 0;
}
  
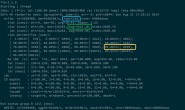
测试数据 in.txt
39 93 84 21 35 193 10 6 8 18 9  86 12 3 20 11 23 92 
运行结果 
InOrderTree: 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 18, 20, 21, 23, 35, 39, 84, 86, 92, 93, 193, 
       List: 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 18, 20, 21, 23, 35, 39, 84, 86, 92, 93, 193,