0、 I/O多路复用机制
I/O多路复用 (I/O multiplexing),提供了同时监测若干个文件描述符是否可以执行IO操作的能力。 select/poll/epoll 函数都提供了这样的机制,能够同时监控多个描述符,当某个描述符就绪(读或写就绪),则立刻通知相应程序进行读或写操作。本文将从内核源码(v5.2.14)入手,尝试简述 poll/select 机制的实现原理。
1、poll/select函数
介绍内核源码前,先来简单介绍 poll/select 函数的调用方式。
1.1 select函数
#include <poll.h> int select (int maxfd, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *tvptr);
- maxfd :代表要监控的最大文件描述符
fd+1 - writefds :监控可写的文件描述符
fd集合 - readfds :监控可读的文件描述符
fd集合 - exceptfds :监控异常事件的文件描述符
fd集合 - timeout :超时时长
select 将监听的文件描述符分为三组,每一组监听不同的I/O操作。 readfds/writefds/exceptfds 分别表示可写、可读、异常事件的文件描述符集合,这三个参数可以用 NULL 来表示对应的事件不需要监听。对信号集合的操作可以利用如下几个函数完成:
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set); int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set); void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set); void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set);
select 的调用会阻塞到有文件描述符可以进行IO操作或被信号打断或者超时才会返回。 timeout 参数用来指定超时时间,含义如下:
- NULL: 表示不设置超时,调用会一直阻塞直到文件描述符上的事件触发
- 0: 表示不等待,立即返回,用于检测文件描述符状态
- 正整数: 表示指定时间内没有事件触发,则超时返回
值得注意的是, select 调用返回时,每个文件描述符集合均会被过滤,只保留得到事件响应的文件描述符。在下一次调用 select 时,描述符集合均需要重新设置。
1.2 poll函数
#include <poll.h> int poll (struct pollfd *fds, unsigned int nfds, int timeout); struct pollfd { int fd; /* file descriptor to check */ short events; /* events of interest on fd */ short revents; /* events that occured on fd */ };
poll 函数与 select 不同,不需要为三种事件分别设置文件描述符集,而是构造了 pollfd 结构的数组,每个数组元素指定一个描述符fd以及对该描述符感兴趣的条件(events)。 poll 调用返回时,每个描述符fd上产生的事件均被保存在 revents 成员内。
和 select 类似, timeout 参数用来指定超时时间(ms)。
2、poll函数机制
poll和select均属于系统调用的方式,先就 poll 函数在Linux中实现的机制进行分析。
poll和select函数在内核源码中的定义均位于 fs/select.c 文件中,poll 函数的原型定义如下:
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(poll, struct pollfd __user *, ufds, unsigned int, nfds, int, timeout_msecs)
首先,会调用 poll_select_set_timeout 函数将超时时间转换为 timespec64 结构变量,注意超时时间将会以当前时间(monotonic clock)为基础,转换为未来的一个超时时间点(绝对时间)。
struct timespec64 end_time, *to = NULL; if (timeout_msecs >= 0) { to = &end_time; poll_select_set_timeout(to, timeout_msecs / MSEC_PER_SEC, NSEC_PER_MSEC * (timeout_msecs % MSEC_PER_SEC)); }
2.1 do_sys_poll
static int do_sys_poll(struct pollfd __user *ufds, unsigned int nfds, struct timespec64 *end_time) { struct poll_wqueues table; int err = -EFAULT, fdcount, len, size; /* 在栈上分配小段空间提高速度,通过`poll_list`链表保存所有的`pollfd` */ long stack_pps[POLL_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)]; struct poll_list *const head = (struct poll_list *)stack_pps; struct poll_list *walk = head; unsigned long todo = nfds; . . . len = min_t(unsigned int, nfds, N_STACK_PPS); for (;;) { walk->next = NULL; walk->len = len; . . . /* 1. 将pollfd从用户空间拷贝到内核空间 */ if (copy_from_user(walk->entries, ufds + nfds-todo, sizeof(struct pollfd) * walk->len)) goto out_fds; todo -= walk->len; if (!todo) break; len = min(todo, POLLFD_PER_PAGE); size = sizeof(struct poll_list) + sizeof(struct pollfd) * len; walk = walk->next = kmalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL); . . . } poll_initwait(&table); /* 2. 调用do_poll完成poll的实际调用处理 */ fdcount = do_poll(head, &table, end_time); poll_freewait(&table); /* 3. 将每个fd上产生的事件revents再从内核空间拷贝到用户空间 */ for (walk = head; walk; walk = walk->next) { struct pollfd *fds = walk->entries; . . . for (j = 0; j < walk->len; j++, ufds++) if (__put_user(fds[j].revents, &ufds->revents)) goto out_fds; } err = fdcount; out_fds: . . . return err; }
do_sys_poll 函数首先将 pollfd 结构体数组从用户空间拷贝至内核空间,同时用名为 poll_list 的链表存储(一部分存储在栈空间上,一部分存储在堆空间),形如:

struct poll_wqueues table = { poll_table pt = { ._qproc = __pollwait; ._key = ~(__poll_t)0; /* all events enabled */ }; struct poll_table_page *table = NULL; struct task_struct *polling_task = current; int triggered = 0; int error = 0; int inline_index = 0; struct poll_table_entry inline_entries[N_INLINE_POLL_ENTRIES]; };
函数指针 table.pt._qproc 被初始化指向 __pollwait 函数,这个和 poll 调用过程中阻塞与唤醒机制相关,后面将介绍。
随后即调用 do_poll 函数完成 poll 操作,最后将每个文件描述符fd产生的事件再拷贝到内核空间。
2.2 do_poll
static int do_poll(struct poll_list *list, struct poll_wqueues *wait, struct timespec64 *end_time) { poll_table* pt = &wait->pt; ktime_t expire, *to = NULL; int timed_out = 0, count = 0; u64 slack = 0; __poll_t busy_flag = net_busy_loop_on() ? POLL_BUSY_LOOP : 0; unsigned long busy_start = 0; /* timeout设置为0时,将pt->_qproc设置为NULL,同时不阻塞,相当于退化为轮询操作 */ if (end_time && !end_time->tv_sec && !end_time->tv_nsec) { pt->_qproc = NULL; timed_out = 1; } /* 超时时间设置并有效的情况下,才设置slack */ if (end_time && !timed_out) slack = select_estimate_accuracy(end_time); for (;;) { struct poll_list *walk; bool can_busy_loop = false; /* 对每一项pollfd进行遍历,调用do_pollfd */ for (walk = list; walk != NULL; walk = walk->next) { struct pollfd * pfd, * pfd_end; pfd = walk->entries; pfd_end = pfd + walk->len; for (; pfd != pfd_end; pfd++) { /* do_pollfd返回非负值,表示发现事件触发,此时无需再将当前进程加入到相应的等待队列 */ if (do_pollfd(pfd, pt, &can_busy_loop, busy_flag)) { count++; pt->_qproc = NULL; /* found something, stop busy polling */ busy_flag = 0; can_busy_loop = false; } } } /* 当前进程已经在上述的遍历中被加入到各个fd对应驱动的等待队列,无需重复加入 */ pt->_qproc = NULL; if (!count) { count = wait->error; /* 被信号中断,后面将返回 */ if (signal_pending(current)) count = -EINTR; } /* 发现事件触发,或者timed_out == 1 提前退出循环 */ if (count || timed_out) break; if (can_busy_loop && !need_resched()) { if (!busy_start) { busy_start = busy_loop_current_time(); continue; } if (!busy_loop_timeout(busy_start)) continue; } busy_flag = 0; /* 超时时间end_time有效时,将timespec64格式的end_time转换为ktime_t格式 */ if (end_time && !to) { expire = timespec64_to_ktime(*end_time); to = &expire; } /* 进行poll进程的休眠工作,让出CPU * 超时时间到达时返回,设置timed_out=1,在下一个轮询后返回上层调用 */ if (!poll_schedule_timeout(wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, to, slack)) timed_out = 1; } return count; }
do_poll 函数首先从头部到尾部遍历链表 poll_list ,对每一项 pollfd 调用 do_pollfd 函数。 do_pollfd 函数主要将当前 poll 调用进程加入到每个 pollfd 对应fd所关联的底层驱动等待队列中,将在下文详细介绍这一点。
do_pollfd 调用后,如果某个fd已经产生事件,那么后续遍历其他fd时,无需再将当前进程加入到对应的等待队列中, poll 调用也将返回而不是睡眠(schedule)。
2.3 do_pollfd
static inline __poll_t do_pollfd(struct pollfd *pollfd, poll_table *pwait, bool *can_busy_poll, __poll_t busy_flag) { int fd = pollfd->fd; __poll_t mask = 0, filter; struct fd f; if (fd < 0) goto out; mask = EPOLLNVAL; f = fdget(fd); if (!f.file) goto out; /* userland u16 ->events contains POLL... bitmap */ filter = demangle_poll(pollfd->events) | EPOLLERR | EPOLLHUP; pwait->_key = filter | busy_flag; mask = vfs_poll(f.file, pwait); if (mask & busy_flag) *can_busy_poll = true; mask &= filter; /* Mask out unneeded events. */ fdput(f); out: /* ... and so does ->revents */ pollfd->revents = mangle_poll(mask); return mask; }
do_pollfd 主要完成与底层VFS中的驱动程序 f_op->poll 的调用,和对事件的过滤(只过滤出对每个文件描述符感兴趣的事件)。最后会把过滤出的事件放入 revents 中,作为结果返回。
static inline __poll_t vfs_poll(struct file *file, struct poll_table_struct *pt) { if (unlikely(!file->f_op->poll)) return DEFAULT_POLLMASK; return file->f_op->poll(file, pt); }
vfs_poll 将调用 file->f_op->poll 函数,而这个函数是在设备驱动程序中定义的。这里通过一个模拟的字符驱动globalfifo程序中定义的 xxx_poll 函数来分析调用过程。
globalfifo_poll 主要完成了如下几方面的工作:
- 锁定设备自定义的互斥量
- 调用 poll_wait 将 poll 进程加入到设备自定义的等待队列中,下文将详细介绍 poll_wait
- 判断等待事件条件是否发生
- 对互斥量解锁
static unsigned int globalfifo_poll(struct file *flip, struct poll_table_struct *poll_table) { struct globalfifo_dev *dev = flip->private_data; unsigned int mask = 0; mutex_lock(&dev->globalfifo_mutex); /* Add poll_table to r_wait/w_wait queue of device driver * then, device driver could wake up poll function of upper layer (do_poll) */ poll_wait(flip, &dev->r_wait, poll_table); poll_wait(flip, &dev->w_wait, poll_table); if (dev->current_len != 0) { mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; } if (dev->current_len != GLOBALFIFO_SIZE) { mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM; } mutex_unlock(&dev->globalfifo_mutex); return mask; }
2.4 poll_wait
void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p) { if (p && p->_qproc && wait_address) p->_qproc(filp, wait_address, p); }
poll_wait 进而调用到 poll_table p->_qproc ,而后者在2.1节中通过 poll_initwait(&table) 被初始化为 __pollwait 。
static void __pollwait(struct file *filp, wait_queue_head_t *wait_address, poll_table *p) { struct poll_wqueues *pwq = container_of(p, struct poll_wqueues, pt); struct poll_table_entry *entry = poll_get_entry(pwq); if (!entry) return; entry->filp = get_file(filp); entry->wait_address = wait_address; entry->key = p->_key; init_waitqueue_func_entry(&entry->wait, pollwake); entry->wait.private = pwq; add_wait_queue(wait_address, &entry->wait); }
__pollwait 初始化等待队列项(关联到当前 poll 进程),最后将等待队列项加入到设备驱动中定义的等待队列中。关于等待队列的介绍,可以参考:Linux等待队列(Wait Queue)。
2.5 do_poll (continued)
static int do_poll(struct poll_list *list, struct poll_wqueues *wait, struct timespec64 *end_time) { . . . for (;;) { struct poll_list *walk; bool can_busy_loop = false; for (walk = list; walk != NULL; walk = walk->next) { struct pollfd * pfd, * pfd_end; pfd = walk->entries; pfd_end = pfd + walk->len; for (; pfd != pfd_end; pfd++) { /* do_pollfd返回非负值,表示发现事件触发,此时无需再将当前进程加入到相应的等待队列 */ if (do_pollfd(pfd, pt, &can_busy_loop, busy_flag)) { count++; pt->_qproc = NULL; /* found something, stop busy polling */ busy_flag = 0; can_busy_loop = false; } } } /* 已经通过遍历处理完所有pollfd,无需再次进行等待队列的处理 */ pt->_qproc = NULL; if (!count) { count = wait->error; /* 被信号中断,将直接返回 */ if (signal_pending(current)) count = -EINTR; } /* 发现事件触发,或者timed_out == 1 提前退出循环 */ if (count || timed_out) break; . . . busy_flag = 0; /* 超时时间end_time有效时,将timespec64格式的end_time转换为ktime_t格式 */ if (end_time && !to) { expire = timespec64_to_ktime(*end_time); to = &expire; } /* 进行poll进程的休眠工作,让出CPU * 超时时间到达时返回,设置timed_out=1,在下一个轮询后返回上层调用 */ if (!poll_schedule_timeout(wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, to, slack)) timed_out = 1; } return count; }
前面几节介绍了do_poll会依次遍历每一个pollfd,调用do_pollfd将当前poll进程加入到文件描述符对应驱动的等待队列中,此过程中会判断等待条件是否已产生。如若任意一个fd的事件event符合要求,对于后面的fd不会把当前进程加入到等待队列中(pt->_qproc = NULL)。这一轮将poll进程都放进等待队列后,在下一个loop就不用重复存放。
存在(产生)下一个loop的条件:
- timeout超时条件发生, 在下一个loop会先判断是否有event满足,满足刚好能够作为结果被返回
- 等待队列被唤醒,在下一个loop对每个
fd进行判断,对相应文件描述符更新revents
do_poll 阻塞条件终止返回上层调用 do_sys_poll 后,如2.1节所述,会依次遍历每一项 pollfd ,将最终产生的事件 revents 从内核空间拷贝到用户空间。
至此,poll调用过程基本结束。
3、select函数机制
select 函数和 poll 函数的实现机制大体一致,同样存在用户空间到内核空间的拷贝过程,以及在等待队列上睡眠和唤醒的过程,关于 select 调用的详细过程分析在此不赘述了。与 poll 调用不同的一点是, select 调用对目标文件描述符的数量受到最大文件描述符 max_fds 的限制,在如下 compat_core_sys_select 函数中可以清晰得看到这点。
static int compat_core_sys_select(int n, compat_ulong_t __user *inp, compat_ulong_t __user *outp, compat_ulong_t __user *exp, struct timespec64 *end_time) { fd_set_bits fds; void *bits; int size, max_fds, ret = -EINVAL; struct fdtable *fdt; long stack_fds[SELECT_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)]; if (n < 0) goto out_nofds; /* max_fds can increase, so grab it once to avoid race */ rcu_read_lock(); fdt = files_fdtable(current->files); max_fds = fdt->max_fds; rcu_read_unlock(); if (n > max_fds) n = max_fds; . . . }
static int compat_core_sys_select(int n, compat_ulong_t __user *inp, compat_ulong_t __user *outp, compat_ulong_t __user *exp, struct timespec64 *end_time) { fd_set_bits fds; void *bits; int size, max_fds, ret = -EINVAL; struct fdtable *fdt; long stack_fds[SELECT_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)]; if (n < 0) goto out_nofds; /* max_fds can increase, so grab it once to avoid race */ rcu_read_lock(); fdt = files_fdtable(current->files); max_fds = fdt->max_fds; rcu_read_unlock(); if (n > max_fds) n = max_fds; . . . }
4、总结
前面几节内容,介绍了 poll 和 select 调用的使用方法,并利用源码重点分析了Linux内核 poll 机制的实现原理。
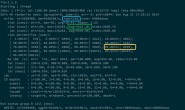
poll 系统调用的整体过程可以概括为下图:
参考资料
[1] select/poll/epoll对比分析:(http://gityuan.com/2015/12/06/linux_epoll/)
[2] 源码解读poll/select内核机制:(http://gityuan.com/2019/01/05/linux-poll-select/)
[3] 一文看懂IO多路复用:(https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/115220699)
[4] POLL机制:(https://www.cnblogs.com/liuqing520/p/12706187.html)